O-RAN Explained: The Future of Open and Intelligent Radio Access Networks

📡 Introduction:
To meet the demand for expanded capacity and lower latency, 5G networks are emerging and expanding globally. As this occurs, operators are looking for flexible, interoperable, and cost-effective solutions for new 5G networks. The traditional Radio Access Network (RAN) model of the past has been disrupted with the introduction of Open RAN (O-RAN), by way of open interfaces, disaggregated architecture, and intelligent automation. Notable operators, including Orange and NTT Docomo, are leading this evolution with a vision that embraces openness and standardization. This blog will clarify the O-RAN architecture, discuss its components, and explore its strategic importance in shaping the next generation of 5G networks.
🧠 What Is O-RAN?
Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) is a standard and inclusive way to construct RAN components and services utilizing open interfaces, software-defined functions and vendor-neutral hardware. The core objectives include:
Disaggregation of hardware and software
Open standards for interoperability
Intelligent management with the integration of AI and ML
Cloud-native deployments with virtualization
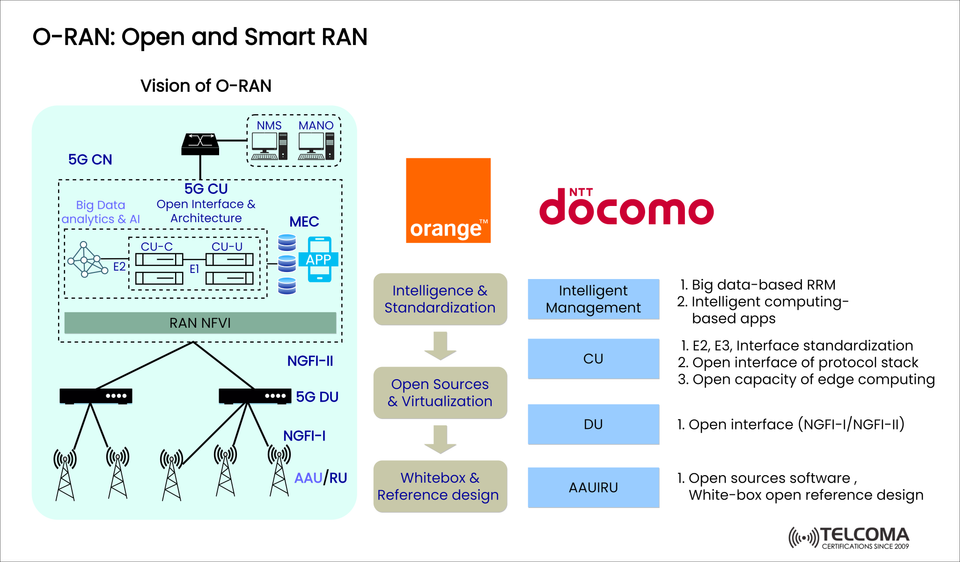
🧱 O-RAN Architecture Explained
🔄 Key Components in the Architecture
Construction Component Description
CU (Central Unit) Recently the CU has been split into CU-CP (Control Plane) and CU-UP (User Plane), it carries out RRM (Radio Resource Management) and maintains the mobility functions.
DU (Distributed Unit) Responsible for real-time baseband processing; connects to RU using NGFI-I; all aspects of gNB running on DU (iso-environment).
RU (Radio Unit / AAU) Converts the digital or baseband to analog (RF) and vice versa; RU connects to antennas.
📡 Open Interfaces Explored
NGFI-I / NGFI-II – Providing connectivity between RU–DU and DU–CU respectively.
E1 Interface – Between CU-CP and CU-UP.
E2 / E3 Interfaces – To interface RIC and AI-based control.
Open APIs – To enable 3rd party applications and edge services.
🧭 O-RAN Vision from Orange & NTT Docomo
🟠 Orange's Roadmap
Intelligence & Standards
Open Source & Virtualisation
White-box Hardware & Reference Design
🔴 NTT Docomo's Focus
RRM Improvement using big data and intelligent computation
Protocol Stack Open-ness E2, E3 opened up, standardised
Edge Enablement: enabling real-time computation and services
Open Hardware: AAU/RU white-box deployment
🧩 O-RAN positives for Telecom Operators
Vendor Interoperability: Easy to mix and match from a broader choice of Vendors.
Reduced TCO: Lower CapEx and OpEx using standard commodity hardware.
AI-enabled Operations: Predictive maintenance, traffic steering and energy efficiency.
Fast-Track Innovation: Open APIs promote more developers to build network apps into new eco-systems.
Scalable: Simple to scale components with a cloud-native deployment.
⚙️ O-RAN vs Traditional RAN
Feature Traditional RAN O-RAN
Hardware Vendor specific White-box / open source
Interfaces Proprietary Open-standard (NGFI, E2, E3)
Control Centralized Distributed with AI/ML
Upgrades Complex and vendor locked Module and dynamic
Ecosystem Closed Open and collaborative.
🔮 The Future of O-RAN: Towards 6G
O-RAN is already beginning to develop the pre-conditions for 6G by enabling:
Real-time orchestration across different networks
Integration with satellite and other non-terrestrial networks
Autonomous operation on a purposely built AI-native infrastructure
With the developments of 5G now maturing, O-RAN standards open up the door for:
More resilient and intelligent networks with lower costs in operations to the telco.
Freedom from current vendor lock-in, in order to innovate at scale.
📝 Overall conclusion
When we say O-RAN is a shift more than product, we are pointing out that this is not a shift in technology, but rather a shift in philosophy. It's a movement towards developer-controlled networks that are open, programmable, and intelligent which dynamically adapts the network to users and future innovation. With full support from leading operators like Orange and NTT Docomo, the O-RAN Alliance will continue to enable global standardization and adoption of this important innovation framework.
🏗️ O-RAN Deployments and Use Cases
🚀 1. Commercial Deployments
A number of leading operators around the world are moving towards O-RAN deployments:
Rakuten Mobile (Japan): The first commercial deployment of a fully virtualized O-RAN network in the world.
Deutsche Telekom: Trials in an O-RAN architecture for automation and cost savings.
Orange: Trials and validations of a white-box DU/CU deployment with a view to achieving vendor-neutral access to 5G.
🧪 2. Trials and Testbeds
TIP (Telecom Infra Project): Working with operators who are conducting live field trials using open interfaces.
NTT Docomo’s multi-operator lab on 5G will encourage the use of O-RAN compliant products from different vendors.
🧠 Intelligent Management in O-RAN
Intelligent management is a key differentiator of O-RAN, and is mainly based on the concept of a RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC):
🔷 Near-Real-Time RIC (nRT-RIC)
Uses AI/ML algorithms to support RRM function decisions in near-real-time.
Examples: Dynamic load traffic balancing, interference management.
🔐 Security Aspects in O-RAN
Open interfaces mean flexibility for network operators, but with openness also comes additional cybersecurity risks. To mitigate risks:
Enforce standardized access control for the API.
Zero-trust security is recommended across open interfaces.
Runtime threat detection for each virtual functions.
Organizations like O-RAN Alliance and 3GPP SA3 are working to create aligned approaches to harden O-RAN against threat evolution.
📈 The Future: O-RAN and Cloud Native
O-RAN builds on cloud-native principles to transform the network architecture:
CI/CD pipelines for continuous updates of features within network functions.
Containerized network function (CNFs) for flexibility at the microservice level.
Multi-cloud orchestration allows connections to public and private or edge cloud.
📚 Further Study Resources
For those wanting to dive deeper:
O-RAN Alliance Website – Official specifications and working groups.
TIP OpenRAN Project Group – Live trials and community discussions.
3GPP TS 38.401 & 38.463 – Technical standards for functional splits and interfaces.
ETSI NFV ISG – Virtualization frameworks for operationalizing O-RAN.
🧾 Finally
While O-RAN is a major new upgrade, it is much more than that - it is a new way of building networks to improve openness, scale with intelligence and evolve with innovation. As demand for low-latency and high-capacity services continues to grow, O-RAN’s modularity, cloud native approach and AI-driven components will become the backbone of next-generation mobile infrastructure.
✅ Summary: Summary – Why O-RAN is the Future of Radio Access Networks
In summary, O-RAN is a creative solution to the fundamental challenges facing the telecommunications industry by adhering to the fundamental principles of openness, intelligence, and interoperability. Not convinced yet? Here’s a summarized rationale of its essentiality to evolution of 5G and beyond:
