MPLS vs SD-WAN: A Clear Comparison for Modern Enterprise Networks

📡 MPLS vs SD-WAN: Choosing the Right Network Architecture for Modern Enterprises
In today's distributed enterprise environment, organizations continue to require networking solutions that are more agile, scalable, and secure. MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) has been the go-to WAN technology for years. That said, due to the rapid increase in cloud-first strategies, SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network) is becoming the preferred network technology of choice for organizations.
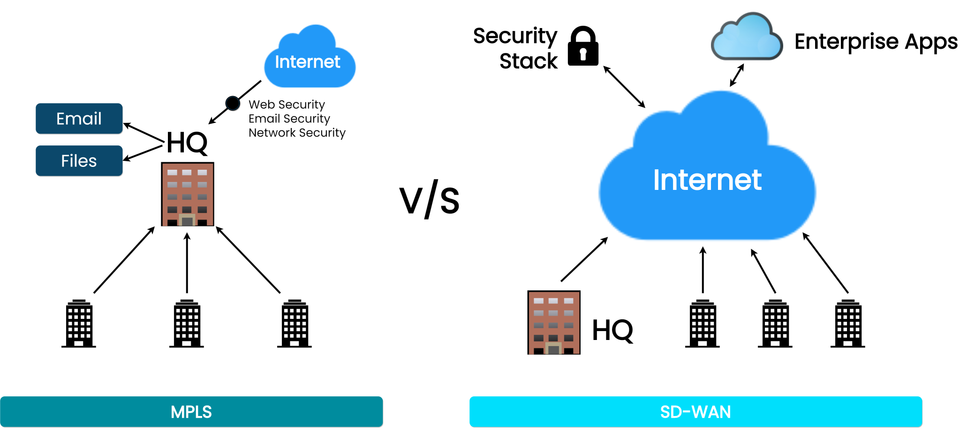
The image above clearly lays out the differences between traditional MPLS and SD-WAN, their architectures, and how each connects, the rest of this post will review the differences to help both telecom professional and IT decision makers choose wisely.
🧱 MPLS Architecture: CENTRALIZED, RIGID
On the left side of the image, it can be seen that MPLS uses a hub-and-spoke architecture and routes all branch traffic through one central HQ.
🔒 What are the Key Characteristics of MPLS?
Centralized, backhaul data and internet traffic to HQ
Excellent, reliable and predictable performance (QoS)
Costly dedicated leased lines with guaranteed SLAs
Centralized security for web, email and file access
❌ What are the limitations of MPLS?
Cost of leased lines
Scalability issues with cloud consumption
Limited visibility and control at the branch level
Inflexible to support dynamic routing or cloud traffic
☁️ SD-WAN Architecture: Cloud-Native and Decentralized
As illustrated on the right side of the image, the SD-WAN solution routes traffic directly from each branch out to the internet and securely access enterprise-grade cloud apps and services.
🚀 SD-WAN offers key benefits:
Low-cost connections through broadband, LTE, or hybrid links
Direct access to the cloud, which improves the performance of SaaS/apps
Centralized orchestrated and zero-touch provisioning
Integrated security stack (firewall, VPN, threat detection)
Traffic steering based on real-time performance
🛡️ Security Built-in with SD-WAN
Provides distributed security at the branch level
Offers support for SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) integration
Provides granular policy enforcement across users, apps, and locations
⚖️ MPLS vs SD-WAN Feature Comparison Table
Feature MPLS SD-WAN
Network Type Private leased line Public internet, LTE, MPLS hybrid
Traffic Flow Centralized via Headquarters Direct access to the cloud from branches
QoS Built-in, predictable Dynamic, policy-based
Security Centralized at Headquarters Distributed + integrated stack
Cloud Support Poor Excellent
Scalability Limited High (cloud-native)
Cost High (leased circuits) Lower (uses commoditized broadband)
Management Manual, router CLI Centralized, GUI-based
🏢 Use Case Scenarios
When to go with MPLS
Legacy systems with a very high SLA
Mission-critical data where guaranteed latency is required
Environments where there is no reliance on the cloud
When to Consider SD-WAN:
Cloud-first organizations (Office 365, Salesforce, Zoom)
Cost-sensitive organizations
Organizations with many remote / global locations
Dynamic traffic routing needs and real-time metrics
🔚 Conclusion: MPLS or SD-WAN - Who Wins?
While MPLS may not be unreliable, it is not the ideal model for a cloud-based world. SD-WAN provides maximum flexibility, performance optimization, and savings for a newer breed of distributed enterprises.
For most organizations in digital transformation, SD-WAN is the most reasonable evolution of the enterprise WAN.
🧠 Common Concerns About Moving From MPLS to SD-WAN
Although SD-WAN has many advantages, many organizations are hesitant because of the following concerns:
- Security Readiness
Concern: Internet-based connectivity feels risky compared to private MPLS.
Recommendation: Best-in-class SD-WANs include strong security features such as end-to-end encryption, next-gen firewalls, and support for SASE frameworks.
- Application Performance
Concern: Business-critical applications will suffer over broadband.
Recommendation: SD-WAN uses application-aware routing to dynamically assess and take the best path based on real-time performance, allowing businesses to maintain the quality of experience.
- Operational Complexity
Concern: SD-WAN creates another layer to pay for and manage.
Recommendations: SD-WAN solutions centralized orchestration and zero-touch provisioning, create less complexity than managing multiple legacy
🔭 Future Trends: Beyond MPALS and SD-WAN
As enterprise networks continue to evolve, expect the following developments:
SASE - a convergence of SD-WAN and cloud-delivered security, including ZTNA, CASB and SWG.
AI-WAN Management - AI will assist in routing, traffic steering and anomaly detection with machine learning.
5G and Edge Computing - SD-WAN will play a critical role in managing the dispersed edge.
Multi-Cloud - Optimising dynamic link selection for traffic going to AWS, Azure, GCP and SaaS platforms.
🧾 Takeaways
SD-WAN marks a shift in enterprise networking from the reliability of a closed MPLS connection to embracing an agile, cloud-enabled, and cost-effective solution. SD-WAN provides a framework to handle all the connections we rely on with applications, users and data increasingly dispersed.
MPLS still has its use cases, particularly for critical legacy applications, but any organization that is forward-looking must have either transitioned or has a plan to transition to an SD-WAN.
📊 MPLS vs. SD-WAN: Feature Comparison Table
Feature MPLS SD-WAN
Connection Type Private leased lines Public internet + hybrid links
Deployment Complexity High (manual provisioning) Low (zero-touch provisioning)
Cost Expensive (price per Mbps) Cost-effective as it consumes broadband
Cloud Access Through data centre Direct to cloud (optimised)
Security Implicit trust (based on circuit) Embedded security stack (dependant on stack e.g. encryption, SASE, etc.
🌐 Real-World Use Case: Global Retailer
A global retailer, with a mere 200+ stores, was routing traffic through its HQ data center over MPLS. Business critical apps were increasingly cloud-based (e.g. Salesforce, Microsoft 365), which was resulting in performance degradation at branches.
Solution:
The organization transitioned to SD-WAN and benefited from:
Improved application performance with a local internet breakout
50% cost reduction on WAN
Rapid onboarding of new stores with zero-touch deployment
Centralized policy enforcement and visibility
✅ Conclusion: The WAN is Changing — Are You?
In the world of cloud, enterprises can no longer afford to remain tethered to costly, inflexible MPLS networks. SD-WAN is not just a trend — it's establishing the foundation for a secure, agile and scalable enterprise WAN.
Whether you are a CIO determining your digital transformation strategy, a network architect scaling designs to fit reality, or a telecommunications professional developing the next-generation solutions, understanding the value of SD-WAN, and embracing it will be key to staying ahead of competition.
