Non-Roaming 5G Core Architecture with Untrusted Non-3GPP Access Explained
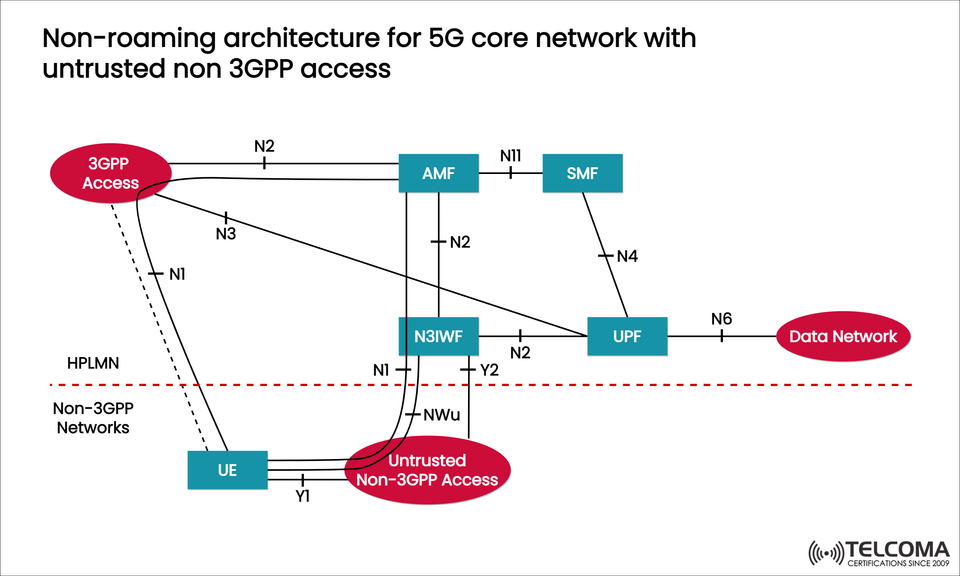

The 5G Core (5GC) aims to deliver seamless connectivity not just through 3GPP access networks like 5G New Radio and LTE, but also through non-3GPP access networks such as Wi-Fi, enterprise LANs, and fixed broadband. This flexibility allows operators to broaden coverage, alleviate network congestion, and elevate user experiences.
That said, not every non-3GPP access network is trustworthy. Public Wi-Fi hotspots, unmanaged company LANs, and some broadband connections might not have the strict security controls that operators impose. To counter this, 5G introduces a framework for untrusted non-3GPP access.
The diagram uploaded shows the non-roaming 5G core architecture with untrusted non-3GPP access, highlighting how the Non-3GPP InterWorking Function (N3IWF) is essential for maintaining secure and reliable connectivity.
Understanding Untrusted Non-3GPP Access
Non-3GPP access refers to networks that don’t adhere to 3GPP standards, like Wi-Fi or fixed broadband. These networks can be categorized into:
Trusted: Managed by the operator or enterprise, featuring strong authentication and encryption.
Untrusted: Networks where the operator lacks control over infrastructure and security.
Untrusted non-3GPP access examples include:
Public Wi-Fi hotspots (in cafes, airports, malls).
Home broadband connections without operator security policies.
Shared enterprise networks where security enforcement is inconsistent.
To handle these issues, the N3IWF serves as a trusted interworking gateway, allowing user equipment (UE) to connect securely to the 5GC, even over less secure networks.
Key Components of the Architecture
The diagram illustrates how untrusted access fits into the 5GC, with the main components and their functions outlined below:
- User Equipment (UE)
Connects to the 5GC through untrusted non-3GPP access networks.
Uses interfaces like Y1 and NWu for communication with the untrusted access network.
Sets up secure IPsec tunnels with the N3IWF before sending traffic to the 5G Core.
- Untrusted Non-3GPP Access Network
Provides the physical connection (like Wi-Fi, broadband, or LAN).
Not inherently secure, so it relies on the N3IWF for protection.
- Non-3GPP Inter Working Function (N3IWF)
Vital for integrating untrusted access.
Provides secure IPsec tunneling between UE and 5GC.
Relays NAS signaling from UE to the AMF using the N1 interface.
Forwards user plane traffic to the UPF via the N3 interface.
Ensures authentication through methods like EAP-AKA’.
- Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF)
Manages signaling, authentication, and mobility for UEs.
Keeps session continuity while UEs move between untrusted Wi-Fi and 3GPP access.
Connects to the N3IWF over N2 and interfaces with the SMF via N11.
- Session Management Function (SMF)
Handles session establishment and policy enforcement.
Works alongside the UPF to keep user sessions going, regardless of access type.
Connects to the UPF through N4.
- User Plane Function (UPF)
Responsible for data forwarding.
Interfaces with N3IWF for UE traffic and external Data Networks (DN) through N6.
Ensures QoS and routing policies are in place.
- Data Network (DN)
The final destination for UE traffic.
This could be the public internet, private enterprise systems, or cloud applications.
Interfaces in the Architecture
Interface Role Entities ConnectedN1NAS signaling relay UE ↔ N3IWF ↔ AMFN2Control plane signaling AMF ↔ N3IWF / UPFN3User plane trafficN3IWF ↔ UPFN4Session control SMF ↔ UPFN6Data delivery UPF ↔ Data NetworkN11Session management AMF ↔ SMF NWu IP sec tunneling UE ↔ N3IWFY1, Y2UE-access communication UE ↔ Untrusted Non-3GPP Access
These interfaces help ensure seamless and secure connectivity, even with the untrusted nature of the underlying access.
Security in Untrusted Non-3GPP Access
Given these access networks' questionable trustworthiness, security is paramount:
IPsec Tunnels: Encrypt data between UE and N3IWF.
EAP-AKA’ Authentication: Authenticates the subscriber using HPLMN credentials.
Signaling Integrity: Prevents tampering with NAS signaling messages.
Session Anchoring: N3IWF acts as the entry point, ensuring only validated traffic reaches the 5G Core.
All this means that even if a Wi-Fi hotspot gets compromised, the 5G Core stays secure.
Benefits of Integrating Untrusted Non-3GPP Access
Extended Coverage: Lets UEs connect via Wi-Fi or broadband where 5G NR isn’t available.
Seamless Mobility: Ensures session continuity while moving between cellular and Wi-Fi connections.
Cost Efficiency: Offloads traffic from pricey cellular spectrum to unlicensed Wi-Fi.
Improved User Experience: Delivers better throughput indoors where 5G signals can be weak.
Enterprise Readiness: Supports IoT devices and enterprise applications over existing Wi-Fi without compromising security.
Use Cases of Untrusted Non-3GPP Access
Public Wi-Fi Offloading: Operators alleviate mobile network congestion by shifting data to Wi-Fi while keeping it secure.
Enterprise IoT Integration: IoT devices on unmanaged Wi-Fi securely link to the 5G Core.
Residential Broadband: Home Wi-Fi networks connect devices securely to the 5G ecosystem.
Indoor Coverage Solutions: Users in places like malls, airports, and offices can depend on Wi-Fi while still connecting securely to the 5GC.
Trusted vs Untrusted Non-3GPP Access
Parameter Trusted Non-3GPP Access Untrusted Non-3GPP Access Example Operator-managed enterprise Wi-Fi Public Wi-Fi, residential broadband Gateway Trusted Non-3GPP Gateway Function (TNGF)N3IWFSecurityOperator-controlled encryption & authentication IP sec tunneling, EAP-AKA ’Use Case Corporate/private networks Public hotspots, unmanaged LANs
This comparison underscores the importance of operators carefully classifying and managing their access networks.
Conclusion
The non-roaming 5G core architecture with untrusted non-3GPP access plays a critical role in delivering secure, flexible, and seamless connectivity across various environments. By leveraging the N3IWF, operators can extend the capabilities of the 5GC to unmanaged networks like Wi-Fi and broadband, ensuring both security and continuity of mobility.
This architecture not only enhances the user experience but also gives operators a path to optimize spectrum use, offload traffic, and incorporate diverse networks.
As 5G continues to advance, the capacity to combine trusted and untrusted access into one secure ecosystem will stand out as a major differentiator.
