ONAP Closed Loop Automation Explained: Real-Time Policy, Analytics, and Self-Healing in Telecom

Introduction: The Move to Autonomous Networks
The telecom sector is going through a significant change. Old static networks just aren’t cutting it anymore for businesses, cloud-based apps, and 5G services. Operators need automation, flexibility, and smarts to scale their services effectively.
This is where the Open Network Automation Platform (ONAP) comes in. ONAP allows for the full automation of network services, which means less manual work and lower operational costs. At the core of ONAP is Closed Loop Automation — a system that makes networks self-monitoring, self-optimizing, and self-healing.
The Closed Loop model within ONAP weaves together service definition, policy enforcement, analytics, event logging, and corrective actions into a continuous loop, helping telecom networks stay resilient and adaptable.
What is ONAP Closed Loop Automation?
Closed Loop Automation in ONAP is all about a cycle of monitoring, analyzing, and acting on network events in near real-time. Unlike traditional automation, which often needed human intervention, ONAP’s closed loop creates autonomous feedback systems.
Monitor services all the time
Trigger analytics on events
Apply policies on the fly
Take corrective measures (like scaling, healing, or reconfiguring)
Log results for ongoing improvement
This closed loop means networks aren’t just reactive; they’re also proactive at preventing issues.
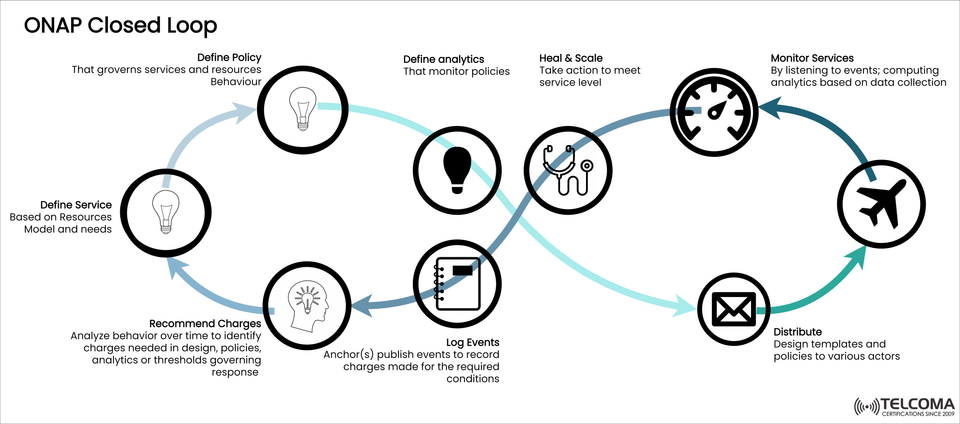
Step-by-Step Breakdown of the ONAP Closed Loop (According to the Diagram)
The diagram shows the lifecycle of ONAP’s Closed Loop. Let’s break it down with some technical insight:
- Define Service
Services are created based on resource models and business needs.
For instance, a telecom operator may set up a new 5G network slice for video streaming, ensuring it meets specific latency and bandwidth targets.
ONAP supports service modeling using TOSCA templates for consistency and reusability.
- Define Policy
Policies dictate how services and resources act under various conditions.
They consist of machine-readable rules that drive the automation.
For example, if bandwidth usage goes over 80%, the system can automatically scale up resources.
- Define Analytics
Analytics modules keep track of data against the established policies.
They monitor network KPIs (like latency, jitter, and packet loss).
For example, AI/ML-driven analytics can spot early signs of congestion before it affects service quality.
- Heal & Scale
When thresholds get exceeded, ONAP kicks in with automated fixes.
Actions can include:
Healing: Restarting failed VNFs (Virtual Network Functions)
Scaling: Adding more computing power or bandwidth
Re-routing traffic to avoid service interruptions
Example: If an SD-WAN tunnel fails, ONAP will automatically fix it by setting up a new encrypted tunnel.
- Monitor Services
ONAP is always listening to network events.
It uses telemetry, logs, and probes to keep an eye on performance in real-time.
Example: Keeping track of customer VPN service availability across different carriers.
- Distribute
Policies and service templates are shared with various actors (like controllers, orchestrators, and VNFs).
This makes sure there’s consistent enforcement across different areas.
Example: Sharing an SLA enforcement policy with both the SOTN controller (for optical transport) and SD-WAN controller (for overlay VPN).
- Log Events
Every action and event is logged for auditing, compliance, and learning.
Example: A scaling event due to high traffic is recorded for future planning.
- Recommend Changes
ONAP looks at long-term patterns and makes suggestions about updating service designs, policies, or analytics.
For instance, if there are repeated congestion events at the same time every day, ONAP might recommend adjusting resource thresholds or changing service policies.
Why ONAP Closed Loop Matters for Telecom Operators
Telecom operators are facing new hurdles in the age of 5G, IoT, and multi-cloud systems:
Higher customer expectations: Businesses want SLA-backed services with no downtime.
Complex networks: Multi-vendor, multi-domain setups need consistent policy enforcement.
High operational costs: Manual monitoring and the need for human intervention drive expenses up.
Growing competition: Companies like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer network services faster.
ONAP Closed Loop tackles these challenges by:
✅ Enabling self-healing networks
✅ Cutting down manual interventions
✅ Ensuring SLA compliance
✅ Boosting resource efficiency
✅ Speeding up time-to-market for new services
Real-World Applications of ONAP Closed Loop
5G Network Slicing:
Automatically keeps an eye on slice performance and fixes any degraded slices.
Example: A slice meant for AR/VR applications can ramp up bandwidth during busy times.
Multi-Carrier VPN Services (CCVPN):
Ensures that VPN SLAs are met across different providers through continuous monitoring and adjustments.
IoT Device Management:
Spots unusual IoT traffic patterns and applies security policies automatically.
Cloud-Native VNFs:
ONAP helps fix failed VNFs in Kubernetes clusters to ensure apps keep running.
Comparing Traditional Automation vs. Closed Loop Automation
Feature Traditional Automation ONAP Closed Loop Automation Monitoring Manual or periodic Real-time, continuous Policy Enforcement Predefined, static Dynamic, adaptive Healing Manual trouble shooting Automatic, AI-driven Scalability Limited On-demand, elastic SLA Assurance Reactive Proactive
The Future of ONAP Closed Loop in Telecom
Looking ahead, we can expect ONAP Closed Loop to incorporate:
AI/ML algorithms for proactive maintenance and spotting anomalies
5G Core networks for dynamic slice management
Edge computing to manage decentralized resources in real-time
Blockchain-based frameworks for enforcing SLAs between multiple operators
As networks shift to become more software-driven, closed loop automation is poised to be the foundation of autonomous, intent-driven networks (IDN).
Final Thoughts
ONAP Closed Loop automation is a key element of today’s telecom networks. By combining service design, policies, analytics, and real-time monitoring, it empowers operators to deliver reliable, smart, and customer-focused services.
From self-healing VPNs to dynamic 5G slices, ONAP Closed Loop helps telecom operators stay ahead in the digital age.
As 5G, IoT, and cloud-native services grow, ONAP’s closed loop features will be essential in crafting the autonomous networks of the future.
