LTE-V2X vs NR-V2X: Key Differences for the Future of Vehicle-to-Everything Communication

LTE-V2X vs NR-V2X: An Exhaustive Comparison of Emerging V2X Technologies
As smart and connected vehicles become more commonplace, the role of Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication technologies is fundamentally important to enable autonomy in vehicles, crucial safety applications, and the exchange of real-time data. The primary V2X communications standards today are LTE-V2X and NR-V2X (This standard is known as New Radio.)
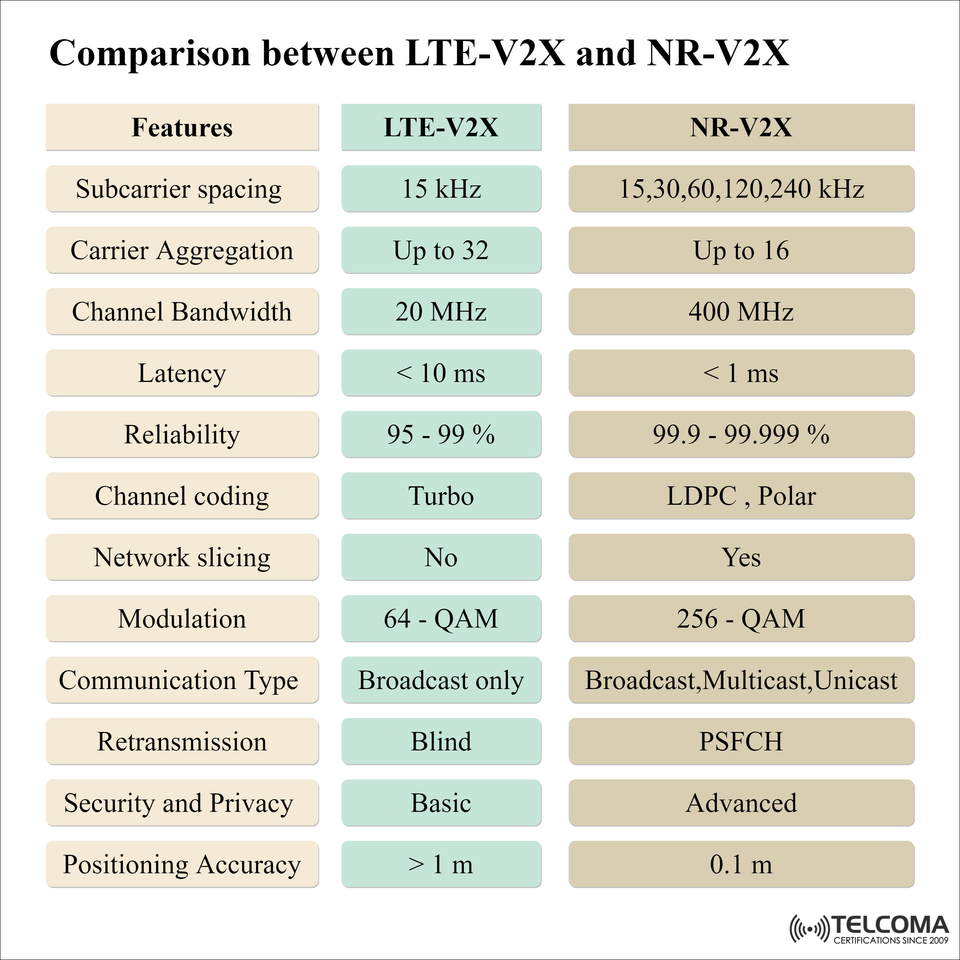
The above image provides a brief overview side by side of each technology, and demonstrates that how 5G NR-V2X exceeds LTE-V2X in nearly every important aspect.
The intent of this blog is to define the two and illustrate their differences and why NR-V2X is needed for new C-V2X deployments especially in 5G and 6G scenarios.
What is LTE-V2X?
LTE-V2X was defined based on 4G LTE technology and was developed to provide fundamental V2X communication such as:
Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V)
Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I)
Vehicle-to-Pedestrian (V2P)
Vehicle-to-Network (V2N)
In addition, it focuses on broadcast only communication as such, it provides some improvements in latency and reliability over legacy systems but not anything substantial in addition to the broadcast.
What is NR-V2X?
5G V2X communication is being called NR-V2X for a reason and it will not only allow:
Ultra-reliable low latency communication (URLLC)
Flexibility of communication types - broadcast, multicast, unicast
New advanced features - network slicing, massive bandwidth, and high-accuracy positioning
NR-V2X will be able to be used for complex, high-speed, and high-reliability applications including:
Autonomous Driving (Level 4 / 5)
Cooperative perception and maneuver
Smart City Traffic Coordination
LTE-V2X vs NR-V2X: Feature Comparison
Feature LTE-V2X NR-V2X
Subcarrier Spacing 15 KHz 15, 30, 60, 120, 240 KHz
Carrier Aggregation Up 32 Up to 16
Channel Bandwidth 20 MHz 400 MHz
Latency < 10 ms < 1 ms
Reliability 95-99% 99.9-99.999%
Channel Coding Turbo LDPC, Polar
Network Slicing No Yes
Modulation 64-QAM 256-QAM
Communication Type Broadcast only Broadcast, Multicast, Unicast
Retransmission Blind PSFCH - Physical Sidelink Feedback Channel
Security & Privacy Basic Advanced
Positioning Accuracy > 1m 0.1m
Why NR-V2X is the Future of V2X
⚡ Ultra-Low Latency
NR-V2X: < 1 ms is important for autonomous emergency braking and avoiding collisions at intersections.
LTE-V2X: < 10 ms is not low enough latency for real-time critical applications.
🧠 Advanced Modulation and Coding
NR-V2X: Using 256-QAM with LDPC/Polar codes allows for greater throughput and reliability in high-speed mobility.
🧩 Network Slicing Support
NR-V2X can allocate slices to different V2X services (for example, safety alerts versus infotainment), allowing more guarantees of QoS.
🔐 Enhanced Security and Privacy
NR-V2X utilizes encryption/enhanced privacy systems to support quality of data, and to help meet the compliance requirements associated with protecting private data.
📍 Accurate Positioning
NR-V2X can achieve < 0.1 m absolute positioning accuracy, providing lane-level precision with a high level of detail in HD maps required for autonomous driving.
Use Case LTE-V2X NR-V2X
Basic Safety Messages
✅ ✓High Speed Platooning
⚠ Limited
✅ Fully Supported
Intersection Collision Avoidance
⚠ Latency is a limiting factor
✅ Real-Time Capable
Sensor Data Sharing (Cooperative Perception)
❌ Not Possible
✅ Capable via URLLC
HD Map Updates and Route Sharing
⚠ Limited data rates
✅ Fast, reliable transmission.
Recommendations for Stakeholders in Telecoms
🚘 Automakers
Emphasize NR-V2X in next generation vehicles.
Leverage telecom networks cooperation for edge-based coordination.
📡 Network Providers
Use NR 5G with its capacity for network slicing and URLLC capabilities for V2X.
Position edge nodes as close to the road infrastructure to lessen latencies.
🏗️ Fixture Providers
Ensure RSUs (Roadside Unit) have NR-V2X capability (if new infrastructure).
Build into smart cities’ sensors and digital twins.
Conclusion:
LTE-V2X to NR-V2X - The Transition Towards Intelligent Transport Systems
LTE-V2X has provided a foundation for organizations to develop safe and effective connected vehicle communications. However, NR-V2X is the paradigm shift that allows true autonomy, reliable low latency and enabled intelligent coordination. The development of NR-V2X will allow 5G-based mobility ecosystems or future 6G mobility ecosystems deeper into communication capacities most notably through enhanced performance across all elements - use case eg modulation to security.
The combination of automotive, telecom and urban infrastructure industries has not been closer than ever (aside from the last year). Consequently, it will be important to invest in NR-V2X technology to support the necessary changes for safer roads, mobility, transport and vehicular networks that are fully autonomous.
Impact of NR-V2X 6G environment.
While NR-V2X is a 5G evolution to date, its architectural structure and capabilities enable underlying 6G connected mobility ecosystems for NR-V2X to become a key enabler. How it could evolve in future 6G-based networks is;
To be a step function closer to AI-derived decision-making systems.
Will benefit from the adjacent opportunities for satellite-based non-terrestrial network (NTN) connectivity, widening coverage.
Create full representation of traffic environments using a digital twin of the environment that is replicated/ animated to support real-time mirroring /simulation.
Encourage traditional modes of travel to move forward with the integration of vehicle swarm competitors and collaborative driving.
Thus NR-V2X is not only an upgrade, it serves as a major building block for connected, cooperative and autonomous mobility frameworks in future networks.
Key Benefits of Moving to NR-V2X:
- Enhanced Traffic Efficiency
By allowing vehicles and infrastructure to share real-time sensor information, NR-V2X allows for optimization of traffic flow on a dynamic basis, thereby decreasing congestion. - Greater Road Safety
With millisecond-level latency, vehicles can react to hazards instantaneously, increasing the reliability of V2X safety messages. - Supports Advanced Use Cases
Advanced use cases, such as platooning, cooperative lane changes, and autonomous intersection management can only be accomplished using NR-V2X. - Integration of 5G with Edge Computing
Edge servers can process V2X data locally using edge computing, thus increasing decision-making speed and alleviating traffic from the core network.
Challenges to NR-V2X Deployment
Despite its technical advantages, NR-V2X also has several deployment challenges.
Infrastructure Upgrade Costs – Table stakes for NR-V2X are roadside units (RSUs) and base stations, which require hardware upgrades and updated software configuration.
Spectrum Allocation – Regulatory decisions related to V2X-specific spectrum use (especially in the 5.9 GHz band) are still evolving.
Interoperability – Seamless communication must be achieved across various vehicle manufacturers (OEMs) and network vendors.
Security Risks – The more connected the V2X system becomes, the more it becomes vulnerable to cyber-attacks.
