Immersive Viewing with Coded Caching: Future of Multi-User Applications in 5G

As we move towards 5G and beyond, the need for immersive, multi-user applications is skyrocketing. We're seeing this across the board, from augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) experiences for consumers to use cases in the industrial IoT. This means that ultra-reliable, low-latency communication (URLLC) and massive connectivity aren't just nice-to-haves anymore—they're absolutely vital.
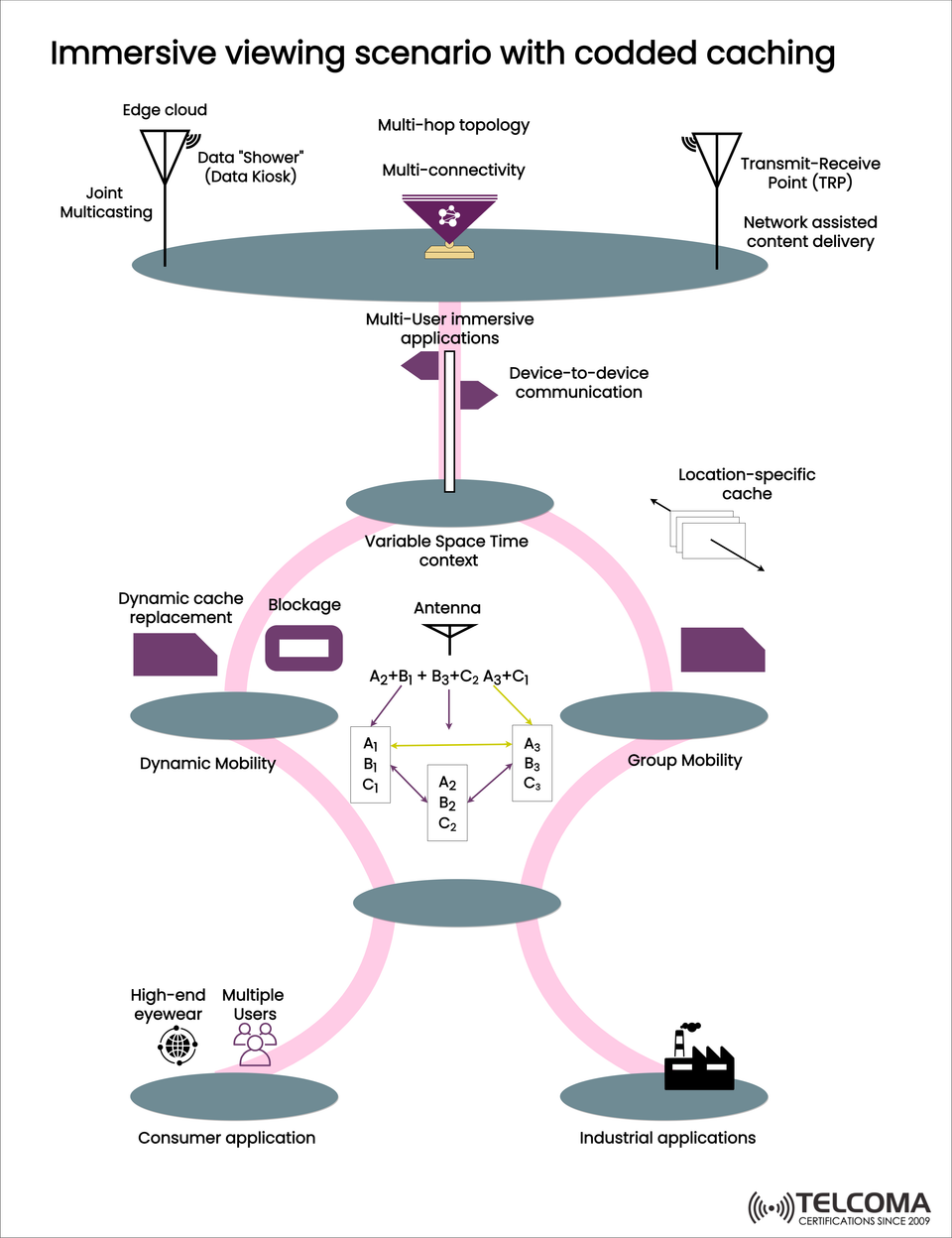
One innovative solution to meet these demands is coded caching. This method boosts content delivery efficiency and helps ensure a smooth user experience, no matter how dynamic the environment. The diagram shared shows an immersive viewing scenario that combines coded caching with edge intelligence, device-to-device communication, and network-assisted delivery, aiming to cater to both consumer and industrial needs.
This blog takes a closer look at the key components of this scenario, emphasizing how multi-hop topologies, location-specific caches, group mobility, and dynamic mobility come together to create efficient immersive experiences.
What is Coded Caching?
Coded caching is a cutting-edge content delivery strategy that merges caching and coding techniques to make the most out of bandwidth and cut down on latency.
Instead of just keeping data at network nodes or devices, coded caching:
Breaks content into coded fragments that can be pieced together in various combinations.
Allows multiple users with different requests to receive content at the same time.
Alleviates network congestion by utilizing distributed cache memories across the network.
In scenarios where high-bandwidth video streams or AR/VR data need to reach lots of users simultaneously, coded caching proves to be incredibly valuable.
Key Components of the Immersive Viewing Scenario
- Edge Cloud and Data Kiosks
The system kicks off at the edge cloud, storing data closer to users to minimize latency. Data kiosks—or "data showers"—deliver content through joint multicasting, ensuring multiple users get their content at the same time.
Benefits:
Quicker response times
Less backhaul congestion
Scalability for immersive applications
- Multi-Hop Topology and Multi-Connectivity
Instead of depending on a single connection, users benefit from a multi-hop topology, allowing data to travel through various intermediate nodes, along with multi-connectivity, which lets them connect to several transmit-receive points (TRPs) at once.
Advantages include:
Better reliability
Efficient load balancing
Broader coverage for dense user situations
- Transmit-Receive Points (TRPs) and Network-Assisted Delivery
TRPs are vital for boosting coverage and capacity. With network-assisted content delivery, TRPs help optimize bandwidth and ensure low-latency transmissions, which are essential for immersive applications like AR gaming or industrial digital twins.
- Device-to-Device (D2D) Communication
In immersive settings, device-to-device communication reduces the need to rely on central network nodes. Users can directly swap cached content fragments, enhancing efficiency and resilience, especially in high-mobility scenarios.
- Dynamic Cache Replacement and Location-Specific Caching
Caching strategies need to adapt on the fly to user demands and mobility patterns:
Dynamic Cache Replacement: Makes sure the most relevant content is available to limit interruptions as users move or run into obstacles.
Location-Specific Caching: Keeps data at local hotspots, so immersive applications can access data quickly in specific places like stadiums, factories, or shopping malls.
- Variable Space-Time Context and Antenna Role
The antenna system works within a variable space-time context, adjusting data transmissions dynamically. Coded fragments (like A2+B1, B3+C2, A3+C1) are shared among users and recombined as needed to optimize throughput and efficiency.
- Dynamic and Group Mobility
The system covers two types of mobility:
Dynamic Mobility: Individual users moving through different environments with changing connectivity.
Group Mobility: Groups of users moving together (think event attendees or workers in a factory), all needing synchronized delivery of immersive content.
- Application Domains
Consumer Applications
High-end eyewear (AR/VR headsets): Great for immersive gaming, entertainment, and interactive learning.
Multiple user scenarios: At concerts, sports games, or during collaborative VR sessions when bandwidth needs peak.
Industrial Applications
Smart factories: Coded caching enables real-time monitoring with AR overlays.
Remote collaboration: Teams use immersive applications for visualizing digital twins, predictive maintenance, or collaborative design work.
Advantages of Coded Caching for Immersive Viewing
Feature Benefit for Immersive Scenarios Joint multicasting Efficient delivery to multiple users Multi-connectivity Reliability and load balancing Device-to-device communication Faster, resilient sharing Dynamic caching Context-aware adaptability Group mobility support Seamless multi-user experiences Edge-enabled content Low-latency performance Network-assisted delivery Optimized bandwidth utilization
Challenges in Implementation
Despite its potential, immersive viewing using coded caching comes with hurdles:
Cache management complexity: Needs smart algorithms to predict user needs.
Mobility handling: Dynamic handovers can't disrupt immersive experiences.
Resource allocation: Finding a balance between spectral efficiency and fairness for users.
Hardware requirements: Demands high-performance edge servers and advanced user devices.
Future Outlook
As we approach 6G networks, immersive applications will stretch beyond entertainment and industry into areas like healthcare, education, and smart cities. Coded caching will play an even bigger role, leveraging AI-driven cache management, blockchain for content security, and holographic communications.
Conclusion
The immersive viewing scenario utilizing coded caching illustrates how next-gen telecom technologies can deliver high-quality, low-latency experiences to many users. By bringing together edge clouds, TRPs, multi-connectivity, device-to-device communication, and dynamic caching, networks can support both consumer-grade immersive entertainment and essential industrial applications.
For those in telecom or tech enthusiasts, coded caching is more than just a way to optimize—it's becoming a fundamental part of the future immersive internet. By connecting user demands with network capabilities, it’s laying the groundwork for seamless, scalable, and truly immersive multi-user experiences.
