Leading the 5G Advanced Evolution Toward 6G: The 3GPP Roadmap and What Lies Ahead

Driving the Transition from 5G to 6G
The global telecommunications industry is undergoing a vital transformation — moving from 5G to 6G. This evolution isn’t sudden; rather, it’s a carefully orchestrated journey filled with small innovations, standardization milestones, and technological growth.
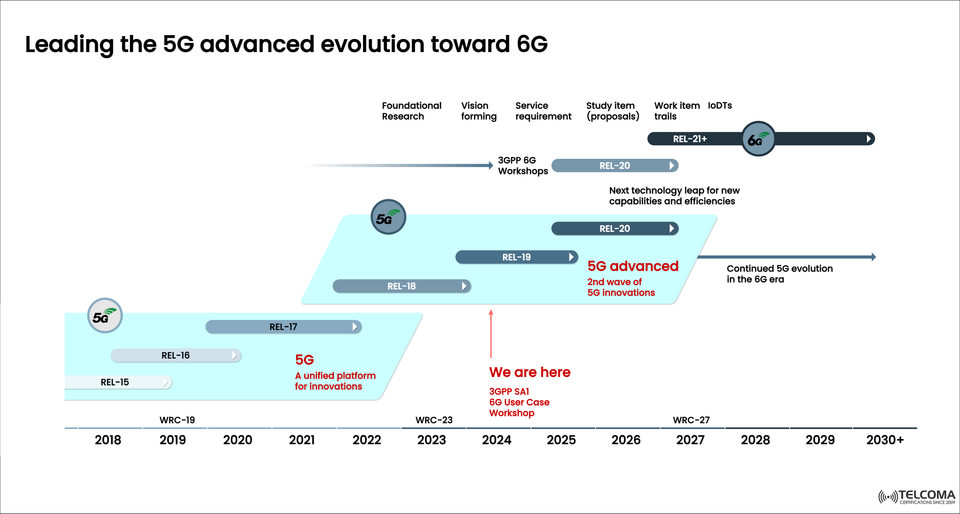
The visual titled “Driving the Transition from 5G to 6G” outlines this path, showcasing how 5G Advanced serves as the connection to the 6G age, with progress marked from 3GPP Release 15 through Release 21+.
Let’s break down what this means for those in telecom, like network architects and tech leaders.
Unpacking the 3GPP Evolution Path
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) sets the standards for mobile technologies worldwide, ensuring smooth interactions and innovation across generations. Each “Release” introduces a batch of standardized features that periodically upgrade network performance and broaden its applications.
Here’s a glance at how 5G has developed and where it’s headed:
3GPP Release Timeline Key Focus Areas Network Generation
Rel-15 (2018): Initial 5G NR (New Radio), enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) – 5G launch.
Rel-16 (2020): URLLC, industrial IoT, private 5G, V2X – Maturing 5G.
Rel-17 (2022): Network slicing, Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN), edge AI – Extending 5G.
Rel-18 (5G Advanced) (2024): AI-native networks, extended reality (XR), low power IoT – Beginning of 5G Advanced.
Rel-19/20 (2025–2027): Massive automation, distributed intelligence, energy efficiency – Second wave of 5G innovation.
Rel-21+ (6G) (2028+): Sensing, terahertz communication, digital twins, native AI – Laying the groundwork for 6G.
5G Advanced: The Link to 6G
As depicted in the image, 5G Advanced symbolizes the second wave of 5G innovation. It leverages the existing framework while incorporating AI, cloud-native design, and smart automation.
The 3GPP Release 18, expected around 2024, kicks off the 5G Advanced phase — merging high-performance connectivity with sustainable network operations.
Core Goals of 5G Advanced:
AI-Native Networks: Integrating AI into network management and optimization.
Enhanced Mobility & Spectrum Efficiency: Dynamic spectrum sharing and ultra-reliable mobility for autonomous operations.
Energy Efficiency: Lowering energy use per transmitted bit, crucial for green telecom initiatives.
Extended Reality (XR) & Metaverse Support: Providing immersive, low-latency experiences.
Non-Terrestrial Integration: Ensuring connectivity through satellites, UAVs, and High-Altitude Platforms (HAPS).
Network Sensing: Allowing networks to detect objects and movements, stepping towards 6G’s environment-aware systems.
5G Advanced isn’t about replacement; it’s more of a transitional enhancement that paves the road for the next-gen architecture of 6G.
Current Landscape: 2024 – Forming the 6G Vision
As shown in the diagram, 2024 is an important milestone — “We are here.”
At this stage, the 3GPP SA1 (Service and System Aspects) group is hosting 6G Use Case Workshops to outline the service requirements and vision for 6G.
This includes:
Looking at 5G Advanced performance benchmarks.
Spotting gaps in capabilities for 6G applications.
Aligning with ITU-R IMT-2030 framework objectives.
Suggesting study items for Rel-20 and Rel-21.
These workshops will lay the technical and architectural groundwork for future releases, making sure that 6G meets not just connectivity demands, but also societal, industrial, and environmental needs.
6G Research and Development Timeline
The roadmap illustrates a structured evolution with overlapping phases that guarantee continuity between 5G Advanced and 6G.
6G Development Phases (2023–2030+)
Foundational Research (2023–2025): Universities, research facilities, and industry experts investigate the terahertz spectrum, new radio configurations, AI-native cores, and integrated sensing.
Vision Forming (2024–2026): Collaborative efforts through 3GPP Workshops and ITU-R IMT-2030 initiatives to define use cases like:
Holographic communications
Digital twins of industrial systems
Ubiquitous robotics
Global real-time sensing
Defining Service Requirements (2025–2026): Setting performance goals: sub-millisecond latency, multi-gigabit uplink speeds, and energy-neutral networks.
Study and Work Items (2026–2028): Standardization kicks off under 3GPP Release 20–21, crafting initial specifications for 6G capabilities.
Field Trials and Early Deployments (2028–2030+): Demonstrations of proof of concept, integrating with the existing 5G Advanced infrastructure, alongside global operator trials.
Next Tech Leap: Moving from Capability to Intelligence
The transition from 5G Advanced to 6G is more than just achieving faster data speeds — it’s about intelligent, adaptive, and context-aware connectivity.
Key Technological Foundations of 6G
Technology Description Impact
AI-Native Core: Machine learning woven into all layers of the network. Predictive self-optimization.
Terahertz Spectrum (THz): Frequencies above 100 GHz enabling ultra-high throughput. Tbps-level speeds.
Joint Communication & Sensing (JCAS): Networks that can sense physical surroundings. Contextual intelligence.
Quantum-Safe Security: Post-quantum cryptography and quantum key distribution. Next-gen security.
Integrated NTN & Terrestrial Networks: Smooth satellite–ground communication. Global reach.
Digital Twins & XR Integration: Real-time mirroring of physical environments. Smart industries and immersive applications.
These advancements will redefine how networks understand, process, and react — shifting connectivity from simply being a data channel to a cognitive ecosystem.
Ongoing 5G Evolution in the 6G Era
Even as 6G takes off, 5G Advanced will still hold its ground well into the 2030s. The diagram highlights a continuation of 5G evolution alongside 6G, emphasizing that the existing infrastructure will develop rather than be discarded.
Key factors in this co-evolution include:
Backward compatibility with 5G NR standards.
Hybrid deployments that blend 5G Advanced and early 6G nodes.
Interoperability through Open RAN and cloud-native systems.
Cross-domain orchestration using AI-driven intent-based networking.
What Telecom Professionals Should Focus On
To stay ahead, telecom industry pros should gear up for the blend of physical and digital intelligence that 6G will usher in.
Key Areas of Focus for Industry Preparedness
AI and Machine Learning Integration – mastering data-driven automation and optimization.
Cloud and Edge Computing – enhancing ultra-low-latency distributed intelligence.
Sustainability and Green Networking – designing carbon-neutral infrastructure.
Standardization and Policy Participation – getting involved in discussions at 3GPP and ITU-R.
Spectrum Strategy – grasping new allocation frameworks for terahertz and NTN bands.
Final Thoughts: From 5G Advanced to the Dawn of 6G
The shift from 5G to 6G isn’t just an upgrade — it’s a fundamental change towards intelligent, sustainable, and globally connected ecosystems.
The 3GPP roadmap clearly shows: 5G Advanced (Releases 18–20) is the bridge to 6G (Release 21+), ensuring a smooth transition driven by AI, edge computing, and new spectrum technologies.
As we approach 2024 — standing at the junction of 5G Advanced and the early 6G vision — those in telecom and tech leadership hold a unique chance to shape the networks that will define the next decade of digital evolution.
