Key Technology Areas Driving 6G Requirements and KPIs

Technology Areas Impacting 6G Needs and KPIs
As the telecom sector moves past 5G, research and standardization groups are laying the groundwork for 6G networks, which should be here around 2030. Unlike 5G that was all about speed and capacity, 6G will focus on intelligence, sustainability, precision, and reliability.
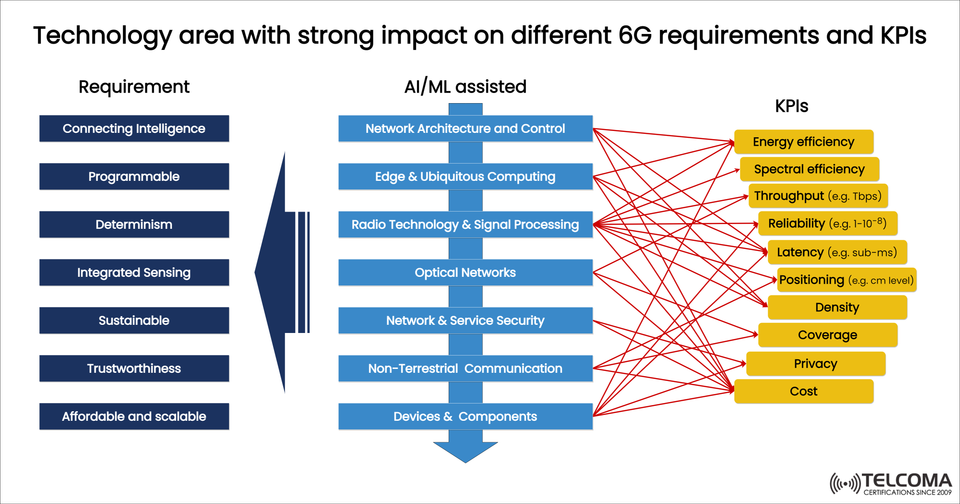
The diagram provided shows how various 6G needs, tech enablers, and KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are connected. By examining these links, we get a clear sense of how 6G will be crafted to support next-gen applications like holographic communications, autonomous mobility, industrial IoT, and the metaverse.
Core 6G Requirements
On the left side of the diagram, there are six main requirements that are key to 6G development:
Connecting Intelligence: Uses AI/ML for predictive and autonomous network management.
Programmable: Features flexible and adaptable architectures to meet changing service demands.
Determinism: Delivers predictable, guaranteed performance for crucial applications.
Integrated Sensing: Communication networks that also serve as sensing systems with centimeter-level accuracy.
Sustainable: Prioritizes energy efficiency and eco-friendly implementations.
Trustworthiness: Incorporates security, privacy, and transparency as foundational elements.
Affordable and Scalable: Ensures access for both urban and rural deployments.
These aren't merely technical aspects — they are societal necessities that make sure 6G is not only faster but also smarter, greener, and more inclusive.
AI/ML-Assisted Technology Areas
At the heart of 6G are the technology areas, many of which will be AI/ML-enabled, meaning they’ll have artificial intelligence integrated into their operation.
Here’s a closer look:
Network Architecture and Control
Emphasizes flexible, cloud-native designs.
AI helps create self-optimizing and self-healing networks.
This directly influences latency, reliability, and cost efficiency.
Edge & Ubiquitous Computing
Brings computing power closer to users.
Cuts down round-trip latency and makes real-time applications like XR and autonomous driving possible.
Boosts privacy by handling sensitive data locally.
Radio Technology & Signal Processing
6G will reach into Terahertz (THz) spectrum.
Advanced MIMO and beamforming techniques enhance spectral efficiency and throughput.
AI is utilized to handle signal interference and dynamic spectrum allocation.
Optical Networks
Form the foundation of 6G transport.
Offer ultra-high capacity to hit Tbps throughput goals.
Decrease end-to-end latency by optimizing light paths.
Network & Service Security
With billions of connected devices, 6G must adopt zero-trust frameworks.
Prioritizes privacy protection, resilience, and attack mitigation.
Essential for ensuring trustworthiness and affordability.
Non-Terrestrial Communication
Brings in satellites, UAVs, and high-altitude platforms for mainstream connectivity.
Expands coverage to remote areas, ensuring global access.
Critical for scalability and inclusivity.
Devices & Components
Involves advanced chipsets, antennas, and energy-efficient hardware.
Affects cost, energy efficiency, and density directly.
Needs to support miniaturization and sustainability.
These tech areas are the building blocks of 6G, each influencing the requirements to shape measurable KPIs.
Key KPIs for 6G Performance
On the right side of the diagram, we see KPIs that represent the measurable outcomes of 6G implementations. Here’s a look at how each is influenced:
Energy Efficiency: Takes advantage of AI-optimized hardware, low-power components, and eco-friendly design principles.
Spectral Efficiency: Utilizes THz spectrum and cutting-edge modulation schemes.
Throughput (Tbps): Supported by optical backhaul, terahertz bands, and ultra-massive MIMO technology.
Reliability (e.g., 10⁻⁸): Mission-critical industries require almost flawless service continuity.
Latency (sub-ms): Important for applications like the tactile internet, remote surgeries, and robotics.
Positioning (cm-level): Integrated sensing ensures accurate geolocation.
Density: Up to 10 million devices per km² for IoT ecosystems.
Coverage: Enhanced via non-terrestrial connections.
Privacy: Improved through local data processing and secure protocols.
Cost: Reduced through scalable architecture, programmable design, and efficient components.
All these KPIs collectively define the real-world success of 6G.
Mapping Requirements to KPIs
What’s great about this framework is how it shows the relationship between requirements and outcomes. For instance:
Connecting Intelligence → Needs AI-driven architecture, which improves reliability, energy efficiency, and spectral efficiency.
Programmable Networks → Realized through edge and ubiquitous computing, affecting latency, cost, and scalability.
Determinism → Depends on signal processing and optical networks, providing predictable latency and throughput.
Integrated Sensing → Made possible by radio and non-terrestrial communications, resulting in cm-level positioning accuracy.
Sustainability → Achieved through efficient devices, optical transport, and AI-optimized resource use, ensuring energy efficiency.
Trustworthiness → Heavily impacted by network security and edge computing, promising privacy and reliability.
Affordability and Scalability → Backed by programmable architecture and cost-efficient components, reducing deployment expenses.
This interconnectivity means 6G isn’t developed in isolation but through holistic, cross-domain innovation.
Comparison Table: Requirements, Technology Areas, and KPIs
Requirement Key Technology Areas KPIs Impacted Connecting Intelligence Network architecture, AI/ML Reliability, Efficiency, Spectral Efficiency Programmable Edge computing, Radio tech Latency, Cost, Flexibility Determinism Signal processing, Optical networks Latency, Throughput, Reliability Integrated Sensing Radio, Non-terrestrial comms Positioning, Density, Coverage Sustainable Devices, Optical networks Energy Efficiency, Cost Trust worthiness Network & service security, Edge Privacy, Reliability, Trust Affordable & Scalable Devices, Programmable networks Cost, Coverage, Scalability
Why This Matters for Telecom Professionals
Getting a grasp of these connections enables operators, vendors, and policymakers to:
Prioritize Investments: Understand which tech areas affect KPIs the most.
Plan Roadmaps: Align R&D with future 6G needs.
Enhance User Experience: Guarantee real-world performance improvements.
Build Sustainable Networks: Balance scalability with green objectives.
For industry professionals, the key takeaway is simple: 6G is more than just speed — it’s about creating a secure, sustainable, and intelligent infrastructure.
Conclusion
The path to 6G is intricate, but by connecting requirements to technology areas and KPIs, we can see how it all falls into place. From AI-driven control to non-terrestrial networks and cm-level positioning, 6G is built to change connectivity into a truly intelligent and inclusive ecosystem.
By 2030, these innovations will define the digital landscape of society, making 6G not merely a telecom upgrade but the backbone of our future economies and ways of life.
