How LTE Lays the Foundation for 5G: Coexistence, Evolution, and Key Enhancements
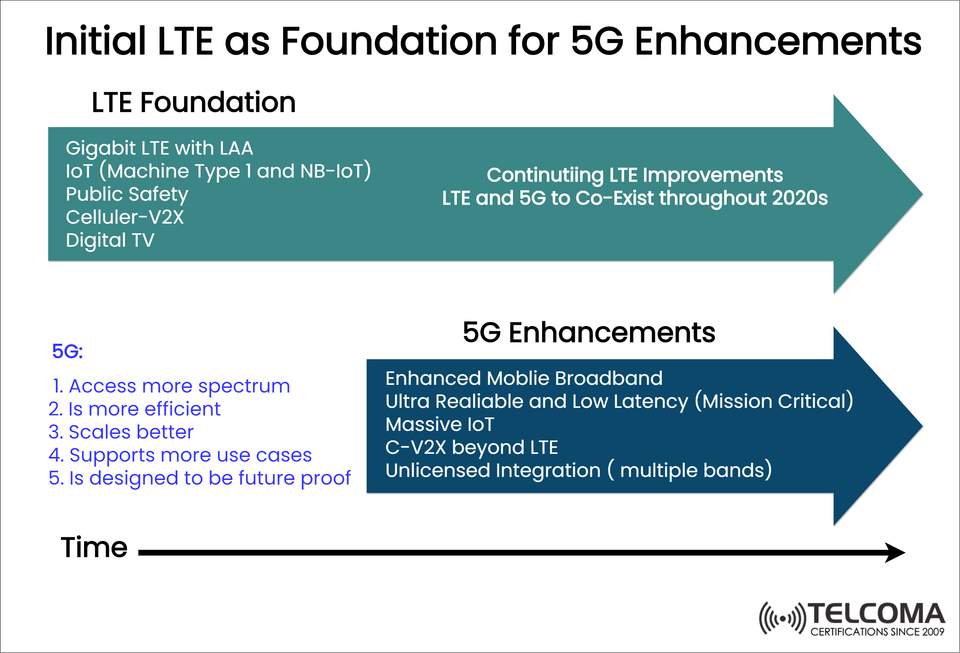

🚀 Initial LTE as Basis for 5G Expansion
The 5G era has arrived, but LTE still serves as important an enabler as it provides the technology and infrastructure that 5G will further build upon. This foundational essence of LTE is not merely historic with its role being the past, as LTE continues to serve in 2020s with LTE and 5G happily coexisting and growing.
The image that I uploaded shows how reliable LTE's already developed capabilities, such as Gigabit LTE, IoT (NB-IoT, MTC), Public Safety networks have built upon LTE use cases which allows operatiors to deliver on the promises set out for 5G in relation to faster speeds, broader connectivity and Mission critical applications.
📶 LTE Foundation: The Bedrock of Current Mobile Applications
LTE underwent many enhancements when 5G was not technically feasible. LTE had many enhancements to extend its own capabilities, address performance demands, and use case applications that evolved, leading to a level of maturity for LTE as it provided LTE networks a roadmap for the evolving transition to 5G.
🔑 LTE Capabilities that lead to:
Gigabit LTE using LAA (Licensed Assisted Access)
Enabling IoT through MTC and NB-IoT
Public Safety Networks (Mission-critical push-to-talk, first responders)
C-V2X (Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything)
Digital TV Broadcasts using LTE Infrastructure
📡 Why 5G Requires LTE: The Benefits
While 5G is being implemented in standalone (SA) and non-standalone (NSA) options, LTE continues to be a necessary part of the implementation process, sure in areas that do not have full 5G coverage yet.
📊 5G Improves Upon LTE With:
Access to more spectrum including mmWave and sub-6 GHz
Higher spectral efficiency
Greater Network capacity ability to be scaled
A wider variety of use cases including autonomous vehicles to remote surgery
A scalable architecture including cloud-native and software-defined capabilities
⚙️ 5G Capabilities: Built on LTE Capabilities
As the image demonstrates, the 5G developments have layers stacked on principles of LTE that enhance its usefulness and capabilities.
Enhancement Area Description
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) Multi-gigabit experience and seamless HD streaming
Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC) Mission critical, high reliability applications (ie. autonomous driving)
Massive IOT Ability to scale to billions of devices
C-V2X Evolution More advanced vehicular connectivity than LTE
Unlicensed Integration Utilizes multiple bands of spectrum (licensed and unlicensed)
🔄 LTE and 5G Coexistence: A Strategic Timeline
In the 2020s, LTE and 5G will work together, not against each other. The benefit of this hybrid type of deployment not only gives operators the opportunity to:
- Maximize their infrastructure ROI by leveraging their LTE core and LTE radio assets,
- Provide a consistent user experience while continuing their 5G build-outs,
- Help bridge the digital divide by providing reliable service in underserved areas by leveraging existing LTE technology.
🧩 Conclusion: LTE as a Springboard to 5G
In short, LTE is not dead—it’s a key springboard to the 5G future. New use cases coming online like AR/VR, smart factories, and autonomous vehicles, will create the legacy of LTE that ensures network robustness (due to its scale, reliability, and adaptability).
Telecom operators need to recognize that LTE’s evolving part in their build-out strategy is critical for deploying networks that are both efficient and future-proof. LTE is not just the past of mobile networking—it is also a part of its future.
🔍 Suggested SEO Keywords:
LTE and 5G coexistence
LTE foundation 5G
Gigabit LTE and 5G
5G enhancements to LTE
5G new use cases
LTE for IoT
5G spectrum efficiency
C-V2X 5G
URLLC 5G
Massive IoT LTE NB-IoT
👥 Audience Specific Insights
🧑💻 For Telecommunication Professionals
Utilize existing LTE infrastructure: NSA 5G (Non-Consultative 5G) deployments are contingent upon LTE cores (EPC) which allows carriers to invest incrementally when deploying 5G NR.
Coordinate a spectrum strategy: Attainable technologies like DSS (Dynamic Spectrum Sharing) allow LTE and 5G NR to operate on the same frequency which ADA provides a smoother coordination for migration.
Improve service agility: LTE already accommodated NB-IoT and eMTC to provide adequate seeding for moving into 5G Massive IoT without redesigns.
🤓 For your Cognoscenti
LTE is not in decline: Regardless of the advancement discussion of 5G, LTE still has gigabit-class performance and supports many of today's apps and services.
5G = evolution, not replacement: Your new 5G is most likely still accomplishing a voice call using LTE, and likely data uses LTE, especially when travelling outside major urban areas.
Anticipate a gradual upgrade path: 5G features, including URLLC and network slicing in RAN, will be deployed post incrementally from enhanced capabilities based on an LTE core.
📘 Quick Glossary
Term Definition
LAA Licensed Assisted Access – LTE over unlicensed spectrum
NB-IoT Narrowband Internet of Things
C-V2X Cellular Vehicle to Everything
URLLC Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications
eMBB Enhanced Mobile BroadBand
DSS Dynamic Spectrum Sharing
NSA Non-Standalone (5G release using LTE core)
SA Standalone (natively 5G core and RAN)
📈 Visual Summary Table
LTE Feature Enables 5G Enhancement
Gigabit LTE High throughput eMBB
NB-IoT / eMTC Wide IoT support Massive IoT
Public Safety LTE Mission critical URLLC
C-V2X Vehicle safety Advanced C-V2X
LAA Spectrum efficiency Unlicensed band integration
🔮 Future Perspectives: LTE in the 6G Era
As 5G continues to unfold, research and standardization of 6G (or at least some aspects of it) has already begun. In an unexpected twist, the implications of LTE's foundations could continue to be felt into the 6G era:
Backward compatibility: LTE will continue to be a fallback layer that extends to rural and legacy systems.
IoT longevity: NB-IoT and LTE-M will also continue alongside 6G for many, many billions of low-power devices.
Teachings learned: The migration from LTE to 5G was relatively simple, and there are many lessons to be learned in terms of how to proceed in planning future networks.
🧠 Final Thoughts
Looking back, there is no leap into a different world, but rather a set of strategic layers on top of LTE. LTE is the foundational structure that enables 5G to be faster, smarter, scalable, and sustainable.
By understanding this relationship, operators and technologists will be better positioned to align roadmaps, investments, and innovations. Moving forward, LTE and 5G's coexistence, both optimally and sufficiently, will play a significant role in global connectivity (5G), smart infrastructure implementation (5G with a MASSIVE IoT feature), and digital transformation.
