O-RAN Explained: Open and Smart RAN Architecture for 5G Networks
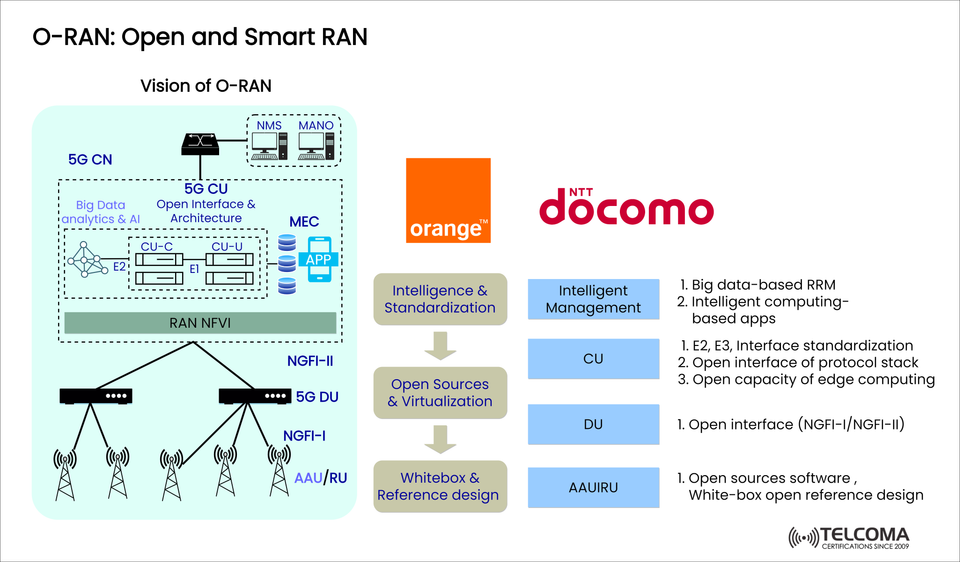

As we continue to build out 5G networks, there has never been a greater need for openness, agility and intelligence in radio access networks. O-RAN, this rare combination of potential that is changing how networks are deployed and operated because O-RAN decouples hardware and software, enables AI/ML, and embraces cloud-native technologies.
This blog will demonstrate the O-RAN architecture using the latest visualization, discuss what we have seen with different players like NTT Docomo and Orange, and explain how open interfaces are changing the RAN.
🔍 What is O-RAN?
O-RAN is a disaggregated, open RAN architecture that seeks to:
- Reduce vendor lock-in
- Introduce intelligence in every layer
- Acquisition of certain components to be interoperable and economically viable
- Effective Deployment both urban and rural.
🧠 Key Pillars of O-RAN Vision
In reference to the image, the O-RAN vision can be broken down into several key components:
- Open Interface/Protocols
E2, E3, NGFI-I, NGFI-II: Were defined to create certain interoperability between vendors.
E1 Interface: E1 interface, which connects CU-C (Control Plane) & CU-U (User Plane).
- Standardization of interface provides modular deployment options of components from different vendors.
- Disaggregated Architecture
Component Function
AAU/RU Active Antenna Units / Radio Units (Radio Frequency layer)
5G DU Distributed Unit, supports real time processing
5G CU - The continued expansion of 5G networks requires ever-greater openness, agility and intelligence in radio access networks. O-RAN is this unique convenience that is changing how networks are deployed and operated because O-RAN disaggregates hardware and software and enables AI/ML, cloud-native technologies.
This blog will present the O-RAN architecture using the newest visualization, discuss what we've observed with various players like NTT Docomo and Orange, and to describe how open interfaces are changing the RAN.
🔍 What is O-RAN?
O-RAN is a de-aggregated, open RAN architecture that is intended to:
- Limit vendor lock
- Introduce intelligence in every layer
- Obtain certain components to be interoperable and economical
- Effective deployment urban/rural
🧠 O-RAN Vision Pillars
Referring to the image, the O-RAN vision can be unbundled into a few key principles:
- Open Interface/Protocols
E2, E3, NGFI-I, NGFI-II: Were defined to enable some interoperability between vendors.
E1 (E1 Interface): E1 interface, which connects CU-C (Control Plane) & CU-U (User Plane).
- Standardized interfaces allow modular deployment options of various components from multiple vendors.
🛠️ Getting Started with O-RAN in Your Network
For telecom operators, network engineers, or systems integrators looking to deploy O-RAN, here is a set of applicable prescriptions:
✅ Implement Change Using a Sector-Wide Approach to Adoption
Assess the current state of RANs
Determine where the vendor lock-in points are
Determine if CU/DU separation is possible.
Assess transport readiness (NGFI capable)
Get started with Open Fronthaul
Install compliant NGFI interfaces between DU and RU.
Implement O-RAN fronthaul conformance test tools
Install the Near-RT RIC (RAN Intelligent Controller)
Use open APIs and xApps to implement automation and RRM optimizations
Get started with traffic steering or QoS prioritization
Virtualize DU/CU Functions
Host DU and CU functions on COTS hardware (using containers or VMs)
Work with open-source NFVI stacks (such as OPNFV, ONAP).
Implement MEC & AI Applications
Host edge applications (video optimization, gaming, URLLC use cases etc)
Leverage big data analytics platforms.
🎓 Training and Skills
In order to enable O-RAN adoption to be successful, teams need to have a range of cross-disciplinary skills:
Skill Area Recommended Focus
RAN Engineering NGFI interfaces, CU/DU separation, RF optimization
Cloud/Virtualization Kubernetes, OpenStack, Containers, SDN
AI & Data Analytics ML model deployment, RIC xApps, policy management
Network Orchestration ONAP, ETSI MANO, SMO tools
Open-Source Development CT/CD pipelines, GitOps, API interactions
📚 O-RAN Resources
O-RAN Alliance: https://www.o-ran.org
Technical specifications, white papers, reference designs.
O-RAN Software Community: https://www.o-ran-sc.org
Open-source implementations of RIC, SMO and E2/E1 interfaces.
ONF SD-RAN project: https://opennetworking.org/sd-ran
Real use cases and software stack to deploy RIC-based disaggregation.
TIP OpenRAN Project Group: https://telecominfraproject.com/openran
Working together with our partners to work on open RAN hardware, software and testing.
🌐 O-RAN is the Future of Mobile Networks O-RAN is transforming the telco environment to be more innovative, open and automated. As we look to transition to the more intelligent 5G, and future 6G networks, O-RAN creates the opportunity for telco operators to:
Accelerate service deployment
Lower operational costs
Untangle from vendor lock
Use AI to optimize network performance
🌍 Real-World Applications of O-RAN
O-RAN is more than an architectural concept—it’s already happening around the world. Here are some examples of how operators and vendors are using O-RAN in the wild:
📡 Use Case Examples
Rural Coverage Expansion
Connecting remote communities with cheap connectivity using white box RU/DU combinations and open source code.
Private 5G Networks
Enterprises deploying O-RAN-based 5G networks in manufacturing facilities, warehouses and ranch campuses—using MEC and AI inclusively for a low latency experience.
AI Traffic Management
Near-RT RIC activating real time RRM functions – AI-based xApps performing real time RRM for congestion control, handovers, load balancers.
Energy Efficiency
As an example, AI-based xApps will manage radio resources to support usage based on real-time traffic demand reducing energy usage where possible during times of low demand.
🔭 O-RAN What Now?
As 5G enters maturity and 6G emerges, O-RAN will play a pivotal role in the evolution of the networks of the future. Anticipate the following:
📈 Future Trends
6G-Ready architectures
The future RANs will leverage the principles of openness established by O-RAN with respect to enabling ultra-dense deployments, utilizing the terahertz spectrum and focusing on AI-native designs.
RIC Market Expansion
The momentum generated by xApp/rApp ecosystems expand and move toward an app-store model of RAN intelligence.
Wider adoption of a multi-vendor approach
Through interoperability testing/certifications (i.e., Plugfests) overall maturity will enhance confidence in multi-vendor approaches.
Cloud-Native Maturity
In one way or another, all stakeholders will fully realize the benefits of containerized network functions and CI/CD vis a vis O-RAN deployments.
