O-RAN O1 Interface Explained: Network Management, Fault Monitoring, and Performance Assurance in Open RAN

Introduction: The Core of Open RAN Management
As mobile networks shift toward Open RAN (O-RAN), flexibility and automation have become essential. Operators are in need of comprehensive tools to monitor, configure, and optimize network components from different vendors.
This is where the O-RAN O1 Interface comes into play. Acting like the central nervous system for network management, it serves as the communication link between the Service Management and Orchestration (SMO) framework and various O-RAN network elements (O-RU, O-DU, O-CU).
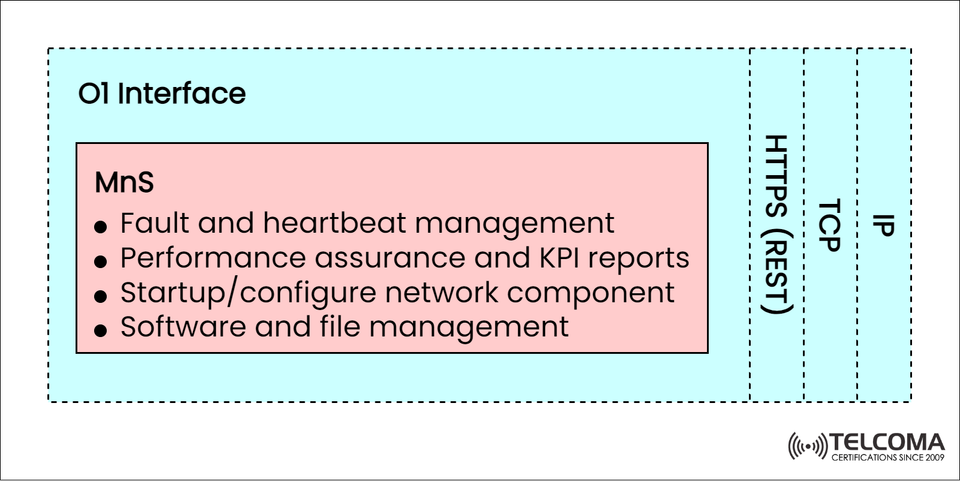
The image above illustrates the structure of the O1 Interface, showing its Management and Orchestration Services (MnS), REST-based communication, and key functions including fault management, KPI reporting, and software configuration.
Getting a Grip on O-RAN Management Architecture
The O-RAN Alliance defines several interfaces to promote open, interoperable, and intelligent RAN systems, with each interface serving a specific function within the RAN ecosystem.
Interface Purpose Key Functionality
A1 Interface AI-driven policy and ML model management — Connects Non-RT RIC and Near-RT RIC
E2 Interface Real-time RAN control — Connects Near-RT RIC to RAN nodes
O1 Interface Operations, administration, and maintenance — Connects SMO to O-RAN network functions
The O1 Interface mainly takes care of Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) tasks, which involve managing network components and making sure everything's running smoothly across the disaggregated RAN.
What Does the O-RAN O1 Interface Entail?
The O1 Interface is a standardized communication link that connects the Service Management and Orchestration (SMO) layer to O-RAN network elements like the O-RU (Radio Unit), O-DU (Distributed Unit), and O-CU (Central Unit).
Through this interface, the SMO carries out management and orchestration tasks using Management Services (MnS), which cover:
Fault and heartbeat management
Performance assurance and KPI reports
Network configuration and initialization
Software and file management
The O1 interface utilizes HTTPS (REST) protocols over TCP/IP for secure, scalable, and cloud-native communication between the SMO and network components.
Understanding the O1 Interface Protocol Stack
The O1 Interface employs a web-friendly protocol stack, as seen in the image.
Layer Protocol Function
Application LayerREST APIs using JSON/XML — Manages operations and notifications
Transport LayerHTTPS — Ensures secure communication
Network LayerTCP/IP — Guarantees reliable data delivery
This design based on REST and APIs makes integration with cloud orchestration platforms a breeze and supports automation using standard APIs, aligning with O-RAN’s principles of openness and interoperability.
O1 Interface Functions You Should Know About
The Management Services (MnS) provided by the O1 Interface are fundamental for RAN management. Let’s dive into each one.
4.1 Fault and Heartbeat Management
Fault management is crucial for keeping the network reliable and the service quality high.
Key Functions:
Fault Detection: Spotting alarms and service anomalies in real time.
Fault Reporting: Sending details about faults (like severity, timestamp, and affected components) to the SMO.
Heartbeat Management: Keeping track of “keep-alive” signals to ensure network elements are functioning properly.
Example Use Case:
If an O-RU loses connection or gets too hot, the O1 interface will quickly alert the SMO. This allows for automated fault isolation and healing workflows, which helps minimize downtime.
4.2 Performance Assurance and KPI Reporting
Managing performance is key to ensure that the network meets its Service Level Agreements (SLAs) and maintains consistent Quality of Service (QoS).
Key Functions:
KPI Collection: Gathers metrics such as throughput, latency, and error rates.
Performance Analysis: Analyzes historical and real-time data to identify any drops in performance.
Optimization Feedback: Sends KPI results to the Non-RT RIC for AI-driven optimization.
Example Use Case:
Using the O1 Interface, the SMO collects KPIs from the RLC/MAC layer in an O-DU, which allows it to detect congestion and adjust scheduling or capacity proactively.
4.3 Startup and Configuration Management
The O1 Interface simplifies network provisioning by automating start-up and configuration tasks.
Key Functions:
Auto-discovery: Finds and registers new O-RAN components as they are added to the network.
Parameter Configuration: Sets logical functions like carrier frequency and transmit power.
Topology Management: Keeps track of how network nodes are arranged hierarchically and geographically.
Example Use Case:
When a new O-DU is set up, the O1 Interface uses template configurations to automate the process, ensuring everything is consistent and reducing setup time.
4.4 Software and File Management
Software management via the O1 ensures that the entire RAN infrastructure stays updated and secure.
Key Functions:
Software Version Control: Manages and tracks firmware or software updates across O-RUs, O-DUs, and O-CUs.
Remote Upgrades: Supports over-the-air (OTA) updates and rollback options.
File Management: Handles logs, performance data, and backups.
Example Use Case:
During a security update, the SMO can use the O1 interface to remotely push new firmware to all O-RUs without interrupting live traffic, ensuring a seamless, zero-touch upgrade.
Overview of MnS (Management Services)
The MnS (Management Services) block shown in the image encompasses all management functions provided through the O1 Interface.
MnS Category Functionality
Fault MnS Handles fault detection, alarm reporting, and recovery actions.
Performance MnS Responsible for KPI reporting, metrics collection, and monitoring SLAs.
Configuration MnS Focuses on initialization, parameter setup, and topology management.
Software MnS Includes firmware upgrades, log file transfers, and backup management.
MnS serves as the operational brain for the O1 interface, ensuring constant visibility, control, and optimization of every RAN component.
Advantages of the O1 Interface
Benefit Description
Unified Management Centralized control over all O-RAN components through SMO.
Vendor Interoperability Open standards allow for multi-vendor RAN environments.
Automation-Ready Facilitates zero-touch provisioning and fault recovery.
Performance Optimization Real-time feedback on KPIs allows for dynamic adjustments.
Scalability REST APIs and cloud integration cater to network expansion.
The O1 interface allows operators to effectively manage thousands of distributed nodes, ensuring consistent performance throughout the network.
Role of O1 Interface in the O-RAN Lifecycle
The O1 Interface is vital throughout the RAN lifecycle:
Deployment Phase: Automates the onboarding and configuration for new network elements.
Operational Phase: Continuously tracks health, performance, and KPIs.
Maintenance Phase: Manages software updates, patches, and faults.
With complete visibility and control, O1 guarantees network uptime, efficiency, and service quality as we move into 5G and beyond into 6G networks.
Conclusion: The O1 Interface – Nerve Center of Open RAN Operations
The O-RAN O1 Interface acts as the backbone of operations, ensuring every component of the RAN — from radio units to distributed units — is efficiently monitored, managed, and optimized.
By offering a unified platform for fault management, performance monitoring, configuration, and software lifecycle management, the O1 Interface paves the way for true network automation and multi-vendor interoperability.
