PNMS Remote Management: Centralized Control for Private 5G in Enterprises

PNMS Remote Management: Centralized Control for Private 5G in Enterprises
The growth of private 5G networks has unlocked fresh opportunities for businesses in sectors like healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing. These networks provide dedicated spectrum, ultra-low latency, and secure connectivity that's tailored to the specific needs of businesses. However, managing these complex systems efficiently, especially on a large scale, can be a real challenge for enterprises.
That's where PNMS (Private Network Management System) remote management comes in—a solution that enables centralized management of various enterprise networks from a single location while keeping secure control at the local level.
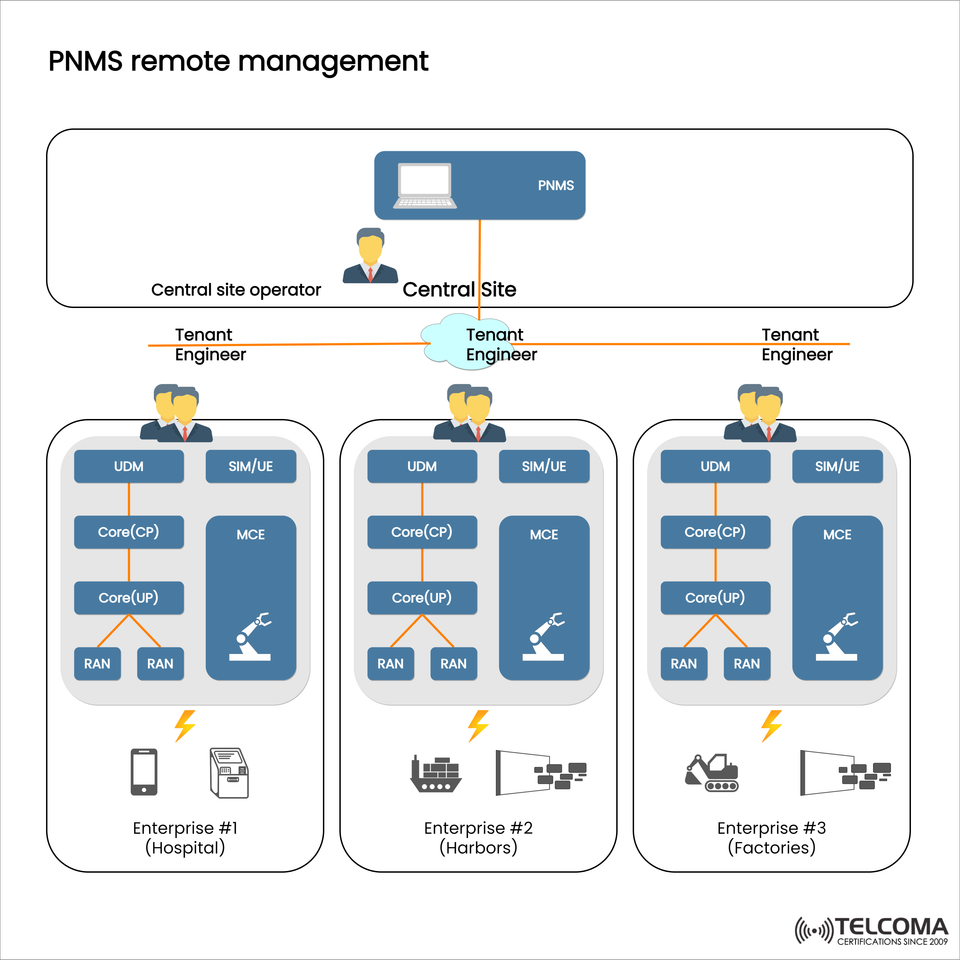
The diagram you shared outlines this model: a central site operator runs PNMS and manages multiple tenants such as hospitals, ports, and factories, with each having its own tenant engineers looking after local operations. Let’s dive into the details.
What is PNMS Remote Management?
PNMS (Private Network Management System) serves as a centralized hub that provides oversight, control, and orchestration of several private 5G networks. A central operator can remotely monitor multiple enterprise sites, while each site has a tenant-specific engineer for everyday support.
This hybrid approach strikes a balance between centralized efficiency and localized autonomy, ensuring both strong performance and compliance with the unique needs of each enterprise.
Key Components in PNMS Remote Management
The diagram highlights the building blocks of PNMS used across enterprises:
Central Site Operator: Manages PNMS remotely to maintain consistency.
Tenant Engineer: Offers local expertise and handles troubleshooting and customization for specific needs.
Core (CP/UP): Control plane (CP) and user plane (UP) functions for private 5G core.
RAN (Radio Access Network): Supplies wireless connectivity to SIMs and user equipment (UE).
UDM (Unified Data Management): Manages subscriber and policy data.
SIM/UE: End devices, ranging from medical equipment to IoT sensors.
MCE (Mobile Core Edge): Provides low-latency processing and application hosting at the edge of the enterprise.
Together, these components ensure end-to-end private 5G orchestration that's tailored to each enterprise tenant.
How PNMS Works in Multi-Tenant Environments
Centralized Oversight
The central operator leverages PNMS to monitor, configure, and troubleshoot multiple private 5G networks from a distance.
Policies, updates, and performance reports flow seamlessly among tenants.
Tenant-Specific Operations
Every enterprise location (like a hospital, port, or factory) has its own tenant engineer to supervise local infrastructure.
This engineer ensures smooth operation of RAN, core, and MEC applications.
Seamless Integration
PNMS connects central management with tenant engineers while keeping tenant operations isolated.
This approach guarantees security, compliance, and SLA commitments across various industries.
Benefits of PNMS Remote Management
- Centralized Efficiency
Cuts down operational costs by consolidating monitoring and control onto a single platform.
Speeds up the rollout of patches, updates, and policies throughout all tenants.
- Scalability
Enterprises can easily scale their private 5G setups without needing to redo management workflows.
Central operators are capable of supporting a range of industries at once.
- Security and Compliance
Tenant isolation guarantees data privacy.
Central oversight allows for early detection of any issues.
- Enterprise-Specific Flexibility
Hospitals emphasize patient safety and device reliability.
Ports aim for efficiency in logistics.
Factories demand reliable networking for their robotics.
PNMS effectively supports these diverse needs within a unified framework.
Industry Applications of PNMS Remote Management
The diagram presents three industry examples:
- Hospitals (Enterprise #1)
Use Case: Safely managing interconnected medical devices, patient monitoring systems, and augmented reality-assisted surgeries.
PNMS Advantage: Enables remote updates and SLA monitoring without interfering with critical medical functions.
- Harbors (Enterprise #2)
Use Case: Coordinating autonomous cranes, tracking cargo, and enhancing logistics security.
PNMS Advantage: Provides centralized oversight across multiple terminals while allowing local engineers to manage specific issues.
- Factories (Enterprise #3)
Use Case: Supporting robotics, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and machine-to-machine communication with low latency.
PNMS Advantage: Integrates TSN (time-sensitive networking) with MEC at the edge, all monitored remotely.
PNMS Architecture Explained
The PNMS architecture combines centralized and distributed elements:
Central Site PNMS: Orchestrates policies, gathers telemetry, and manages tenant-level SLAs.
Tenant Engineers: Serve as the human interface for enterprise-specific customization.
Enterprise Networks: Each tenant operates its own:
RAN (radio coverage for devices and sensors)
Core CP/UP (routing, mobility management, authentication)
UDM & SIM/UE (subscriber data and devices)
MCE (edge computing for low-latency applications)
This layered architecture allows for responsibility separation: the central site operator manages shared functions while tenant engineers focus on industry-specific needs.
Why PNMS is Essential for Private 5G
Private 5G networks can be complicated. Each enterprise typically needs:
Reliable connectivity for critical operations.
Edge computing for real-time applications.
Security and isolation to safeguard sensitive information.
Customization to match industry workflows.
PNMS addresses these requirements by providing:
Remote control without sacrificing autonomy.
Multi-tenant orchestration suited for large-scale deployments.
Operational efficiency through centralized visibility.
Without PNMS, businesses could face fragmented management, rising costs, and operational inefficiencies.
Comparing Centralized vs. Decentralized Management
Feature Centralized PNMS Decentralized (No PNMS)Scalability High, supports many tenants Limited, site-specific Operational Efficiency Centralized monitoring and updates Redundant management overhead Security Consistent policies across tenants Risk of inconsistent security Customization Local tenant engineers tailor needs Fully local, harder to standardize Cost Lower through consolidation Higher due to duplication
Clearly, centralized PNMS remote management offers better scalability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Challenges in PNMS Remote Management
While PNMS has its perks, there are still some hurdles to overcome:
Integration with legacy systems – Some enterprises still depend on older technology.
Training tenant engineers – It's essential to have skilled staff at each site.
Data privacy issues – Central operators must ensure strict separation between tenants.
Latency in remote control – Essential operations may still need local autonomy.
Tackling these challenges involves strong SLAs, standardized processes, and a secure multi-tenant architecture.
The Future of PNMS in 5G and Beyond
As industries move towards Industry 4.0 and beyond, PNMS is set to become even more critical:
AI-Driven PNMS: Using predictive analytics for proactive troubleshooting.
Zero-Touch Automation: Enabling fully automated policy rollouts with minimal human involvement.
Edge-AI Integration: Facilitating real-time decision-making closer to enterprise locations.
6G Ready PNMS: Developing platforms that can handle advanced 6G technologies like holographic communications.
PNMS will continue to be the central nervous system for private networks in enterprises, evolving alongside telecommunications standards.
Conclusion
PNMS remote management is fundamental to creating scalable, secure, and efficient private 5G operations. By blending centralized oversight with tenant-level autonomy, PNMS empowers sectors like hospitals, ports, and factories to operate crucial applications with confidence.
For professionals in telecom, PNMS is more than just a management tool—it’s a strategic enabler for Industry 4.0. Enterprises looking to adopt private 5G on a large scale need to embrace PNMS for reliable, secure, and future-ready operations.
