Key Enablers for Verticals in RAN | 5G Transformation Across Industries

Introduction
The advancement of 5G networks goes beyond just speeding up internet connectivity; it's really about empowering vertical industries with improved Radio Access Network (RAN) features. Industries like automotive, healthcare, public safety, Industry 4.0, and utilities have specific networking needs to support critical services, automation, and the vast world of IoT.
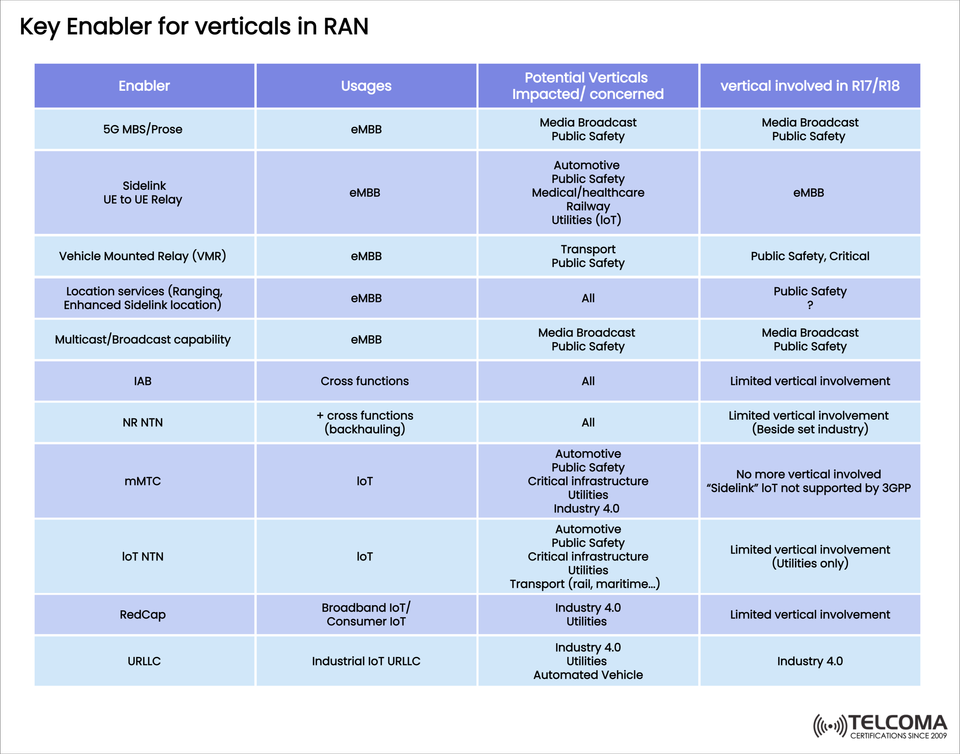
The graphic above, “Key Enabler for Verticals in RAN”, outlines important enablers, how they’re utilized in various scenarios, the verticals they affect, and their roles in 3GPP Releases 17 and 18 (R17/R18).
In this blog, we’ll explore each enabler, describe what it does, and connect how it helps with the adoption of 5G in different industries.
What are RAN Enablers for Verticals?
RAN enablers are specialized features within the 5G Radio Access Network aimed at addressing the unique challenges of vertical industries. They improve coverage, reliability, latency, and scalability to meet the specific needs of sectors like:
Automotive: Connected cars, self-driving tech, vehicle-mounted relays.
Healthcare: Remote monitoring of patients, emergency services.
Public Safety: Crucial communication for emergencies, response to disasters.
Utilities: Smart grid management, proactive maintenance.
Industry 4.0: Automation in manufacturing, robotics, systems focused on URLLC.
Breakdown of Key RAN Enablers
Here’s an overview of the major enablers, their applications, the verticals they influence, and their relevance in R17/R18.
- 5G MBS/Pro Se (Multimedia Broadcast Services / Proximity Services)
Usage: e MBB
Impacted Verticals: Media Broadcast, Public Safety
R17/R18 Role: Actively involved in media distribution and safety sectors.
Key Advantage: Facilitates effective media sharing and communication between devices during emergencies.
- Side link UE-to-UE Relay
Usage: e MBB
Impacted Verticals: Automotive, Public Safety, Healthcare, Railways, Utilities (IoT)
R17/R18 Role: Supported under e MBB
Key Advantage: Improves connectivity in areas with weak signals by relaying between devices.
- Vehicle Mounted Relay (VMR)
Usage: e MBB
Impacted Verticals: Transport, Public Safety
R17/R18 Role: Backing for Public Safety and Critical Communications
Key Advantage: Boosts connectivity for moving vehicles, including trains, buses, and emergency services.
- Location Services (Ranging, Enhanced Side link Location)
Usage: e MBB
Impacted Verticals: Public Safety, Automotive
R17/R18 Role: Noted for its importance in Public Safety
Key Advantage: Offers accurate location data essential for navigation, autonomous driving, and emergency response.
- Multicast/Broadcast Capability
Usage: e MBB
Impacted Verticals: Media Broadcast, Public Safety
R17/R18 Role: Strong engagement
Key Advantage: Efficiently shares multimedia content with multiple users at once, easing bandwidth demand.
- IAB (Integrated Access and Backhaul)
Usage: Cross Functions
Impacted Verticals: All
R17/R18 Role: Limited beyond specific use in industries
Key Advantage: Allows for flexible backhaul solutions in areas lacking fiber infrastructure.
- NR NTN (New Radio Non-Terrestrial Networks)
Usage: Cross Functions, Backhauling
Impacted Verticals: All, including maritime and remote regions
R17/R18 Role: Limited involvement, generally outside mainstream industries
Key Advantage: Expands 5G coverage through satellites to reach rural and isolated areas.
m MTC (Massive Machine-Type Communication)
Usage: IoT
Impacted Verticals: Automotive, Public Safety, Critical Infrastructure, Utilities, Industry 4.0
R17/R18 Role: IoT sidelink not supported by 3GPP past R17
Key Advantage: Links millions of low-power IoT devices for smart city and industrial applications.
- IoT NTN
Usage: IoT
Impacted Verticals: Automotive, Utilities, Transport (rail, maritime), Public Safety
R17/R18 Role: Limited involvement, mainly focused on utilities
Key Advantage: Satellite-enabled IoT ensures global connectivity, even in off-grid locations.
- Red Cap (Reduced Capability Devices)
Usage: Broadband IoT, Consumer IoT
Impacted Verticals: Industry 4.0, Utilities
R17/R18 Role: Limited industry application
Key Advantage: Provides cost-effective, energy-efficient devices fine-tuned for IoT, balancing performance with affordability.
- URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication)
Usage: Industrial IoT
Impacted Verticals: Industry 4.0, Utilities, Automated Vehicles
R17/R18 Role: Fully integrated into Industry 4.0 sectors
Key Advantage: Guarantees critical reliability for automation, robotics, and self-driving technology.
Summary Table
Enabler | Usage | Verticals Impacted | R17/R18 Involvement
5G MBS / Pro Se | MBB | Media Broadcast, Public Safety | Media Broadcast, Public Safety
Side link UE Relay | e MBB | Automotive, Healthcare, Utilities, Railway | eMBB
Vehicle Mounted Relay | e MBB | Transport, Public Safety | Public Safety, Critical
Location Services | e MBB | All | Public Safety
Multicast/Broadcast | e MBB | Media, Public Safety | Media, Public Safety
IAB | Cross Functions | All | Limited
NR NTN | Backhaul + Cross | All | Limited
m MTC | IoT | Automotive, Utilities, Industry 4.0 | Not supported after R17
IoT NTN | IoT | Utilities, Transport, Automotive | Limited
Red Cap | IoT | Industry 4.0, Utilities | Limited
URLLC | Industrial IoT | Industry 4.0, Vehicles | Industry 4.0
Key Drivers for RAN Verticals – Transforming 5G
5G goes beyond just faster speeds; it’s all about empowering different industries. New RAN capabilities such as URLLC, RedCap, mMTC, and IoT NTN are making waves in sectors like:
✅ Automotive – Think connected and self-driving cars.
✅ Public Safety – Critical communication systems.
✅ Healthcare – Monitoring patients from afar and responding to emergencies.
✅ Utilities – Smart grids and IoT technology.
✅ Industry 4.0 – Automation, robotics, and networks with low latency.
According to 3GPP Releases 17 & 18, some features—like URLLC—are already fully integrated into industrial IoT. Others, such as RedCap and NTN, offer adaptable and scalable solutions for wider use.
🔑 Ultimately, the advancement of 5G hinges on how these RAN enablers link up technology with the actual needs of various industries.
Conclusion
The key enablers in RAN form the backbone of the 5G evolution, connecting powerful network capabilities with the specific needs of vertical industries. Some features like URLLC, RedCap, and IoT NTN are pushing forward Industry 4.0 and automation, while others—like sidelink relays and vehicle-mounted relays—are essential for ensuring public safety and enhancing transportation.
As 3GPP releases continue to develop (R17/R18), we’re seeing a clearer picture of how various industries will be impacted. Some enablers may have limited roles, but others are set to be major players in shaping the future of connectivity in different sectors.
For telecom pros and tech aficionados, getting a handle on these enablers isn’t just about understanding the technical details of 5G—it's also about predicting its influence across a wide range of industries in this connected digital age.
