Open RAN vs 3GPP RAN: Understanding the Architecture, Efficiencies, and Threats in 5G Networks

Open 5G RAN Architecture: Efficiency, Threats and Future of Disaggregated Networks
The deployment of 5G networks has emerged with enormous performance potential yet complexity and demand for flexibility. Open RAN (O-RAN) challenges traditional (3GPP) RAN architecture and works to create vendor-agnostic, modular components for greater flexibility in the physical and operational layers of 5G network operation. This blog will discuss the comparison of architecture, operational efficiencies and possible security threats to Open RAN based 5G v deployments, and a use case of existing architectural diagram to literally 'map-out" the issues.
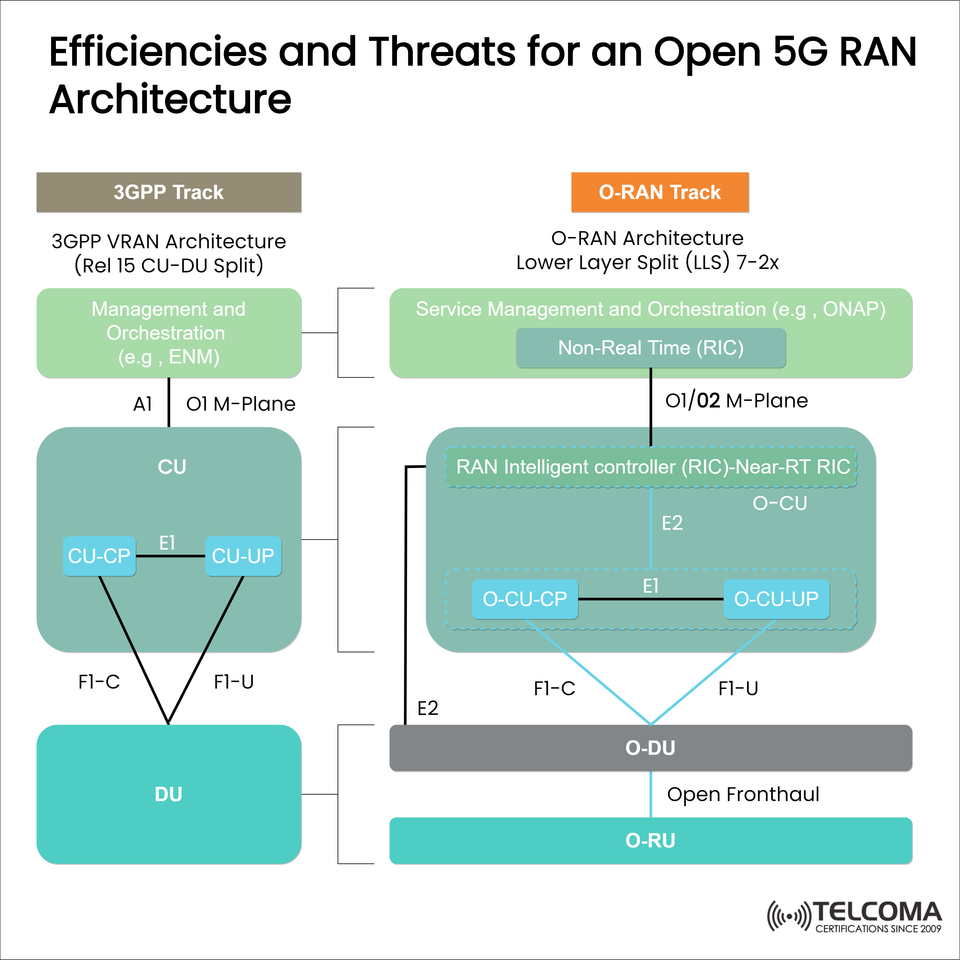
📐 What the Image Shows
The image includes a side-by-side comparison and look at:
3GPP Track: Based on 3GPP VRAN Architecture (Release 15) with the traditional Centralized Unit (CU) - Distributed Unit (DU) split.
O-RAN Track: aligned to O-RAN Alliance specifications with open interfaces, RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC), and functionally disaggregate layers.
🧱 Explanation of Elements
🔷 3GPP Architecture: Centralized and Vendorized
CU (Centralized Unit):
CU-CP: Control Plane
CU-UP: User Plane
DU (Distributed Unit): provides the real-time baseband processing physically closer to the user. In this scenario, the DU is in the RAN itself.
Interfaces:
E1: connects CU-CP and CU-UP
F1-C/F1-U: Control Plane interface between CU - DU and User Plane interface between CU - DU
Management Plane: has ENM for orchestration over A1 and O1.
🟧 O-RAN Architecture: Modular, Disaggregated, Intelligent
- O-CU & O-DU: Virtualized and split similarly to CU and DU, but open and interoperable.
- O-RU (Radio Unit): Open fronthaul interface enabling multi-vendor support.
- RIC (RAN Intelligent Controller):Non-Real-Time RIC: For policy control and AI/ML model training.Near-Real-Time RIC: Interfaces with O-CU via E2 for real-time optimization.
- Management Plane: Based on ONAP or similar SMO platforms using O1/O2 interfaces.
⚙️ The Benefits of Open 5G RAN Architecture
Benefit Explanation
Vendor Interoperability Operator can use hardware/software from multiple vendors, interchangeably.
Cost effectiveness Reduced reliance on independent proprietary systems from a single vendor.
Speed of innovation Open Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) allow for the integration of Artificial Intelligence-driven applications via a Reconfigurable Intelligent Controller (RIC).
Edge flexibility Easier to distribute Distributed Unit (DU) functions at the edge for latency sensitive applications.
⚠️ Threats and Challenges of Open RAN
While Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN) architecture embraces openness, it has presented new types of risk:
Interface security: The open nature of interfaces (E2, F1, O1/O2) needs to not be susceptible to malicious acts, like man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks and Denial of Service (DoS) attacks.
RIC exposure: The near Real-Time (RT) RIC can be subject to manipulation in the control plane if there's not secure integration of behaviors.
Supply chain complexity: The multi-vendor architecture can increase the burden of integration and testing.
Performance overhead: The virtualization of the Open RAN architecture can introduce delays and handling of packets unless properly engineered.
🧠 RIC and Intelligent RAN
One of the differentiators of Open RAN is the RIC. There are two implementations of the RIC in Open RAN:
Near-RT RIC: Executes xApps (e.g., handover optimization, interference management) based on control loops that are about ~10ms.
Non-RT RIC: Uses Machine Learning (ML) models and analytics to perform training and develop a policy for the Near-RT RIC.
💡 Conclusion: Open RAN represents a flexible way forward, but it needs guardrails
The promise of Open RAN lies in its potential efficiency, agility and innovation in the space of 5G RAN, but Open RAN is not a panacea. It is up to telecommunications professionals to design networks that achieve the synergy of developing on the Open RAN architecture and the security reliability of the 3GPP standards families.
To help network operators and integrators, the way forward should include:
Tactical vendor selection
RIC governing structure
API security framework
Edge-native orchestration models
Once network operators, integrators and telecommunications professional understand how Open RAN is layered while weighing trade-offs, they can deploy Open RAN with confidence amidst performance and security risk.
📖 Conclusion: Open RAN is transforming the 5G market environment
The now-prophetic journey from traditional 3GPP RAN architectures to the revolutionary open and interoperable O-RAN systems is not only a technology change, but a strategic change and as global telecommunications operators realize the benefits of virtualization, software-defined networking and human-like automation, Open RAN offers more than an opportunity that benefits operators: it also offers benefits of lower costs, increased agility and vendor diversification.
However, this opportunity has disadvantages: complexity in security, integration of legacy technologies, standardized testing and orchestration layers . Telecommunications professionals must weigh humanity's desire for innovation against reputable diligence in the process of constructing a secure, scaled network that can seamlessly provide agile service to any new advancements and/or emerging 5G services from ultra-low latency industrial IOT to cloud-native edge services.
✒️SEO Summary
📌SEO Title:
Open 5G RAN Architecture Demystified: Opportunities, Obstacles & Comparison of 3GPP & O-RAN
📌Excerpt (less than 250 characters):
Deep dive into the opportunities, risks and architectural demarcation of Open RAN & 3GPP in 5G as it relates to RIC, CU-DU splits and open interfaces shaping the next-generation mobile systems.
📌Meta Description (less than 160 characters):
Learn about Open RAN and 3GPP architecture and use cases, interfaces, security risks, and future of telecommunication technology innovation.
✅Suggested Keywords for SEO Optimization:
Open RAN architecture
5G RAN split
3GPP CU DU
O-RAN Alliance
RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC)
5G xApps
Open vs. traditional RAN
5G network security
O-RU, O-DU, O-CU
Near-RT RIC and Non-RT RIC
Service Management and Orchestration (SMO)
📌Suggested Next Steps for Readers:
If you are a network architect, systems engineer or telecom strategist, do the following:
Evaluate Open RAN vendors who offer solutions aligned with your deployment and milestoning those vendors towards milestone deliverables responsibly
Build a RIC/xApp development laboratory utilizing and ONAP architecture with open source simulators and characterizing the proxy as a development simulator variation
Join the O-RAN Alliance to keep stakeholders on track, with testbeds and new specifications that will be regularly released as budgets allow
Attend industry events such as MWC or 5G World Summit to collaboratively engage with the emerging O-RAN community.
