NG-RAN Architecture with PC5 Interface Explained: D2D, V2X, and Sidelink in 5G

Why the PC5 Interface Matters in 5G
In 5G and LTE-Advanced Pro networks, the PC5 interface is super important for enabling direct communication between user equipment (UEs), so they don't always have to go through the base station. This interface is essential for things like:
Device-to-Device (D2D) communication
Sidelink communication in 5G NR
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) services
Public safety and mission-critical applications
The Next-Generation Radio Access Network (NG-RAN), which includes both gNB (5G base station) and ng-eNB (enhanced LTE eNodeB), supports the PC5 interface whether you're within the RAN coverage or not. This means you get seamless connectivity, lower latency, and an extended communication range.
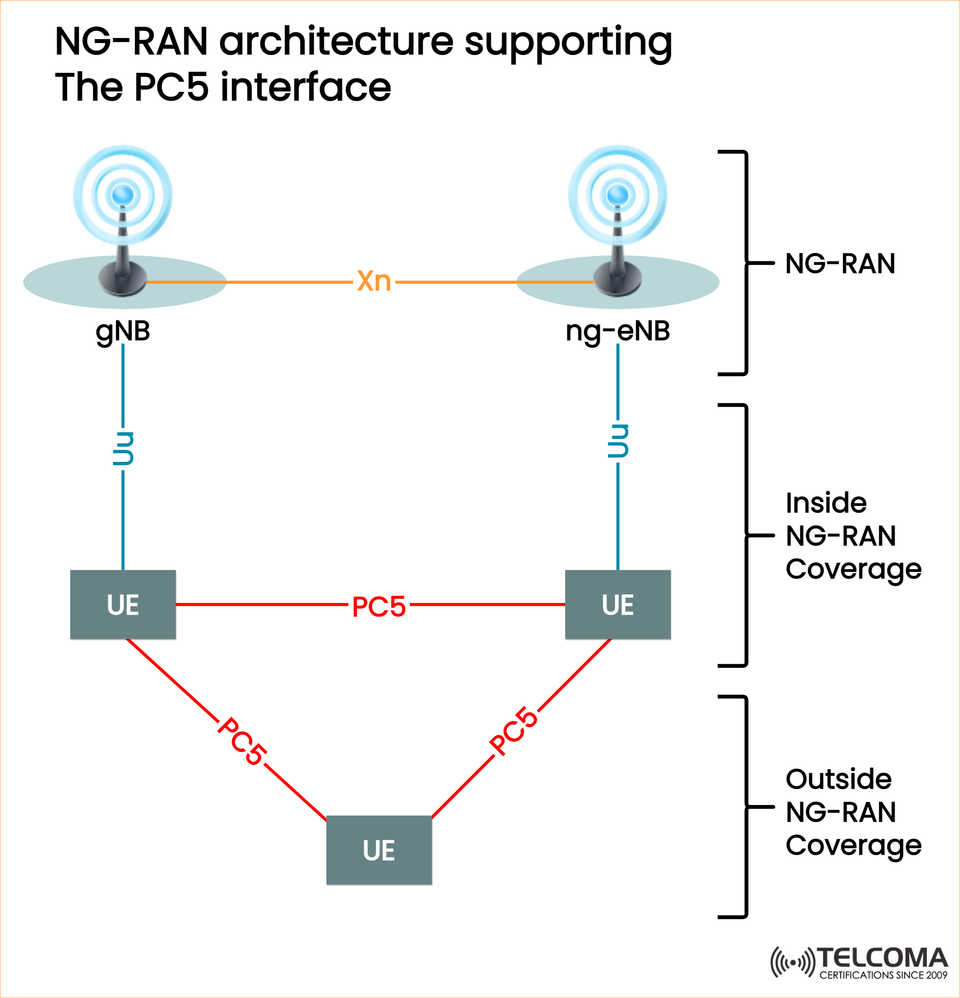
NG-RAN Architecture Supporting PC5
The diagram shows how UEs (User Equipment) communicate through the PC5 interface both when they’re within coverage and outside of it.
Here’s a quick breakdown:
Components in the Architecture
gNB (Next Generation Node B): This is the 5G NR base station that manages radio resources.
ng-eNB (Next Generation eNodeB): This LTE base station has been upgraded for 5G core connectivity.
UE (User Equipment): Think smartphones, IoT devices, or vehicles.
Xn Interface: This connects gNB and ng-eNB for seamless interworking.
PC5 Interface: This is what allows direct communication between UEs (sidelink).
Inside NG-RAN Coverage
When UEs are within the NG-RAN coverage:
They can communicate directly using PC5 while being managed by the gNB/ng-eNB.
The base station takes care of synchronization, resource allocation, and QoS management.
PC5 is used for: * Proximity services (ProSe) in public safety. * Low-latency applications like AR/VR or multiplayer gaming. * V2X communication (vehicles sharing real-time data).
This setup offers high reliability because the RAN can coordinate sidelink transmissions to avoid interference.
Outside NG-RAN Coverage
When UEs are outside the NG-RAN coverage:
The PC5 interface allows for direct device-to-device communication without needing the gNB/ng-eNB.
UEs can handle their own synchronization and resource selection.
It’s critical for: * Disaster recovery situations where networks may not exist. * Remote or rural areas lacking RAN coverage. * Ad-hoc vehicular networks that help avoid collisions.
So, PC5 makes sure communication stays alive even in no-service zones.
The Role of PC5 in 5G Sidelink
The PC5 interface is often referred to as the sidelink interface in 5G NR. Here’s what it does:
Direct Communication: UEs can exchange data without going through the gNB.
Low Latency: This is really important for mission-critical services like V2X.
Flexibility: Works in both coverage and non-coverage situations.
Energy Efficiency: Reduces the need for core networks when exchanging local data.
Applications of PC5 Interface
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication
Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V): Cars share details about speed, position, and safety alerts.
Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I): Communication with roadside units.
Vehicle-to-Pedestrian (V2P): Alerts to pedestrians for enhanced safety.
Vehicle-to-Network (V2N): Complements PC5 with traditional network communication.
PC5 gives ultra-reliable, low-latency links crucial for avoiding collisions and supporting autonomous driving.
- Public Safety and Mission-Critical Services
First responders like police and medical teams can directly communicate using PC5 when networks are down or overloaded.
It backs up ProSe (Proximity Services), which are vital during natural disasters or big public events.
- IoT and Smart Devices
IoT devices can create local communication clusters without needing the network all the time.
Think about industrial automation, drone swarms, and sensor networks.
- Commercial Use Cases
Gaming & AR/VR: Low-latency D2D connections boost user experience.
Content Sharing: Quick file transfers between nearby devices without relying on the core network.
How PC5 Differs from Traditional Interfaces
Interface Purpose Latency Dependency
Uu (RAN ↔ UE) Standard LTE/5G access Higher (network-involved) Depends on gNB/eNB
Xn (gNB ↔ ng-eNB) Base station coordination Medium Requires NG-RAN
PC5 (UE ↔ UE) Direct device-to-device Ultra-low Works with or without NG-RAN
What makes PC5 stand out is its ability to keep communication going even when the network is down.
Technical Advantages of PC5
Reduced Latency: Direct connections cut down on transmission delays.
Extended Coverage: UEs can talk even when the network isn’t available.
Network Offloading: Less reliance on gNB for local communication.
High Reliability: Crucial for applications where safety is key.
Flexibility: Supports 5G NR sidelink, V2X, and critical public safety services.
Challenges with PC5
Despite its strengths, PC5 does have some challenges:
Interference Management: Without a gNB, UEs must manage their own resources.
Security: Direct communication can increase risks if not properly encrypted.
Synchronization Issues: UEs outside of coverage need different ways to sync up.
Standardization Complexity: Must align with LTE, 5G NR, and future tech upgrades.
Evolution of PC5 in 5G and Beyond
LTE ProSe (Release 12-14): Brought PC5 in for public safety and early D2D.
5G NR Sidelink (Release 16+): Expanded PC5 for V2X, URLLC, and IoT capabilities.
Future 6G Vision: Plans for enhanced sidelink with AI-based coordination, spectrum agility, and extreme reliability.
In this way, PC5 will continue to be a key player in beyond-5G communication models.
Conclusion
The NG-RAN architecture that supports the PC5 interface is vital for today's mobile communication landscape. It enables direct communication between UEs both within and outside coverage, ensuring reliable, low-latency connections.
Inside coverage: PC5 works with gNB/ng-eNB for efficient sidelink operations.
Outside coverage: PC5 allows for independent D2D communication without network support.
Its applications span across V2X, public safety, IoT, and the next generation of consumer services.
For telecom pros, getting a grip on the PC5 interface within NG-RAN is key for building robust, adaptable, and future-proof 5G networks.
