O-RAN vs 3GPP Architecture: Functional Splits, Interfaces, and RIC Explained
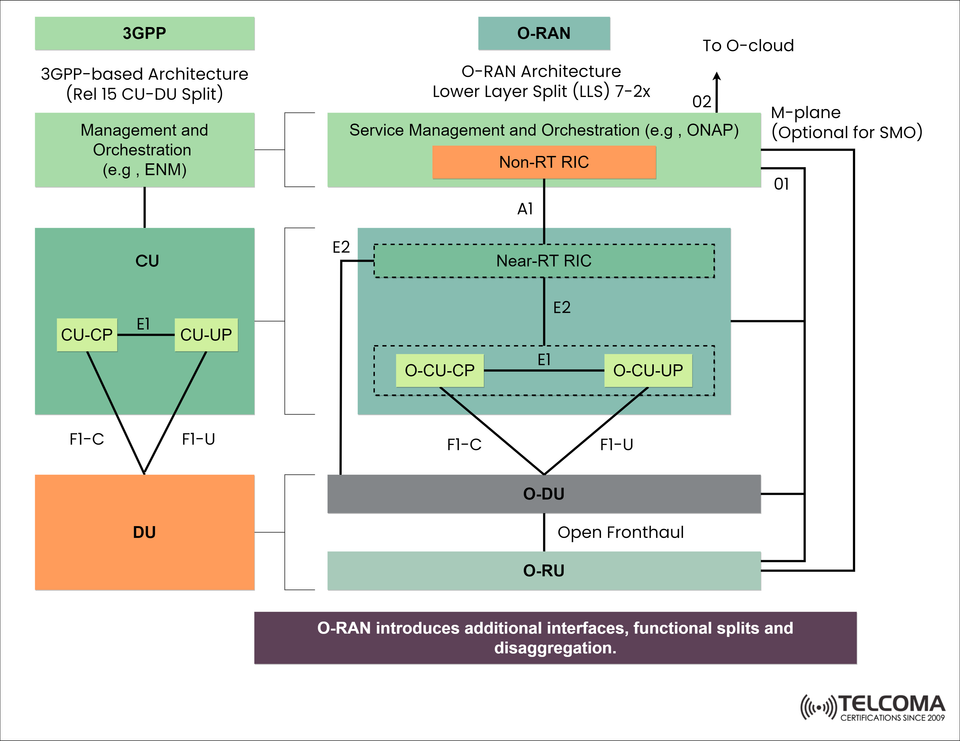

O-RAN vs 3GPP Architecture: Disaggregated RAN with Functional Splits and Interfaces
With 5G and open networking at the center of recent RAN developments, O-RAN (Open Radio Access Network) represents a sleek, flexible, vendor agnostic alternative to 3GPP-based architectures that existed before it. While 3GPP Release 15 introduced the CU-DU split (Centralized Unit and Distributed Unit), with O-RAN we now have a completely disaggregated RAN architecture that enables multi-vendor capabilities, cloud-native deployments, and AI based automation.
This blog post is going to look at the architectural differences between 3GPP CU-DU and O-RAN, which should be apparent in the picture we have on the top of the document. RAN Interfaces like E1, F1-C/U and E2 along with 'RAN' components such as RIC (RAN Intelligent Controller) and SMO (Service Management and Orchestration) within the O-RAN architecture provide intelligent, open and modular RAN deployments.
🧱 3GPP Architecture (Rel-15): CU-DU Split Details
3GPP Release 15 introduced the split of the functions for the CU and DU which established the prerequisite scaling and deployments for 5G RAN:
🔹 CU (Central Unit)
Manages the higher layer RAN functionalities.
CU is split into:
CU Control Plane (CP): RRC, part of PDCP
CU User Plane (UP): PDCP, SDAP
The two layers are connected with the E1 interface internally.
Interfaces:
F1 Control Plane (CP): Between CU-CP and DU
F1 User Plane (UP): Between CU-UP and DU
⚙ Management
Management typically occurs in a centralized manner utilizing ENM (Ericsson Network Manager) or by using selected vendor tools.
🧭 O-RAN Architecture: Disaggregated and Intelligent RAN
The O-RAN Alliance architecture is an extension of the 3GPP architecture (with added interfaces, functional splits [e.g. Split 7-2x], and intelligence layers) in an effort to foster openness, disaggregation, and innovation.
⚙ O-RAN Which Adds Components
Components Function
O-CU Sub split into O-CU-CP and O-CU-UP that mirrors 3GPP split but with open standards
O-DU -Contains Layers 1-2 and connects to O-RU via Open Fronthaul interface
O-RU Radio Unit that contains Layer 1 (Lower PHY) functions, decouples via open fronthaul
Near-RT RIC (RAN Intelligent Controller) Controls RAN behavior when in near real-time (10 ms - 1 s). Uses E2 Interface.
Non-RT RIC Deal with policy and AI ML model management (>1 s latency). Interfaces thru A1
SMO (Service Management and Orchestration) Provides lifecycle and configuration management. Uses O1 and O2 interfaces.
🔌 Interface Comparison of 3GPP and O-RAN
Interface Description Applies To
E1 CU-CP ↔ CU-UP communications 3GPP & O-RAN
F1-C / F1-U CU ↔ DU for control/user plane split 3GPP & O-RAN
Open Fronthaul DU ↔ RU open interface (e.g., eCPRI) reporting interoperability difficulties, poor sound quality, other
E2 Near-RT RIC ↔ CU/DU nodes <1 s communication 3GPP & O-RAN
🔍 Key Differences Between 3GPP and O-RAN
Category 3GPP O-RAN
Architecture CU-DU Split CU-DU-RU with open interfaces
Vendor Interoperability Vendor-locked Multi-vendor support
Intelligence Not modularized Near-RT and Non-RT RICs
Management ENM/NMS SMO + ONAP
Functional Splits Up to Split 2 (CU-DU) Includes Split 7-2x, Split 6, etc.
Fronthaul Proprietary Open (e.g., eCPRI, ORAN Fronthaul Spec)
🚀 Why O-RAN Matters for the Future of 5G
✅ Benefits of O-RAN:
Disaggregation: Enables flexible deployment models with best-in-class vendors.
Automation: Supports AI/ML-driven network optimization via RIC.
Cost Efficiency: Reduces vendor lock-in and dependence on proprietary hardware.
Edge Readiness: Suitable for cloud-native, containerized 5G architectures.
🧠 Real-World Applications:
Enterprise and private 5G networks using modular DU/RU solutions.
Rural/remote deployments that leverage RICs for intelligent optimization.
Open RAN labs testing vendor interoperability using standardized interfaces (E2, O1, etc.).
🧩 O-RAN: A Modular, Open 5G Future
O-RAN's design philosophy will allow telecom providers to:
Deploy cloud-native components across the RAN stack.
Leverage vendor-neutral orchestration tools like ONAP.
Optimize traffic, mobility, and resource usage with real-time AI engines.
For engineers and architects, O-RAN is not just a technology evolution .
🏁 Conclusion
While 3GPP provided a structural platform with the CU-DU split, O-RAN takes it a step further as an open, intelligent, modular architecture. With standardized interfaces such as E2, O1, and A1, as well as intelligent controllers and disaggregated units, O-RAN allows telecom operators to escape monolithic RAN stacks and create future-proof, agile 5G networks.
🔍 Further Details into O-RAN Components and Functional Roles
🧠 1. Near-Real-Time RIC (Near-RT RAN Intelligent Controller)
Functionality:
The Near-RT RIC provides the capability for intelligent control of RAN functionality while keeping latency between 10 ms and 1 second. It will interface with CU and DU nodes over the that E2 interface to enable:
a. Load balancing
b. Handover optimization
c. Interference management
d. QoS based scheduling
Use Case:
Dynamically deploy AI/ML models to enhance spectral efficiency in highly populated urban environments.
🧠 2. Non-Real-Time RIC (Non-RT RIC)
Functionality:
The Non-RT RIC operates on timescales of greater than 1 second and interacts with the Near-RT RIC using the A1 interface. The Non-RT RIC can provide:
a. AI/ML model training and lifecycle management
b. Policy generation and distribution
c. Performance trend analysis and long term planning
Use Case:
Use analytics-based insights to optimize mobility policies within regions based on subscriber behaviours.
📈 Performance & Challenges
While O-RAN allows for openness and intelligence, it also adds operational complexity:
⚠️ Challenges:
Interoperability testing with multiple vendors
Security and trust approaches related to AI-based controllers
Latency requirements on open fronthaul
O-Cloud orchestration complexity
✅ Mitigation Strategies:
Using RIC testbeds and open platforms like O-RAN SC
Engaging in multi-vendor PoCs and Plugfests
Using containerized RAN elements (CNFs) to allow ease of scaling within the system process
🏗️ The Future: Open RAN in 6G and Beyond
As networks get closer to 6G, O-RAN is expected to enable these ways by allowing:
More network-as-code paradigms
Ultra low touch
Introductions of beyond-5G features like reconfigurable intelligent surfaces and integrated sensing
