Interfaces and Function Split between O-RAN and 3GPP: A Complete Guide for 5G Networks

As 5G continues to develop, the demand for flexible, interoperable, and open networks is at an all-time high. The traditional telecom networks, shaped by the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project), set the groundwork for 5G architecture by establishing standards for the gNB (Next Generation Node B), which includes interfaces and functions.
To keep pushing innovation and avoid being locked into one vendor, the O-RAN Alliance has come into play. They've rolled out new functions and interfaces that work alongside 3GPP, helping to open up the RAN ecosystem.
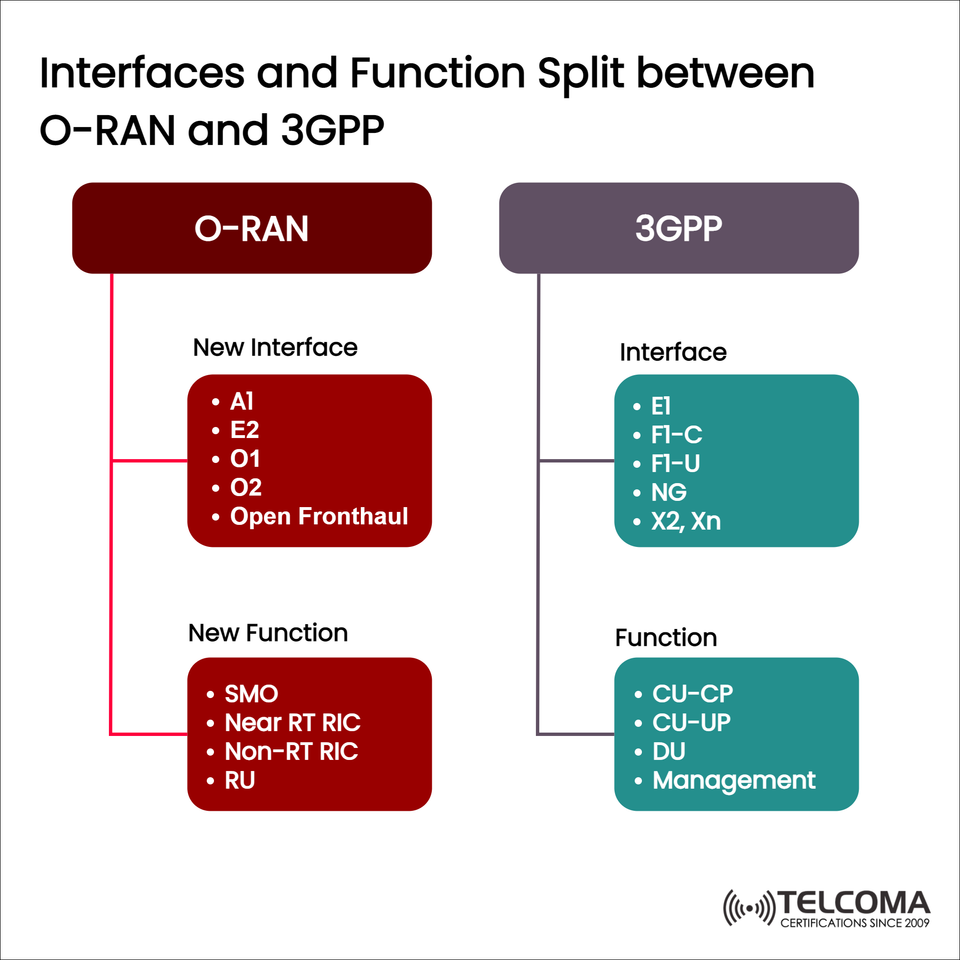
The diagram we uploaded illustrates how O-RAN and 3GPP separate functions and interfaces, making up the framework of next-gen 5G networks. In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at these distinctions, why they’re important, and how they’ll influence the future of telecommunications.
3GPP: Standardized Functions and Interfaces
The 3GPP lays out how gNB functions are organized and how the various components interact.
Key Interfaces in 3GPP
E1: Between gNB-CU-CP (Control Plane) and gNB-CU-UP (User Plane).
F1-C and F1-U: Between gNB-CU and gNB-DU for control and user plane, respectively.
NG: Interface linking gNB with the 5G Core (5GC).
X2, Xn: Interfaces between gNBs for communicating between cells and handling mobility management.
Functions in 3GPP
CU-CP (Central Unit – Control Plane): Manages signaling, RRC, mobility, and session oversight.
CU-UP (Central Unit – User Plane): Deals with user data traffic, enforces QoS, and handles tunneling.
DU (Distributed Unit): Takes care of real-time radio functions such as MAC, RLC, and PHY layers.
Management: Offers OAM (Operations, Administration, and Maintenance) support.
These standards make sure there's interoperability among vendors and serve as the baseline architecture for 5G RAN.
O-RAN: Extending and Opening the RAN
While 3GPP standardizes the gNB, the O-RAN Alliance goes beyond that, introducing new functions and open interfaces designed to improve flexibility, support vendor diversity, and enable AI-driven automation.
New Interfaces in O-RAN
A1: Between Non-RT RIC and Near-RT RIC for sharing policies and guidance.
E2: Between Near-RT RIC and RAN nodes for real-time control and optimization.
O1: Management interface for SMO (Service Management and Orchestration).
O2: Connects SMO to cloud infrastructure for resource orchestration.
Open Fronthaul: Standardizes communication between O-DU and O-RU, allowing multi-vendor cooperation.
New Functions in O-RAN
SMO (Service Management and Orchestration): Automates managing the lifecycle, configuration, and monitoring of RAN components.
Near-RT RIC (RAN Intelligent Controller): Enables real-time control and optimization (10 ms – 1 s response times). It's home to xApps that perform functions like load balancing or mobility optimization.
Non-RT RIC: Takes care of policy, trains AI/ML models, and handles long-term optimizations (>1 s response times). It's where rApps are hosted.
RU (Radio Unit): Manages RF functions and connects to antennas, collaborating with DU via Open Fronthaul.
O-RAN introduces intelligence and openness to the RAN, creating an environment where various vendors and AI applications can thrive.
Comparing O-RAN and 3GPP
Here’s a quick comparison:
Aspect3GPPO-RANPrimary Role Defines standardized RAN architecture (gNB split).Extends RAN with openness, intelligence, and support for multiple vendors.InterfacesE1, F1-C, F1-U, NG, X2/Xn.A1, E2, O1, O2, Open Fronthaul. Functions CU-CP, CU-UP, DU, Management. SMO, Near-RT RIC, Non-RT RIC, RU. Focus Interoperability, baseline architecture. Intelligence, automation, openness. Deployment Traditional vendor-led. Multi-vendor, cloud-native, AI-driven.
Why the Split Matters
The separation of functions and interfaces between O-RAN and 3GPP isn’t redundant—it's actually complementary. Together, they:
Enable multi-vendor interoperability through open interfaces.
Support automation and AI/ML in the RAN.
Allow for flexible deployment models: centralized, distributed, or hybrid.
Lay the foundation for network slicing and private 5G.
For operators, this translates to lower costs, quicker innovation, and freedom from vendor lock-in.
Real-World Use Cases
Network Optimization with AI: * Near-RT RIC uses xApps for dynamic spectrum allocation, interference management, and load balancing.
Private 5G for Enterprises: * O-RU and O-DU with open fronthaul let businesses create custom networks without depending on one vendor.
Energy Efficiency: * Non-RT RIC and SMO utilize AI to handle energy savings by dynamically powering down cells during low-traffic times.
Multi-Vendor Interoperability: * Operators can mix RU from one vendor, DU from another, and RIC from a third—ensuring best-of-breed solutions.
Challenges in Implementation
Despite its potential, O-RAN has some challenges:
Transport Requirements: Open fronthaul needs low-latency, high-bandwidth connections.
Complexity: Managing multi-vendor setups necessitates sophisticated orchestration.
Maturity: Some O-RAN interfaces and functions are still in development compared to the more established 3GPP standards.
Security Risks: Open interfaces can broaden the attack surface if not properly secured.
Operators need to find a balance between innovation and operational realities.
Future Outlook
The future of telecommunications relies on the synergy between 3GPP and O-RAN.
3GPP will keep defining baseline standards for interoperability.
O-RAN will continue to drive progress with AI, automation, and openness.
Together, they will form the backbone for cloud-native, intelligent 5G and beyond (6G).
Conclusion
The function and interface separation between O-RAN and 3GPP marks a significant milestone in the evolution of mobile networks.
3GPP establishes the baseline with CU, DU, and standardized interfaces like E1 and F1.
O-RAN builds on this foundation by introducing intelligence (RIC), orchestration (SMO), and openness (Open Fronthaul).
For those in the telecom industry, grasping both realms is crucial. 3GPP guarantees stability and global interoperability, while O-RAN fosters innovation, flexibility, and multi-vendor environments.
