Key 5G Enabling Aspects: Spectrum, Radio, Access, and Core Explained

5G, the fifth generation of mobile networks, is more than just a step up from 4G/LTE; it's a total game changer for wireless communication. With super-fast data speeds, ultra-low latency, massive connectivity, and flexible networks, 5G sets the stage for cutting-edge technologies like self-driving cars, smart cities, Industry 4.0, and immersive AR/VR experiences.
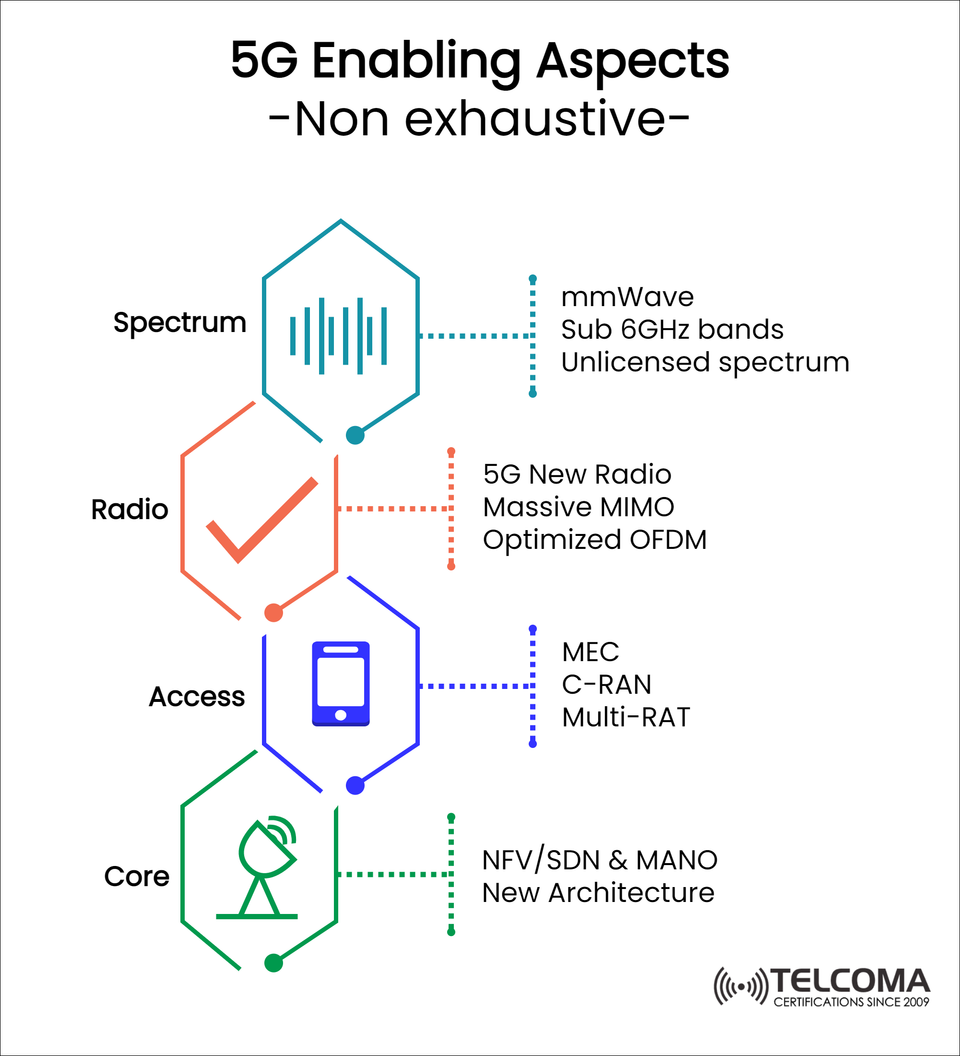
The image below outlines the key enabling aspects of 5G, organized into four main pillars:
Spectrum – a range of new frequency bands, including mmWave and sub-6 GHz.
Radio – cutting-edge technologies such as 5G New Radio (NR), Massive MIMO, and Enhanced OFDM.
Access – upgrades like MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing), C-RAN, and Multi-RAT.
Core – a completely revamped architecture using NFV, SDN, and MANO.
In this blog, we’ll dig into each of these aspects, discussing their significance and how they're helping shape the future of telecom networks.
Spectrum: Expanding Frequency Horizons
To cater to various use cases, 5G networks rely on a varied spectrum portfolio. Unlike 4G, which mainly used frequencies below 3 GHz, 5G takes advantage of a broader range.
Key Spectrum Bands in 5G:
mmWave (Millimeter Wave): * Frequency range: 24 GHz to 100 GHz. * Delivers incredibly high capacity and blazing fast speeds. * Perfect for crowded urban settings, stadiums, and high-bandwidth tasks. * Downsides: Limited coverage and penetration.
Sub-6 GHz bands: * Frequency range: Below 6 GHz. * Balances coverage and capacity effectively. * Essential for nationwide 5G rollout.
Unlicensed spectrum: * Supports shared usage models. * Fuels innovations like 5G private networks and Wi-Fi integration.
Why spectrum matters:
The variety in frequency bands means 5G can deliver nationwide coverage, private networks for companies, and super-fast urban hotspots, depending on how it's deployed.
Radio: The Heart of 5G Performance
Radio technology forms the foundation of 5G performance enhancements, allowing for increased capacity, reduced interference, and greater efficiency.
Core Radio Enablers in 5G:
5G New Radio (NR): * A new global standard enabling flexible spectrum use. * Boosts spectral efficiency through scalable settings and frame structures.
Massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output): * Uses multiple antennas at base stations. * Enhances capacity by connecting with multiple users at once. * Offers better beamforming for more precise coverage.
Optimized OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing): * Builds on 4G’s OFDM while optimizing for lower latency and wider bandwidth. * Supports dynamic spectrum sharing and flexible carrier aggregation.
Why radio matters:
These advanced radio technologies help 5G manage the expected 100x traffic growth and ultra-low latency that’s on the horizon.
Access: Bridging Devices and Networks
The access layer makes sure users and devices can easily connect to the 5G network. It integrates different technologies to support low-latency applications and high-density device connectivity.
Key Access Enablers:
MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing): * Moves computing resources closer to users. * Cuts down on latency by processing data at the edge instead of in centralized data centers. * Supports real-time applications like self-driving cars and AR/VR.
C-RAN (Cloud Radio Access Network): * Centralizes baseband processing in the cloud. * Improves how resources are used and lowers costs. * Allows for dynamic resource allocation across different sites.
Multi-RAT (Radio Access Technology): * Ensures smooth coexistence with 4G, Wi-Fi, and other wireless technologies. * Makes the transition and integration easier.
Why access matters:
These access upgrades let 5G handle a wide range of use cases at once—from low-power IoT devices to heavy-duty mobile broadband users.
Core: A Redesigned Network Foundation
The 5G core network marks a significant change from the classic 4G EPC (Evolved Packet Core). It’s now cloud-native, adaptable, and service-oriented.
Core Enabling Aspects:
NFV (Network Function Virtualization): * Swaps out dedicated hardware for virtualized network functions (VNFs) running on standard hardware. * Boosts agility and cuts down on costs.
SDN (Software Defined Networking): * Splits control and forwarding functions. * Offers centralized oversight and programmability. * Enables dynamic network slicing.
MANO (Management and Orchestration): * Manages virtualized functions and resources. * Guarantees automated scaling, fault management, and enforcement of policies.
New Service-Based Architecture (SBA): * Fully modular and API-driven. * Allows for flexible service deployment tailored to different industries.
Why the core matters:
A cloud-native 5G core enables providers to offer custom network slices for various sectors—whether it’s healthcare, automotive, manufacturing, or media—without needing separate infrastructures.
Comparative View: 4G vs 5G Enabling Aspects
Aspect 4G LTE | 5G NR
Spectrum: Primarily <3 GHz | mmWave, Sub-6 GHz, Unlicensed
Radio: OFDM, MIMO | Optimized OFDM, Massive MIMO, 5G NR
Access: eNodeB, centralized RAN | MEC, C-RAN, Multi-RAT
Core: EPC, hardware-centric | NFV, SDN, MANO, Service-Based Architecture
Real-World Impact of 5G Enabling Aspects
Smart Cities: Millions of IoT sensors linked through dense spectrum and access upgrades.
Autonomous Vehicles: Achieves ultra-low latency via MEC and enhanced radio technology.
Healthcare: Allows for remote surgeries made possible by edge computing and reliable spectrum.
Industry 4.0: Customized private networks through network slicing in the 5G core.
Entertainment: Immersive AR/VR experiences made possible by mmWave and Massive MIMO.
Conclusion
The road to 5G involves a blend of spectrum innovation, state-of-the-art radio technologies, improved access methods, and a redesigned core architecture. Each of these elements plays a distinct role in reaching the ambitious performance targets of 5G, from 20 Gbps peak speeds to 1 ms latency and massive device connectivity.
For telecom professionals, grasping these enablers is key for effective network planning and optimization. For tech lovers, they highlight how 5G will reshape daily digital experiences—from streaming and gaming to healthcare and transport.
In the end, these enabling aspects of 5G are what set the stage for not just an upgrade but a foundation for the next digital revolution.
