Immediate MDT in LTE and 5G: Real-Time Network Measurement & Optimization

Network operators are always trying to keep the experience for users top-notch while also making the best use of their resources. Historically, drive tests were the go-to method for collecting radio network data, but we all know they can be pricey, take a lot of time, and have limited reach.
Minimization of Drive Tests (MDT), which has been standardized by 3GPP, really shakes things up when it comes to optimizing networks. It uses actual user equipment (UE) to gather data in real-world network conditions. MDT has two primary modes: Immediate MDT and Logged MDT. This article dives into Immediate MDT, covering how it works, its use cases, and why it matters for LTE and 5G networks.
What is Immediate MDT?
Immediate MDT is all about collecting data in real-time. When a trigger event occurs, UEs send measurement results straight to the network. The RAN node processes these measurements and sends them over to the Trace Collection Entity (TCE) for further analysis.
This mode is super handy for operators who need quick insights into network conditions to fix performance issues efficiently.
Immediate MDT Call Flow Explained
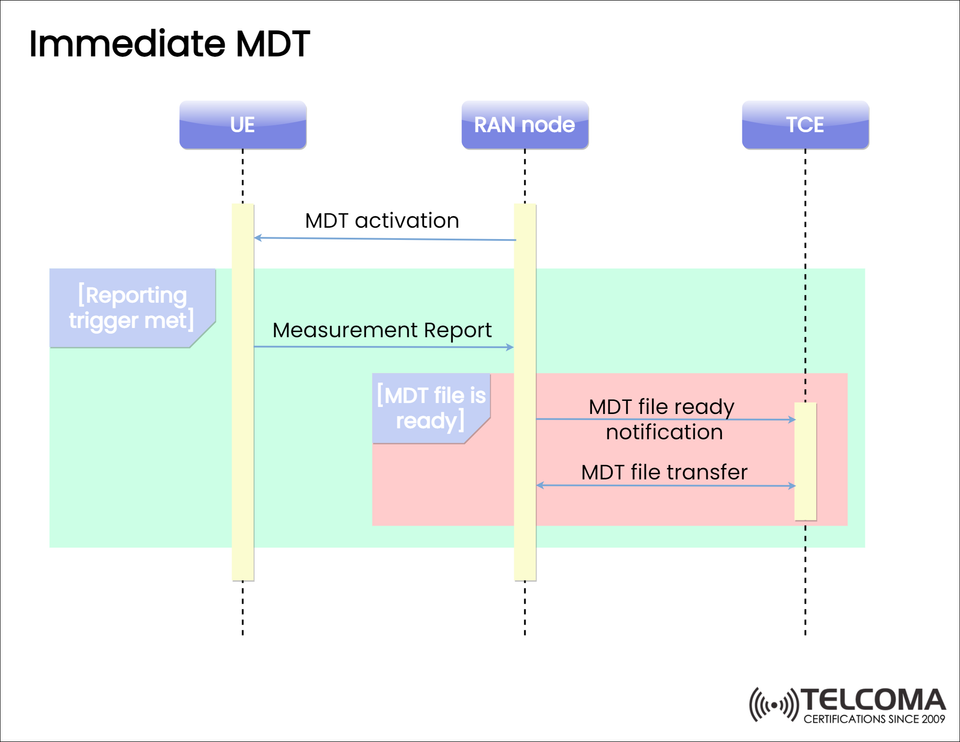
The image shared illustrates how the signaling flow works step-by-step for Immediate MDT:
- MDT Activation
The RAN node (like an eNodeB or gNodeB) turns on MDT for a UE based on the setup from the core network or OSS.
This activation specifies which measurements to track (RSRP, RSRQ, SINR, event-triggered reports, etc.).
- Reporting Trigger Met
The UE keeps an eye on the conditions it’s been configured to monitor.
Once the trigger condition is met (for instance, if RSRP dips below a certain point), the UE gets ready to send a measurement report.
- Measurement Report
The UE quickly sends the measurement report back to the RAN node.
This report includes the real-time radio parameters and events the UE encountered at its location.
- MDT File Ready
The RAN node collects the reports and compiles an MDT file.
Once that file’s complete, it sends an MDT file ready notification to the TCE.
- MDT File Transfer
The RAN node then moves the MDT file to the TCE, where it’s stored and analyzed.
This information is used for performance checks, optimizing coverage, and troubleshooting issues.
Advantages of Immediate MDT
Benefit Description Real-Time Insights Gives immediate visibility into network conditions as they happen. Reduced OPEX Cuts down on the reliance on physical drive tests, saving time and costs. Improved Coverage Optimization Quickly spots coverage gaps and areas with weak signals. Better QoE Ensures the user experience is monitored in real-time, allowing for quicker fixes. Supports 5G Network Evolution Operates in multi-RAT setups, covering both LTE and 5G NR.
Use Cases of Immediate MDT
Call Drop Investigation: Figure out why calls drop unexpectedly in certain areas.
Coverage Verification: Check how well cell edges perform and how handovers are going.
Capacity Planning: Keep an eye on congestion in real-time and adjust resources on the fly.
Customer Complaints: Quickly look into network issues reported by users as they come up.
Immediate MDT vs. Logged MDT
Aspect Immediate MDT Logged MDT Reporting Type Real-time reporting Stored in UE memory, sent later Use Case Immediate troubleshooting, quick fixes Long-term analysis, coverage studies Network Load Higher (continuous reporting)Lower (periodic file uploading)Battery Impact Slightly higher (continuous measurements)Minimal (just logging until upload)
Immediate MDT shines when rapid network correction is vital, while Logged MDT is better for later analysis and planning.
Role of Immediate MDT in 5G Networks
With 5G rolling out features like ultra-low latency, massive MIMO, and network slicing, getting quick insights into network performance is more important than ever.
Edge Analytics: Real-time MDT data can be processed at the edge, reducing troubleshooting latency.
Dynamic Network Slicing: Immediate MDT helps check if each slice meets its SLA in real-time.
Beamforming Verification: Measures signal quality across various beams to fine-tune beamforming algorithms.
Challenges in Implementing Immediate MDT
Even though Immediate MDT has a lot of benefits, there are also some challenges:
Signaling Overhead: Constant reporting could bump up uplink signaling loads.
Data Volume: Handling large amounts of data requires good storage and processing capabilities.
Battery Consumption: Frequent measuring can drain UE batteries quicker.
Privacy Concerns: It’s crucial to anonymize location data to protect user privacy.
Operators tackle these issues by optimizing reporting intervals, utilizing AI-driven data analytics, and ensuring they comply with privacy laws like GDPR.
Quick Comparison: Immediate MDT vs. Logged MDT
Here’s a handy comparison table for you to use in your blog post that will improve readability and SEO—Google really likes clear tables:
Parameter Immediate MDT Logged MDT Data Reporting Real-time, sent immediately when a trigger happens Stored in UE memory and sent later Use Case Great for troubleshooting live issues and call drop analysis Best for long-term performance studies Network Load Higher, since it reports continuously Lower, as it uploads in batches Battery Impact Moderate, given that continuous measurement uses some power Lower, since the UE logs data and uploads it less frequently Best For Quick root-cause analysis and immediate corrective actions Planning, optimization, and spotting trends
This table offers readers a quick way to compare the two types of MDT, boosting engagement and possibly getting your post featured in search results as a snippet.
Best Practices for Operators Using Immediate MDT
If operators want to get the most out of Immediate MDT while keeping challenges at bay, here are some tips to consider:
Optimize Reporting Intervals: Try to avoid reporting too often to cut down on signaling overhead and ease the battery impact on UE.
Utilize AI/ML for Data Processing: Leverage smart analytics to quickly spot network anomalies in large MDT datasets.
Combine with Logged MDT: Use Immediate MDT for urgent troubleshooting and turn to Logged MDT for in-depth analysis over time.
Make Sure to Follow Privacy & Compliance: Remember to anonymize user data and stick to regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Conclusion
Immediate MDT is a game-changing tool that transforms how network operators keep tabs on and optimize LTE and 5G networks. By pulling in real-time measurement data directly from UEs, operators can quickly handle issues, reduce outages, and enhance overall QoE without solely depending on costly drive tests.
As networks progress towards 6G, having real-time intelligence will be even more essential — and Immediate MDT will continue to be a key player in automated network operations, AI-driven optimization, and self-healing networks.
