Implementation Modes of Edge Computing: A Complete Guide for Telecom and Tech Professionals

Understanding Edge Computing Implementation: An Overview
Edge Computing is making waves in various industries by bringing computation and storage closer to where the data is generated. Rather than just relying on big cloud servers, edge computing leads to quicker decision-making, less latency, and better efficiency across areas like telecom, IoT, manufacturing, energy, transport, and public services.
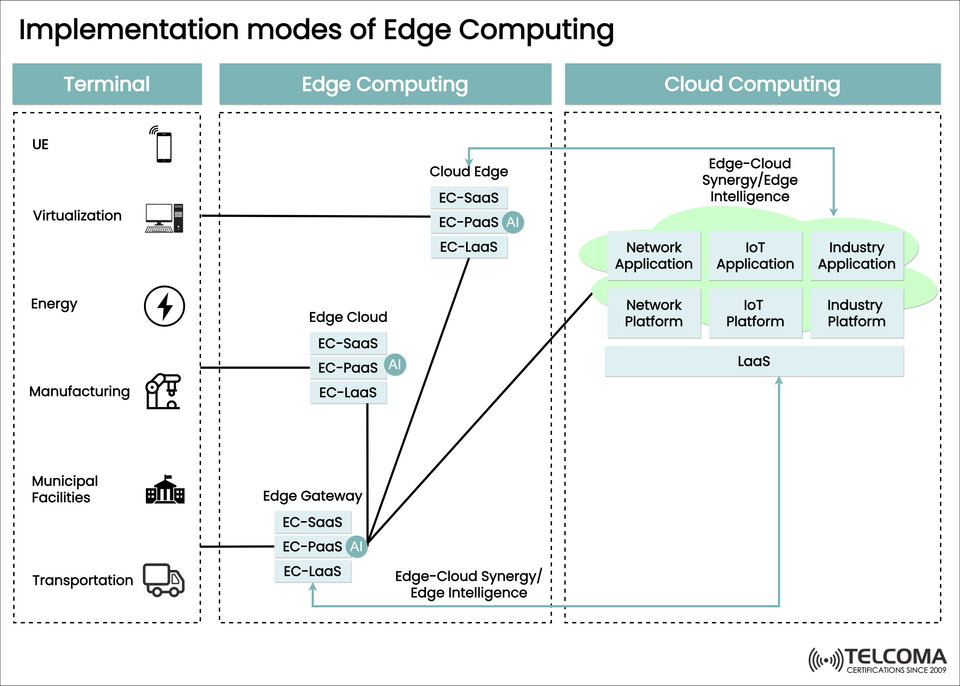
The image above lays out the implementation modes of Edge Computing and shows how different layers—terminals, edge, and cloud—work together to create a robust, decentralized computing environment. Let’s dive into the details.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge Computing is all about processing data close to its source (the “edge” of the network) instead of sending everything off to distant cloud data centers. This method helps to cut down on latency, lessens bandwidth use, boosts security, and allows for real-time applications.
Industries such as telecom, smart cities, self-driving cars, and energy grids are turning to edge computing to keep up with the increasing need for super-low latency, reliable service, and instant insights.
Key Components of Edge Computing Implementation
The image depicts a layered approach to implementing edge computing. Let’s take a closer look at each layer:
- Terminal Layer
The terminal consists of the devices and systems that create data. This includes:
UE (User Equipment): Smartphones, IoT devices, wearables.
Virtualization Systems: Computers, virtual machines, or containers that handle local tasks.
Energy Systems: Smart meters, renewable energy sources, EV charging stations.
Manufacturing Machines: Industrial robots, sensors, assembly line controllers.
Municipal Facilities: Smart lighting, surveillance systems, traffic control.
Transportation Systems: Connected vehicles, logistics trackers, fleet management systems.
These terminals act as the entry point for edge data before it gets processed.
Edge Computing Layer
This is where the real magic happens. Data coming from the terminals is processed right at or near the source through:
a. Edge Gateway
This serves as a link between local devices and the cloud, providing computing, storage, and connections through services like:
EC-SaaS (Edge Computing Software-as-a-Service): Software that runs at the edge for analytics or applications.
EC-PaaS (Edge Computing Platform-as-a-Service): Platforms that offer APIs, tools, and AI processing right at the edge.
EC-LaaS (Edge Computing Infrastructure-as-a-Service): On-demand computing resources and infrastructure located near the edge.
b. Edge Cloud
A distributed cloud environment that's hosted close to users or devices. It supports advanced features such as:
AI-driven real-time decision-making.
Data pre-processing before sending crucial insights to the central cloud.
Quicker responses for telecom services like 5G slicing and Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC).
c. Cloud Edge
A hybrid setup where cloud capabilities are brought closer to users through regional data centers, boosting reliability and making it easier to scale.
Cloud Computing Layer
The cloud still plays a vital role in this mix. While edge computing deals with immediate, time-sensitive data, the cloud covers:
Network Applications & Platforms: Supporting large-scale telecom networks and orchestration.
IoT Applications & Platforms: Managing the vast number of IoT devices and their gathered insights.
Industry Applications & Platforms: Enabling specific use cases like smart manufacturing or healthcare.
IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service): Full-scale computing resources to back up edge nodes.
This partnership between edge and cloud is known as Edge-Cloud Synergy/Edge Intelligence—where both edges and cloud enhance one another.
Why Edge-Cloud Synergy is Important
Edge and Cloud aren't competitors—they're allies in digital transformation.
Edge guarantees real-time processing (think autonomous vehicles or smart grids).
Cloud provides scalability and centralized intelligence (like predictive analytics or training AI models).
Together, they create Edge Intelligence, a system that balances latency, reliability, and scalability.
Applications Across Different Industries
Edge Computing is a significant advancement for many sectors. Here’s a look at some of them:
Industry Edge Use Cases Telecom (UE + Virtualization)5G network slicing, AR/VR services, low-latency mobile applications. Energy Smart grids, predictive maintenance for turbines, managing EV charging. Manufacturing Real-time quality control, robotics, and predictive analytics to prevent downtime. Municipal Facilities Smart lighting, traffic management, waste monitoring, and surveillance analytics. Transportation Connected vehicles, fleet optimization, autonomous driving, logistics improvements.
Benefits of Implementing Edge Computing
Ultra-low Latency: Fast data processing for critical tasks.
Bandwidth Efficiency: Cuts down on the traffic sent to central clouds.
Scalability: Can manage billions of IoT devices without bogging down networks.
Enhanced Security: Keeping data close minimizes interception risks.
Business Agility: Allows for the quick rollout of AI, IoT, and real-time services.
Challenges to Keep in Mind
Even though edge computing has so many benefits, telecom and tech experts need to tackle certain challenges such as:
Complex Deployment: Merging edge and cloud requires strong orchestration.
Standardization Issues: The absence of universal standards can slow things down.
Data Privacy: Sensitive information at the edge needs top-notch encryption.
Costs: Initial setup costs can be substantial.
The Future of Edge Computing
Edge computing is more than just a tech shift; it’s a paradigm shift. With the rise of 5G, IoT, AI, and Industry 4.0, edge-cloud synergy will become the backbone of digital ecosystems.
Emerging trends to look out for include:
AI-driven Edge Intelligence for swift decision-making.
5G Edge Integration to enable autonomous systems.
Edge-native Applications designed specifically for distributed settings.
Sustainability through energy-efficient localized processing.
Wrapping Up
The different implementation modes of edge computing—covering terminals, edge gateways, edge clouds, and their synergy with centralized cloud computing—set the stage for the next wave of digital transformation. For professionals in telecom and tech, grasping these layers is key to building strong, scalable, and future-ready networks.
By embracing edge-cloud synergy, industries can achieve quicker response times, improved efficiency, and smarter applications, paving the way for innovations in telecom, IoT, manufacturing, and much more.
