Network Slicing in Private 5G Networks: A Complete Guide for Enterprises and Telecom Professionals

Network Slicing for Private 5G Networks: Enhancing Enterprise Connectivity
The rise of 5G is opening up exciting opportunities for industries, businesses, and telecom providers alike. One of the standout features in 5G technology is network slicing, which allows multiple virtual networks to operate on a single physical framework.
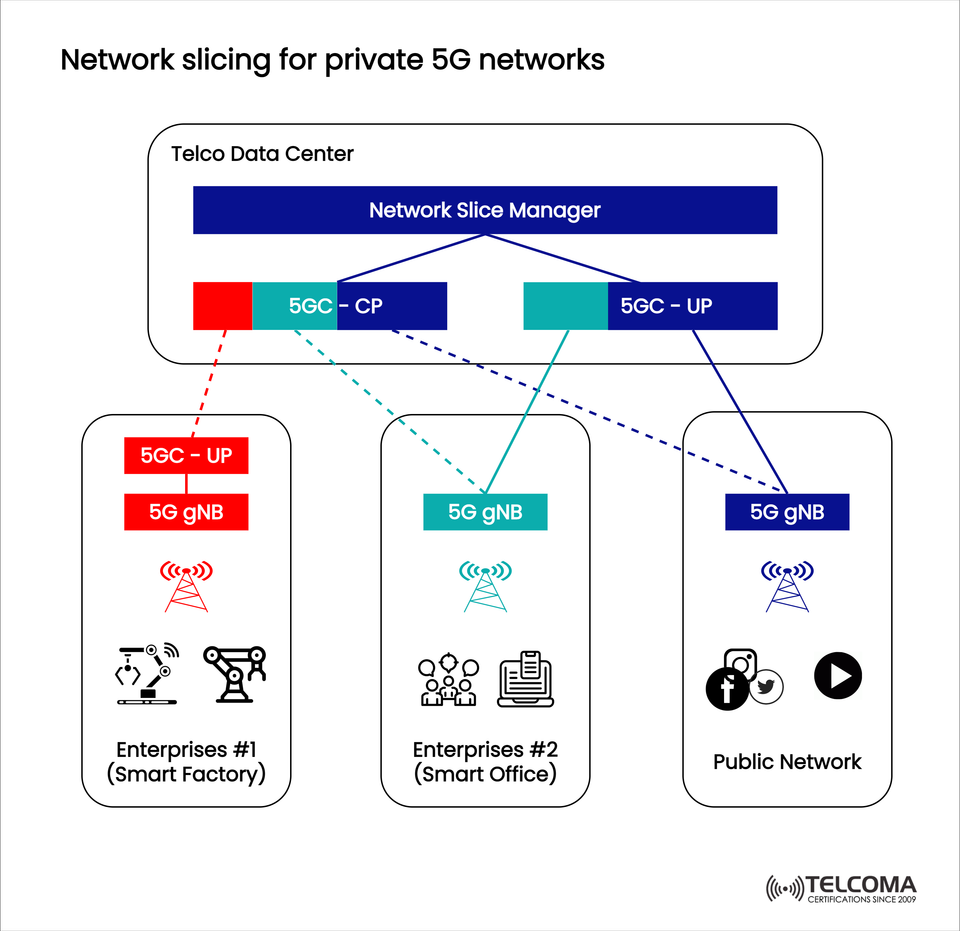
The diagram provided shows how network slicing functions within private 5G networks, demonstrating how various enterprises and the public sector can securely share resources while still keeping their performance and services separate. Let’s explore this important innovation in more detail.
What is Network Slicing in 5G?
Network slicing is a feature of 5G that lets operators create several logical networks (slices) on a shared physical infrastructure. Each slice is crafted for a specific application, use case, or requirement from a business.
You can think of it like adding several “virtual lanes” to a highway where each lane is designed for a specific type of traffic. For instance:
One slice optimized for industrial IoT with ultra-low latency
Another tailored for a smart office with stable broadband
Yet another for public use with high-capacity streaming and social media
This setup means that industries, offices, and consumers can utilize the same 5G network infrastructure without sacrificing performance.
The Role of Private 5G Networks
Private 5G networks are dedicated setups meant for enterprises like factories, logistics centers, hospitals, or office buildings. Unlike public 5G, which spreads resources across millions of users, private 5G guarantees:
Better security
Consistent Quality of Service (QoS)
Control over data sovereignty
Tailored performance
When paired with network slicing, private 5G networks can create customized slices for different enterprise applications while remaining unaffected by public network traffic.
How Network Slicing Works: A Breakdown of the Architecture
The uploaded image breaks down the network slicing architecture in a Telco Data Center setting. Here’s how it flows:
Telco Data Center * Houses the Network Slice Manager * Allocates resources for each enterprise or service * Contains Control Plane (5GC-CP) and User Plane (5GC-UP) functionalities
Network Slice Manager * Serves as the “brain” behind slicing * Dynamically provisions slices for enterprises or public users * Ensures isolation and performance guarantees
Enterprises #1 (Smart Factory) * Utilizes a dedicated User Plane (5GC-UP) and 5G gNB (base station) * Fine-tuned for low-latency, high-reliability communications (key for robotics, automation, and real-time monitoring)
Enterprises #2 (Smart Office) * Shares a Control Plane but has its own 5G gNB * Concentrated on stable broadband, secure communication, and collaboration tools
Public Network * Operates its own slice using a 5G gNB * Crafted for massive broadband demands (think social media, video streaming, and general consumer use)
This architecture ensures that no matter the application—whether it’s industrial automation or video streaming—each service is getting the right network features.
Key Benefits of Network Slicing for Private 5G
- Performance Isolation
Each slice has its own resources.
Prevents the traffic from one enterprise from disrupting another.
- Customization for Enterprises
Smart factories can require ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC).
Offices might need enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB).
Public networks focus on massive machine-type connectivity (mMTC).
- Security and Data Sovereignty
Enterprise data stays isolated and secure.
Crucial information remains within the enterprise rather than flowing into public networks.
- Efficient Resource Use
Multiple services operate on one 5G infrastructure.
Cuts down CAPEX and OPEX for telecom operators.
- Scalability and Flexibility
New slices can be created without having to overhaul existing infrastructure.
Businesses can scale based on real-time needs.
Use Cases of Network Slicing in Private 5G
Enterprise Type Network Slice Characteristics Example Applications Smart Factory Ultra-reliable low-latency, high throughput Robotics, autonomous vehicles, AR/VR Smart Office Secure broadband, low jitter Video conferencing, cloud apps Healthcare Facility Low latency, high reliability, extreme security Remote surgery, connected devices Public Network High capacity, scalable bandwidth Social media, video streaming, IoT
Challenges in Deploying Network Slicing
While there’s a lot of promise here, network slicing does have its hurdles:
Complex orchestration – It requires advanced automation and AI for managing slices.
Security policies – Each slice needs to maintain strict separation.
Regulatory compliance – Enterprises must adhere to spectrum and data legislation.
Deployment costs – Initial setup can be pricey, especially for smaller businesses.
Future of Network Slicing in Private 5G
As industries embrace Industry 4.0 and the pace of digital transformation speeds up, network slicing is set to become a key element of enterprise connectivity. With improvements in AI-driven orchestration and cloud-native 5G core functions, we can look forward to:
On-demand slice creation for enterprises.
Pay-as-you-go slicing options for SMEs.
Integration with edge computing for real-time analytics.
Smarter security measures using AI.
SEO Keyword Ideas
Here are some key terms that fit well with your topic and audience:
Main Keywords (high intent, core topic)
Network slicing in 5G
Private 5G networks
5G network slicing architecture
Enterprise 5G solutions
5G slicing use cases
Supporting Keywords (long-tail)
Smart factory 5G connectivity
Private 5G for enterprises
5G network slice manager
5GC Control Plane and User Plane
Benefits of network slicing
Network slicing for IoT
5G industrial automation
5G URLLC, e MBB, m MTC
On-Page Optimization Tips
To help your blog rank higher:
✅ Title Optimization
Keep your SEO title under 60 characters.
Include “Network Slicing” and “Private 5G” near the front.
✅ Meta Description
Use action words like (Learn, Discover, Explore).
Limit it to under 160 characters.
✅ Keyword Placement
Include them in the first 100 words (your intro).
Use at least one subheading (H2/H3).
Add alt text for images you upload (like “Diagram showing network slicing architecture in private 5G networks for enterprises and public use”).
✅ Content Formatting
Use bullet points and tables (like you have).
Include internal links (if it's on a telecom site, link to related articles).
Add external links to standard bodies (like 3GPP, GSMA).
✅ Readability
Keep paragraphs short (2–3 sentences each).
Balance technical jargon with clear explanations that readers can understand.
✅ Schema Markup (if you can)
Add Article schema for better indexing.
Highlight FAQs such as “What is network slicing in 5G?” and “What are private 5G networks?”
Suggested FAQs to Consider (Good for SEO)
What’s the difference between public 5G and private 5G? Public 5G targets mass consumers, while private 5G is specifically for enterprises that need top-tier performance and security.
How does network slicing enhance enterprise connectivity? It creates dedicated logical slices customized for different needs, ensuring isolation, security, and high performance.
Which industries gain the most from network slicing? Sectors like manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, smart cities, and office environments benefit because of their unique connectivity needs.
Can businesses set up their own 5G slices? Absolutely, with the help of an operator or by using standalone private 5G systems, enterprises can manage specific slices.
Conclusion
Network slicing isn’t just a trend—it’s the foundation of private 5G networks. By developing dedicated logical networks over shared infrastructure, telecom operators can offer businesses reliable, secure, and customized connectivity.
The diagram shows how smart factories, offices, and public networks can all function within the same infrastructure while enjoying their own optimized slices. For businesses, this means quicker innovation, better security, and greater control. For telecom professionals, it’s an opportunity to provide next-gen services more efficiently.
As 5G evolves, network slicing will be crucial in maximizing the potential of enterprise digital transformation.
