Open 5G RAN Architecture: Efficiencies, Threats, and the Future of Virtualized Networks

🌐 Open 5G RAN Architecture: Efficiencies and Threats Discussed
The Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) initiative is changing how telecom operators deploy and operate their 5G infrastructures. O-RAN is a movement from the proprietary RAN architectures that telecom operators catch predominantly had to deploy to now taking advantage of openness, interoperability, and vendor diversity.
This blog post will breakdown the architecture (more on that later), compare the 3GPP VRAN (Virtual RAN) version vs. the O-RAN version, and lastly, discuss the efficiencies and threats to the evolving ecosystem.
🔍 Summary:
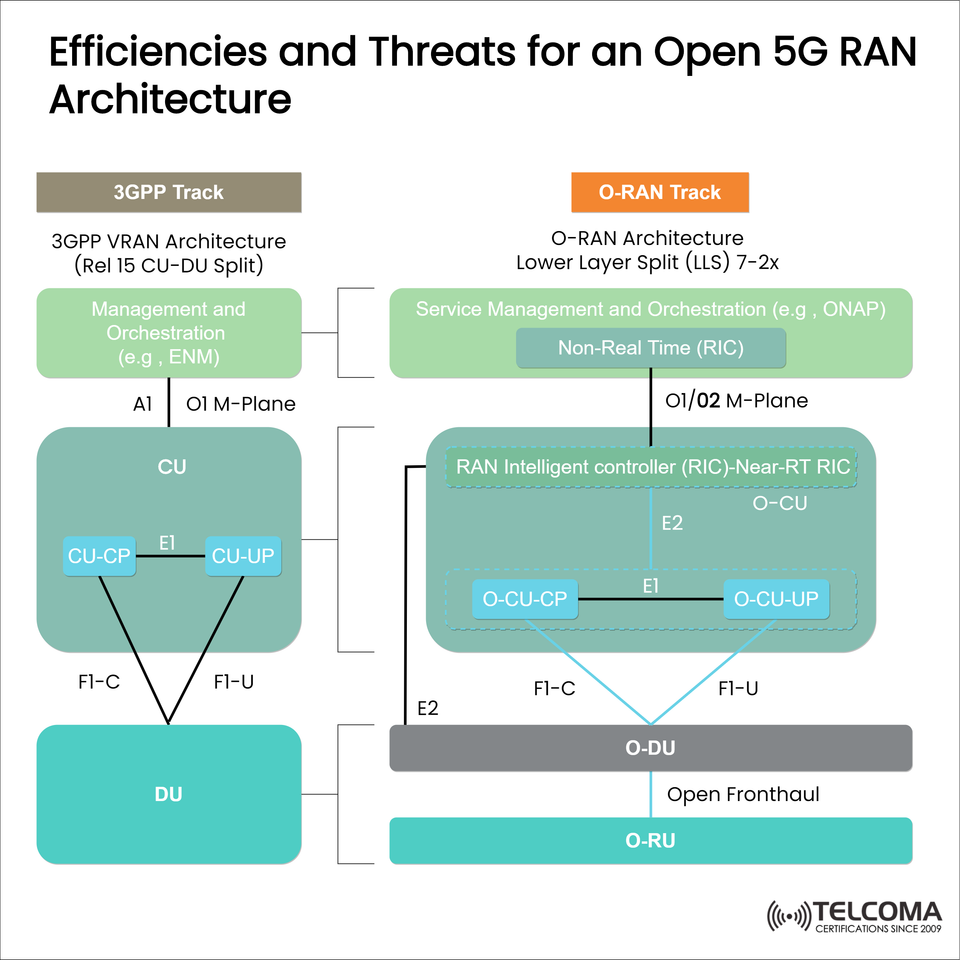
3GPP VRAN versus O-RAN Architectures
The diagram below represents the two parallel tracks:
🟫 3GPP Track (Traditional Virtual RAN).
Based on 3GPP Release 15 CU-DU (Central Unit - Distributed Unit) split.
Managed using an ENM or orchestration equivalent.
Operates using standard interfaces such as E1, F1-C, or F1-U to exchange data between plans (control/user) and the DU.
🟧 O-RAN Track (open RAN model).
Similar to the native 3GPP release partitions, but more modular architecture with open interfaces.
Includes RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) to enable automation, optimization, and network intelligence.
Has separated near-RT RIC and non-RT RIC to allow for AI/ML.
The O-CU, O-DU, and O-RU components replace the traditional functions of a RAN while connected on the open fronthaul.
📐 Key Components & Interfaces
Component Role
CU (Central Unit) Manages the high-layer functions of the protocol stack (CU-CP and -UP).
DU (Distributed Unit) Manages the real-time lower layer functions, including MAC and RLC.
O-CU / O-DU / O-RU Open RAN equivalents which support open interfaces for modular integration.
RIC (RAN Intelligent Controller) Provides policy control to optimize the RAN through analytics and AI.
E1, F1, E2 Standard interfaces for communication between RAN component.
A1, O1/O2 Interfaces for management, orchestration and the RIC.
⚙️ Efficiencies of Open 5G RAN
The O-RAN architecture provides significant benefits for operators, developers, and enterprises:
✅ Advantages:
Vendor Interoperability
Vendor lock-in is broken and provides an opportunity to mix-and-match hardware/software.
Cost Efficiency
Significantly reduces both CapEx and OpEx through white-box hardware and cloud-native software.
Faster Innovation
AI/ML-enabled RICs allows for dynamic network optimization and automated policy control.
Edge-Native Deployment
O-DUs can be deployed closer to the user for less latency.
Cloud Integration
Integrates with orchestrator tools, such as ONAP, to provide automated manangement.
⚠️ Open RAN Threats / Issues
Open RAN has potential, but it also includes complexities and potential risks to:
Security Risks
Open interfaces increase the attack surfaces, necessitating greater isolation, encryption, and threat detection.
Integration Complexity
Multi-vendor takes considerable deep testing of interoperability, initial profiling, and configuration management.
Performance Overhang
Virtualized environments may introduce round trip latency regardless of whether Hardware Acceleration (e.g. FPGAs, SmartNICs) is leveraged.
Maturity Gap
Traditional RAN vendors still outperform in term of radio performance, power efficiency, and scale.
🛠️ Use Cases Where Open RAN Makes Sense
Use Case Why Open RAN is Appropriate
Private 5G for Enterprises Modular, scale from a vendor agnostic silo for industry needs
Rural Connectivity Cost-effective deployment with disaggregated hardware
Smart Cities / IoT Hubs Leverage AI/ML for resource allocation, or dynamic spectrum sharing
Cloud-native Network Builds Integrations into public cloud or private cloud workloads are seamless
🧠 Expert Corner - RIC Advances
”RAN Intelligent Controller” (RIC) is an important advancement of Open RAN, that provides support for:
Non-Real Time (non-RT RIC): Long term operational strategies leveraging AI/ML (i.e. load balancing, anomaly detection).
Near-Real Time (Near-RT RIC): Short time operational strategies with low latency decisions on radio resource management (i.e. handovers, power control).
📌 Final Thoughts
Open RAN isn't merely a buzzword; it represents a significant change in the way telecom networks are constructed, optimized, and managed. By opening the architecture, the industry gets greater flexibility, new sources of innovation, and cost-savings - but it must also cope with higher levels of complexity and risk.
Both the 3GPP and O-RAN tracks are likely coexist to give operators the ability to configure their architectures around its performance, security, and business requisites.
🧭 Strategic Recommendations for Industry Stakeholders
Transitioning to Open RAN is more than just merely architecturally aligned; it requires strategic thinking impacting the entire telecom value chain.
👷 For Network Operators:
Begin with Hybrid Deployments
Start with Open RAN trials in non-critical environments (for example rural areas, enterprise private 5G) before scaling to urban macro networks.
Invest in Vendor Ecosystem Management
Having integration labs, pre-integrated and interoperability testing environments to validate multi-vendor interoperability and functionality performance.
Enhance Security Framework
Implement zero-trust security principles leveraging the E1, F1, E2, O1/O2, A1 interfaces. Consider using AI/ML-based threat monitoring and observability.
🧠 For System Integrators and Developers:
Utilize RIC SDK's and APIs
Develop xApps (Near-RT) and rApps (Non-RT) for use cases such as load-balancing, interference mitigation, and/or beamforming optimization.
🏢 For Enterprises and Private Network Developers:
Leverage O-RAN to be Disruptive
Customize your 5G system with separate hardware and software building blocks that are optimized for your industrial workload.
Enforce Service Level Agreement Compliance
Immediately apply quality-of-service policies in a loop with orchestration, RIC + stack.
🔮 The Future: Open RAN and 5G-Advanced
As we move to 5G-Advanced (Release 18 and beyond), Open RAN will become a foundational enabler for:
AI-native RAN operations
Network-as-Code principles
New green RAN architectures for energy compliance
Pre-integration for 6G with tighter RIC and radio interface work
The ecosystem is being de-risked at an extraordinary pace, through the work of the O-RAN Alliance, TIP (Telecom Infra Project), and Open RAN Software Community.
The future of radio access is modular, intelligent, open, and automated - and Open RAN is leading us there.
🧾Summary
Aspect Open RAN Strengths Potential Weaknesses
Architecture Flexibility Modular, mix and match components Very dynamic relationships among a variety of vendors
Cost Model Reduced CapEx through use of white-box hardware Upfront costs to integrate and tune the components
Intelligence Layer Having RIC provide network optimization DYNAMICALLY and NON-DYNAMICALLY An immature xApp/rApp marketplace
Ecosystem Openness Avoid vendor lock-in and innovate more More security exposure
Deployment Speed Ability to scale to an enterprise and rural deployments
