PDCP Duplication in 5G: Carrier Aggregation & Dual Connectivity

Introduction
In the realm of 5G networks, having reliability, low latency, and high throughput is essential for supporting advanced applications like autonomous driving, critical IoT functions, AR/VR, and industrial automation. A key player in meeting these tough standards is the Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP) Duplication.
This approach entails sending out duplicate versions of PDCP Protocol Data Units (PDUs) through various transmission paths. By duplicating data packets at the PDCP level, the network guarantees that if one pathway faces packet loss, the backup still gets to the user equipment (UE), thus preserving the integrity and reliability of the data.
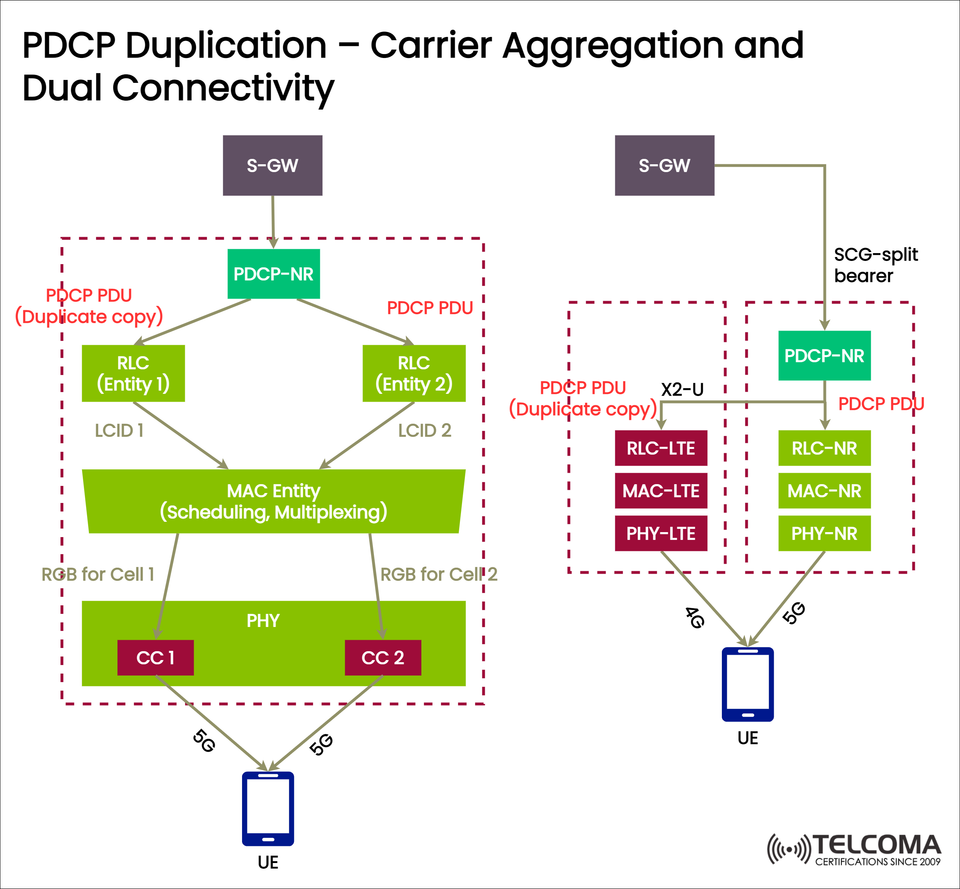
The accompanying diagram showcases two scenarios:
Carrier Aggregation (CA) within a single g NB (5G base station).
Dual Connectivity (DC) connecting LTE and NR (5G New Radio).
Now, let’s dive into these concepts and see why they're important for the next generation of telecom networks.
What is PDCP Duplication?
PDCP (Packet Data Convergence Protocol) is a layer in the 5G protocol stack that handles several tasks like header compression, ciphering, integrity protection, and, in this case, packet duplication.
Duplication Mode: When it's turned on, PDCP creates and sends duplicate copies of the same PDU over different radio bearers or carriers.
Reliability Assurance: If one connection hits a snag—like errors or packet drops—the duplicate ensures that the data still reaches the UE without the annoying delays of retransmission.
Target Use Cases: This is particularly useful for Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC), smart factories, connected vehicles, healthcare applications, and real-time AR/VR.
PDCP Duplication with Carrier Aggregation
In Carrier Aggregation (CA), multiple component carriers (CCs) from the same g NB come together to boost bandwidth and throughput.
How it works (as shown in the diagram):
A PDCP-NR entity gets data from the serving gateway (S-GW).
It generates two copies of the PDCP PDU: one original and one duplicate.
These copies get sent to two Radio Link Control (RLC) entities, each linked to a different Logical Channel ID (LCID).
The MAC (Medium Access Control) entity oversees scheduling and multiplexing between carriers.
Each carrier (CC1 and CC2) sends data to the UE.
The UE receives info across multiple carriers (both in 5G), which boosts reliability and cuts down on latency.
Key Benefits in Carrier Aggregation:
Increased data speeds thanks to combined bandwidth.
Greater reliability from duplicated PDUs across carriers.
Smooth transmission without needing multiple g NBs.
PDCP Duplication with Dual Connectivity
Dual Connectivity (DC) lets a UE connect to two different base stations at the same time: a Master g NB (Mg NB) and a Secondary g NB (Sg NB). In LTE-NR dual connectivity, one link is LTE and the other is 5G NR.
How it works (again, based on the diagram):
The S-GW sends data to the PDCP-NR entity.
The PDCP entity duplicates the PDUs.
One copy travels through the LTE stack (RLC-LTE, MAC-LTE, PHY-LTE).
The other copy moves through the NR stack (RLC-NR, MAC-NR, PHY-NR).
Both routes (4G and 5G) deliver packets to the UE.
The UE processes whichever packet shows up first, ensuring reliability.
Key Benefits in Dual Connectivity:
Utilizes different radio technologies (LTE + NR).
Guarantees continuity during mobility scenarios (like handovers).
Boosts coverage by taking advantage of LTE’s broad availability alongside NR’s higher capacity.
Offers redundancy by sending duplicates over different RATs (Radio Access Technologies).
PDCP Duplication: Technical Advantages
PDCP Duplication isn’t just about redundancy; it’s a strategic facilitator for achieving 5G performance goals.
Benefits at a glance:
Reliability: Ensures packet delivery, even in challenging radio conditions.
Low Latency: Dodges retransmission delays by guaranteeing packets come through at least one path.
Throughput Boost: Leverages the advantages of multiple carriers or radio technologies.
Mobility Support: Smooths out handovers between LTE and NR cells.
URLLC Enablement: Meets strict latency and reliability needs for critical applications.
PDCP Duplication in Action: Carrier Aggregation vs Dual Connectivity
Let’s quickly compare how PDCP duplication works in both methods:
Feature Carrier Aggregation (CA)Dual Connectivity (DC)Network Nodes Single g NB Multiple nodes (LTE e NB + 5G g NB)Carriers/Technologies Multiple 5G NR carriers LTE + NR (mixed)Duplication Path Across component carriers Across different RATs (4G & 5G)Primary Goal Enhance throughput and reliability Boost mobility, coverage, and reliability Latency Handling Low latency due to intra-g NB operation Low latency by using parallel 4G/5G paths Use Case Fit High-capacity scenarios within a 5G cell Mobility and coverage-critical applications
Real-World Applications of PDCP Duplication
Autonomous Vehicles: Ensures continuous connectivity and ultra-reliable data exchange to avoid accidents.
Remote Surgery: High reliability to prevent data packet loss during critical surgeries.
Industrial Automation: Machinery communicates with almost zero downtime in smart factories.
AR/VR and Gaming: Provides seamless experiences without lag or packet loss.
Public Safety Networks: Guarantees reliable communication during emergencies.
Challenges and Considerations
Even though PDCP duplication brings plenty of benefits, it does come with some challenges:
Resource Overhead: It doubles the packet transmissions, leading to more radio resource usage.
Energy Consumption: UEs use more power because of processing duplicate packets.
Network Optimization: It needs smart scheduling to avoid unnecessary duplication.
Latency Management: We have to ensure that duplicate copies don’t slow down processing at the UE.
Operators must weigh the perks of duplication against these challenges, only enabling it for services that truly need ultra-reliability.
Conclusion
PDCP Duplication is a crucial component in 5G’s mission to deliver ultra-reliable, low-latency communication (URLLC). By sending duplicate packets through various carriers (Carrier Aggregation) or diverse technologies (Dual Connectivity), it makes sure that vital data arrives at its destination quickly and reliably.
In Carrier Aggregation, duplication boosts reliability within a 5G cell by spreading packets across component carriers.
In Dual Connectivity, duplication taps into both LTE and 5G at the same time, providing advantages in robustness, coverage, and mobility.
As we see 5G networks grow and new applications come into play, PDCP duplication will remain essential in building a strong, high-performance telecom environment.
