MEC Edge-Cloud Synergy and Edge-Edge Synergy: Driving the Future of 5G Networks

The Importance of MEC in the 5G Landscape
Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) plays a vital role in the rollout of 5G and the next phase of telecom networks. By bringing computational and storage resources closer to users, MEC cuts down on latency, boosts bandwidth efficiency, and supports real-time applications such as IoT, augmented and virtual reality, connected vehicles, and industrial automation.
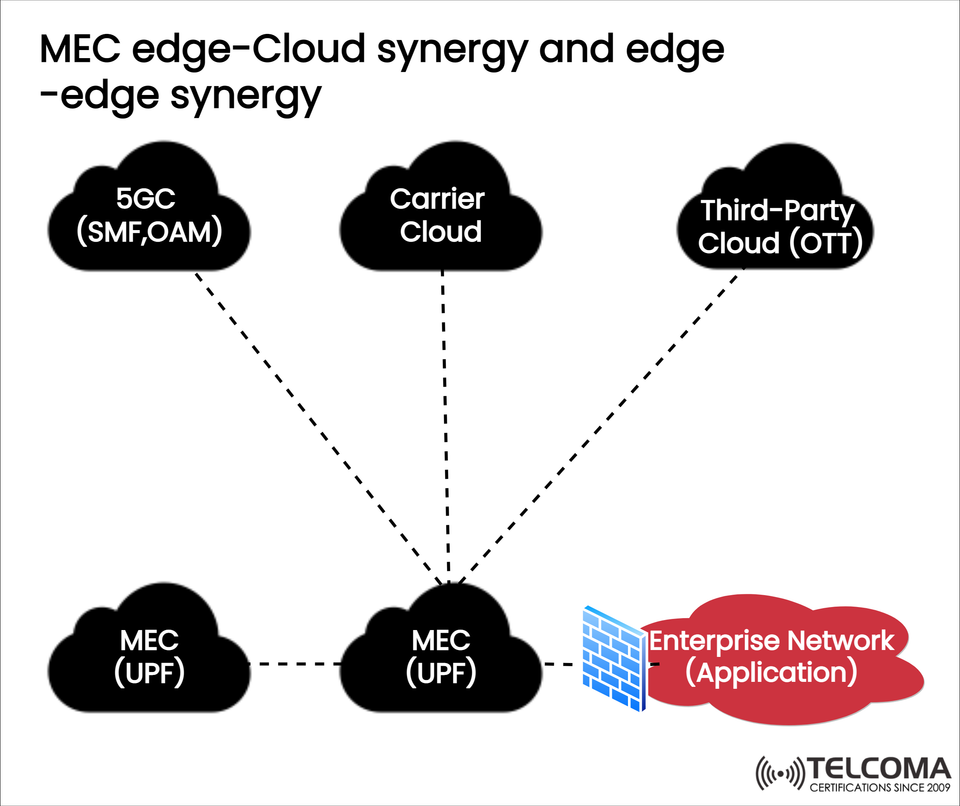
The diagram uploaded illustrates the synergy between MEC edge-cloud and edge-edge—two architectural strategies designed to facilitate smooth interactions among the 5G Core (5GC), Carrier Cloud, Third-party Cloud (OTT providers), MEC nodes, and Enterprise Networks.
To get a clearer picture of this, let’s unpack the concepts and connections outlined in the image.
Grasping MEC Edge-Cloud Synergy
Edge-cloud synergy has to do with how edge nodes (MEC) team up with cloud platforms (including carrier cloud, third-party OTT cloud, and components from 5GC).
From the diagram:
5GC (SMF, OAM): Responsible for control and management tasks. Both the Session Management Function (SMF) and Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) components work with MEC nodes.
Carrier Cloud: This is the operator’s centralized cloud infrastructure, which interacts with MEC for effective workload distribution, orchestration, and scaling.
Third-Party Cloud (OTT): Public clouds like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, which provide applications or additional processing power linked to MEC nodes.
This collaboration ensures that applications and services can function effectively at the edge while still leveraging the scalability, orchestration, and advanced capabilities of both central and third-party clouds.
Main Benefits of MEC Edge-Cloud Synergy:
Ultra-Low Latency: Processing happens closer to users, reducing delays.
Scalability: Large workloads can be shifted to central or third-party clouds.
Flexibility: Applications can move dynamically between edge and cloud settings.
Enhanced QoS: Operators can better manage service quality by connecting MEC with 5GC and the carrier cloud.
Grasping MEC Edge-Edge Synergy
Edge-edge synergy is about the cooperation among multiple MEC nodes.
In the diagram, you can see that two MEC nodes, both with a User Plane Function (UPF), connect to one another and to enterprise networks. This setup allows MEC nodes to share workloads, sync application data, and keep services running smoothly.
For example:
In autonomous driving, vehicles traveling between regions can switch from one MEC node to another without losing service.
In industrial automation, two factories equipped with MEC nodes can share real-time data to streamline operations.
Main Benefits of MEC Edge-Edge Synergy:
Service Continuity: Smooth transitions of sessions between MEC nodes.
Load Balancing: Processing tasks are shared across multiple edges.
Resilience: If one MEC node goes down, another can step in to take over.
Enterprise Integration: Connects enterprise networks and applications directly with multiple MEC nodes for better reliability.
MEC, UPF, and Enterprise Applications
The diagram also shows the relationship between MEC UPF nodes and enterprise networks.
MEC (UPF): The User Plane Function at the edge allows local data breakout, processing traffic right at the MEC node instead of sending it to the central cloud.
Enterprise Network (Application): Businesses deploy latency-sensitive applications—like AI-driven analytics, IoT platforms, or private 5G applications—directly at the MEC node.
This setup not only reduces latency but also boosts security, data privacy, and compliance by keeping enterprise data local.
Real-World Applications of MEC Edge-Cloud and Edge-Edge Synergy
The synergy models in the diagram aren’t just theoretical; they’re powering real-world 5G environments.
- Smart Cities
Different districts’ edge nodes coordinate (edge-edge synergy).
Cloud systems analyze long-term data trends (edge-cloud synergy).
- Connected Vehicles (V2X Communication)
MEC UPF provides local breakout for ultra-low latency communication.
Edge-edge synergy ensures seamless handovers when vehicles cross coverage areas.
Edge-cloud synergy supports backend analytics and fleet management.
- Industrial Automation
Factory machinery depends on local MEC for real-time automation.
Edge-edge synergy connects multiple plants or warehouses.
Carrier or third-party cloud offers long-term storage and AI-driven analytics.
- AR/VR and Gaming
Rendering is done at the MEC node to minimize lag.
Edge-cloud synergy allows for scalability during peak demand periods.
- Private 5G Networks for Enterprises
Enterprise applications connect directly to MEC nodes for minimal latency.
Integration with 5GC guarantees control and policy enforcement.
MEC Synergy in the 5G Framework
Here’s a simplified look at how everything interacts:
Component Role in MEC Synergy Example Functionality 5GC (SMF, OAM) Core network control and management Session handling, orchestration Carrier Cloud Operator’s central infrastructure Scaling, orchestration Third-Party Cloud OTT services integration Cloud-native apps, AI, ML MEC (UPF) Local edge data breakout Low latency processing Enterprise Network Direct application hosting Smart factories, IoT platforms
Advantages of MEC Edge-Cloud and Edge-Edge Synergy
Operational Efficiency: Operators optimize resources across both edge and cloud environments.
Better User Experience: End-users enjoy reduced latency and increased reliability.
Ecosystem Collaboration: Enterprises, operators, and OTT providers work within a unified framework.
Future-Proofing: Supports advanced applications like the metaverse, holographic communication, and mission-critical IoT.
Challenges to Keep in Mind
While the advantages are substantial, both operators and enterprises need to tackle a few challenges:
Standardization: Ensuring different vendors’ MEC and cloud systems can work together.
Security: Safeguarding data across various edge and cloud environments.
Orchestration Complexity: Dynamically managing workloads in distributed systems.
Cost: Setting up MEC nodes demands a significant investment.
Final Thoughts
MEC edge-cloud and edge-edge synergy form the backbone of next-generation telecom networks. The diagram shows how MEC nodes connect not only with the 5G Core, carrier cloud, and OTT clouds, but also with other MEC nodes and enterprise applications.
This cooperative ecosystem empowers operators, enterprises, and cloud providers to deliver ultra-low latency, reliable, and scalable services across various fields—from smart cities and autonomous driving to immersive entertainment and industrial IoT.
By mastering MEC synergy models, telecom professionals can tap into the full potential of 5G and beyond, paving the way for an interconnected and intelligent digital landscape.
