Inside the O-RAN E2 Interface: Understanding E2AP and E2SM for Intelligent RAN Control

Getting to Know the O-RAN E2 Interface: The Backbone of Smart RAN Management
The O-RAN (Open Radio Access Network) framework marks a significant shift in mobile network design, moving away from closed-off, hardware-based systems toward more open, interoperable, and software-oriented networks.
At the core of this change is the E2 Interface, which acts as a vital connection between the Near-Real-Time RIC (RAN Intelligent Controller) and the E2 Nodes (like O-DU or O-CU).
This interface allows for real-time control, policy enforcement, and data sharing, which are key for AI-driven automation and optimization within the RAN.
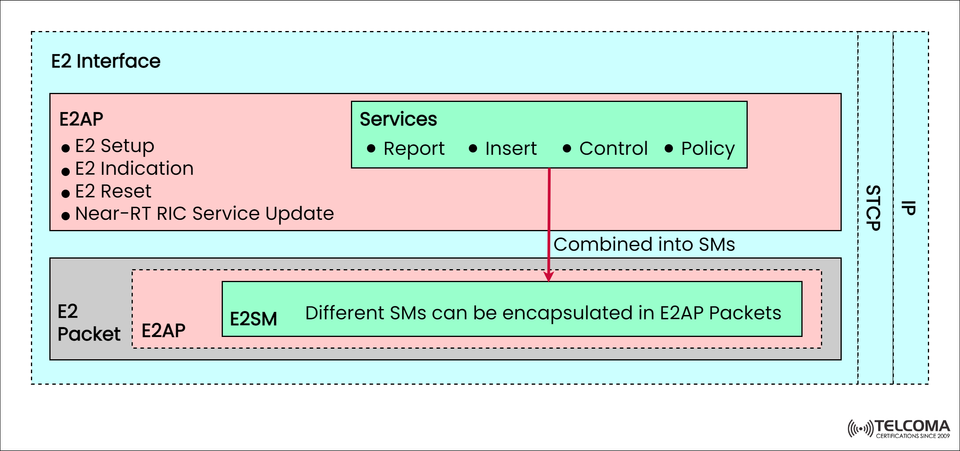
The image included helps visualize how E2AP (E2 Application Protocol) and E2SM (E2 Service Models) are foundational for E2 communication, incorporating control messages, policies, and performance data.
The Importance of the E2 Interface in O-RAN
The E2 Interface is a standardized framework laid out by the O-RAN Alliance. It facilitates communication between the Near-RT RIC and E2 Nodes using clearly defined signaling and data exchange protocols.
Goals of the E2 Interface:
To enable real-time monitoring and control of RAN operations
To support multi-vendor compatibility between RIC and RAN components
To assist with xApp-based automation through open protocols
To offer a flexible framework for adding new services and intelligence models
Basically, the E2 interface serves as the “nervous system” for the intelligent RAN, allowing data to flow between decision-making bodies (the RIC) and execution points (E2 Nodes).
Breaking Down the E2 Interface Components
As shown in the diagram, the E2 interface is made up of several key layers that work together to ensure strong, dependable communication:
Layer / Protocol / Component / Function
Transport Layer / SCTP (Stream Control Transmission Protocol) over IP / Guarantees reliable, ordered message delivery
Application Layer / E2AP (E2 Application Protocol) / Manages signaling, setup, and control messaging
Service Model Layer / E2SM (E2 Service Models) / Defines data structures and control semantics for specific scenarios
These components create structured E2 packets, which enable smooth collaboration between the RIC and E2 Nodes.
What You Need to Know About E2AP (E2 Application Protocol)
E2AP is the control and signaling protocol used in the E2 interface. It sets up, maintains, and oversees communication between the Near-RT RIC and E2 Nodes.
Main Functions of E2AP:
E2 Setup: Starts the connection between the RIC and E2 Node.
E2 Indication: Sends regular or event-based reports (like KPM data).
E2 Reset: Manages reinitialization in case of errors or topology shifts.
Near-RT RIC Service Update: Adjusts or alters active service configurations on the fly.
These processes ensure that both parts stay in sync, functional, and responsive to real-time conditions.
E2AP serves as the “language” for communication — defining how messages are put together, sent, and acknowledged.
Services Provided by the E2 Interface
Within E2AP, various service types outline how RIC and E2 Nodes interact. As illustrated in the image, these services include:
Report: Lets E2 Nodes send measurement updates (like KPMs) to the RIC.
Insert: Allows the RIC to implement specific actions or settings into the E2 Node.
Control: Offers command and policy-driven control capabilities.
Policy: Establishes long-term network policies for consistent behavior and optimization.
Together, these services enable real-time control loops, where decisions made by the RIC are quickly acted upon by E2 Nodes, keeping the network running efficiently.
Introducing E2SM (E2 Service Models)
While E2AP focuses on how messages are communicated, E2SM specifies what those messages entail.
Each E2 Service Model (E2SM) is tied to a specific use case or application area in the RAN.
Definition:
E2SM supplies the data model, coding rules, and semantic clarifications for every service type in the E2 interface.
This means that E2SMs serve as blueprints for how data like KPIs, configurations, and policies are formatted and interpreted by both the RIC and E2 Node.
How E2AP and E2SM Work Together
The diagram illustrates how E2AP and E2SM interact:
E2AP manages the procedural control and message transport.
E2SM provides the content and meaning for those messages.
Example Flow:
A Near-RT RIC xApp asks for KPI data (like UE throughput).
The E2AP message carries the request structure.
The E2SM specifies the exact KPI metrics and encoding format.
The E2 Node replies with an E2 Indication that includes KPI data using the same E2SM definition.
Multiple service models (E2SMs) can fit into E2AP packets, allowing different functions — like control, policy, and reporting — to run at the same time and work independently.
Popular E2 Service Models (E2SMs)
E2SM Type / Purpose / Use Case / Example Metrics
E2SM-KPM / Key Performance Measurement / UE throughput, resource utilization, CQI
E2SM-RC / RAN Control / Adjusting transmission power, scheduling
E2SM-NI / Network Information / Topology and load status updates
E2SM-MHO / Mobility and Handover / Handover events and performance
E2SM-QoS / Quality of Service Control / Traffic prioritization, QoS adjustments
These E2SMs empower xApps to dynamically enhance performance — ensuring the RIC can make data-driven decisions throughout the RAN.
E2 Interface Data Organization
As shown in the image:
E2AP and its services are packed into Service Models (SMs).
Each E2 packet may contain an E2AP message with one or multiple E2SMs.
The packet is sent using SCTP over IP, ensuring reliability and low latency.
This modular design allows for extensibility, meaning new service models can be added without interfering with existing systems.
The Significance of the E2 Interface in O-RAN Development
The E2 interface is more than just a technical connection; it’s a strategic enabler for O-RAN’s primary goals:
Vendor Interoperability: Allows RICs and RAN nodes from different vendors to work together seamlessly.
Intelligent Automation: Provides the data flow for AI/ML-powered xApps.
Scalability: Facilitates the addition of new RAN functions using fresh E2SMs.
Operational Efficiency: Cuts down on manual efforts through automated processes.
Future-Proofing: Adapts easily to the evolving needs of 5G and 6G.
By enabling real-time exchanges of performance and control data, the E2 interface transforms the RAN into a programmable, intelligent network.
- Quick Summary of the E2 Interface Structure
Layer / Component / Purpose / Key Features
IP + SCTP / Transport / Reliable packet delivery
E2AP / Application Signaling / Setup, Indication, Reset, Service Update
Services / Functional Behavior / Report, Control, Insert, Policy
E2SM / Service Model / Encapsulates specific RAN scenarios
E2 Packet / Encapsulation Unit / Combines E2AP and E2SM into a single packet for transmission
Conclusion
The E2 Interface is a key element of the O-RAN intelligent control architecture, linking the Near-Real-Time RIC with E2 Nodes using open, standardized protocols.
Through E2AP and E2SM, this interface guarantees that control messages, policies, and performance data are shared seamlessly — making real-time automation, multi-vendor compatibility, and network intelligence a reality.
As telecom networks evolve toward AI-driven 5G and 6G, getting a solid grasp on the E2 interface — and how E2AP and E2SM interact — is crucial for any engineer or operator looking to build, optimize, and prepare open RAN environments for the future.
