Independent Private 5G Networks: Architecture, Benefits, and Use Cases
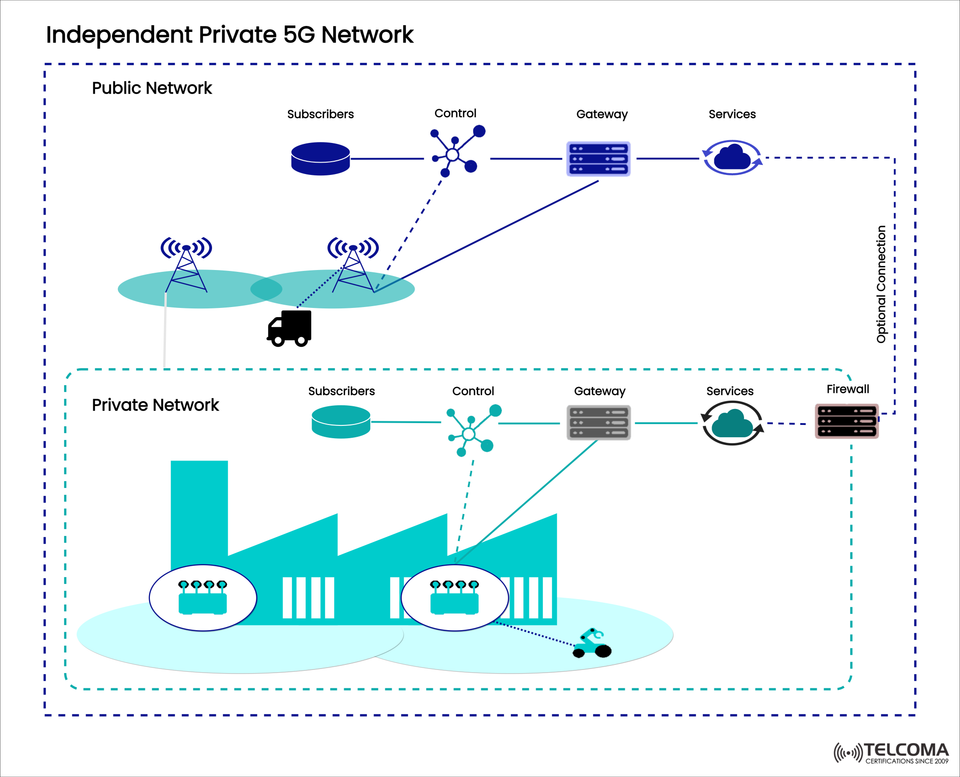

Independent Private 5G Network: An Overview
The emergence of 5G technology has paved the way for tailored, enterprise-focused connectivity solutions. Among the different ways to deploy this technology, the independent private 5G network stands out as a significant option for businesses looking for security, performance, and independence.
The diagram we've included illustrates how these networks function, highlighting the clear distinction between public and private 5G networks, while also showing how they can connect if necessary.
In this blog, we’ll dive into the architecture, how these networks work, their benefits, and some of the industries that are using independent private 5G networks.
What is an Independent Private 5G Network?
An independent private 5G network is its own standalone infrastructure set up right inside a business's premises. Unlike hybrid systems that share resources with public networks, this setup:
Runs independently from public mobile operators.
Has its own subscriber database, control and user planes, and services.
Gives businesses full ownership and control.
Can connect to public networks through a secure gateway if desired.
This design is perfect for sectors that have strict security, compliance, and performance needs.
Independent Private 5G vs Public 5G
Feature Public 5G Network Independent Private 5G Network Control Managed by telecom operators Fully managed by the enterprise Data Security Shared infrastructure, operator control On-premises, enterprise-managed Customization Limited Highly customizable (QoS, slices)Latency Depends on operator’s core Ultra-low with local breakout Integration Standardized services Tailored to industrial/enterprise needs Optional Public Access N/A Possible through secure interconnection
Architecture of Independent Private 5G Networks
The diagram shows the clear separation between public and private networks. Here are the main components:
- Public Network Segment
Subscribers: Handled by the telecom operator.
Control & Gateway: Take care of mobility, user data authentication, and routing.
Services: Provided by the operator, including cloud or application services.
Connectivity: Public gNBs (base stations) ensure mobile device coverage.
- Private Network Segment
Subscribers: Managed by the enterprise for SIM/eSIM administration.
Control Plane: Manages signaling, user authentication, and policy administration.
Gateway: Connects private devices to the enterprise's internal services.
Services: Run on enterprise servers (like robotics, IoT platforms, and analytics).
Firewall: Provides robust security, monitoring incoming and outgoing traffic.
gNB (Private 5G Base Stations): Installed on enterprise property to serve local devices.
- Optional Connection
Through a secure link between the private and public networks, selected information can pass through the operator systems, while core operations remain isolated.
Key Benefits of Independent Private 5G Networks
- Total Control over Network
Companies can tailor QoS, slicing, and security settings to fit their specific operational needs.
- Improved Security
All sensitive information stays on-site, protected by enterprise firewalls, lowering the risk of outside threats.
- Ultra-Reliable Low Latency
Because traffic doesn’t go through a public core, latency is reduced—this is essential for real-time applications like robotics and AR/VR.
- Customization and Flexibility
From network slicing to custom subscriber management, businesses enjoy unparalleled flexibility.
- Regulatory Compliance and Data Control
Perfect for sectors where laws mandate that data must stay within a facility or country.
Independent Private 5G: Use Cases in Industry
Manufacturing (Smart Factories)
Uses autonomous robots and conveyor systems.
Employs predictive maintenance with connected sensors.
Implements augmented reality for training and repairs in real-time.
Logistics & Warehousing
Features automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and drones.
Real-time stock management with IoT sensors.
High-bandwidth video surveillance for security purposes.
Energy and Utilities
Smart grids relying on ultra-reliable communication links.
Enables remote monitoring of power plants and substations.
Provides secure, site-specific connectivity for critical infrastructure.
Healthcare
Hospitals with private 5G enable real-time patient monitoring.
Robotic surgeries that require ultra-low latency.
Secure management of sensitive patient information.
Automotive and Transportation
Testing connected vehicles on private tracks.
V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) communication in controlled settings.
Real-time tracking and management of fleets.
Challenges of Implementing Independent Private 5G
Despite its many benefits, there are hurdles to consider:
Cost: Building dedicated infrastructure (core systems, gNBs, gateways) can be pricey.
Complexity: Needs specialized knowledge of 5G architecture and operations.
Spectrum Access: Companies must secure licensed or shared spectrum.
Maintenance: Enterprises bear full responsibility, unlike with public networks.
Looking Ahead
The drive for independent private 5G is picking up speed, fueled by Industry 4.0, smart cities, and digital transformation projects.
Future trends will likely emphasize:
5G Advanced (Release 18): Better support for enterprise setups.
AI-driven Network Automation: Smarter, self-optimizing private networks.
Integration with Edge Computing: Offering ultra-low latency for immediate data analysis and automation.
Broader Spectrum Availability: Governments making more spectrum bands accessible for private use.
In Summary
The independent private 5G network represents the pinnacle of enterprise connectivity—secure, isolated, and completely within an organization’s control. Unlike shared or hybrid solutions, it provides incredible freedom, making it especially suitable for mission-critical, latency-sensitive, and compliance-oriented industries.
As businesses move forward in their digital transformation journeys, independent private 5G will play a crucial role in delivering high performance, security, and reliability. Its influence on the future of Industry 4.0, healthcare, logistics, and smart infrastructure is clear.
By investing in this network design today, organizations aren’t just meeting their current operational needs but are also future-proofing their systems for the ever-changing world of 5G and beyond.
