Potential Distribution of 5G Use Cases Across Humans and Machines
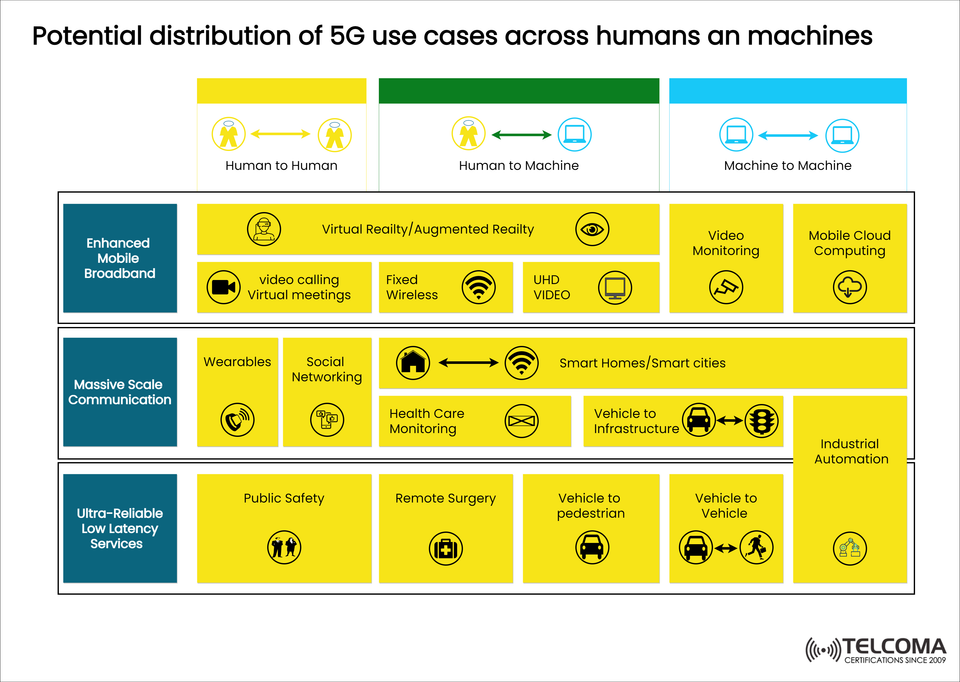

The 5G era is changing the way we connect, bringing in capabilities that go way beyond just faster internet. Unlike previous generations, 5G is built to handle different types of communication: human-to-human, human-to-machine, and machine-to-machine. Each of these interactions unlocks new possibilities, from engaging virtual meetings to remote surgeries and smarter industrial processes.
This blog post dives into the variety of 5G use cases involving both humans and machines, organized into three service categories: Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC), and Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (URLLC).
Communication Models in 5G
- Human-to-Human (H2H)
This area covers the classic realm of telecommunications but with a fresh perspective.
5G improves how we connect with:
Video calls & virtual meetings featuring ultra-high-definition video.
Social media interactions supported by quicker data speeds.
Virtual and augmented reality experiences shared between users.
- Human-to-Machine (H2M)
In this model, people engage with connected tools, wearables, or IoT systems:
Remote health monitoring through wearables.
Smart homes where users can manage appliances, security, and energy use.
Vehicle-to-infrastructure communication that facilitates smarter transport solutions.
- Machine-to-Machine (M2M)
This is where the IoT revolution really takes off, with devices talking to each other on their own:
Industrial automation systems that sync in real time.
Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication for self-driving cars.
Smart city setups that oversee traffic, utilities, and safety.
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) Use Cases
eMBB showcases the most obvious advancements of 5G: better, more dependable, and high-capacity connections. It enables experiences that were once thought to be impossible.
Virtual Reality (VR) & Augmented Reality (AR): Immersive experiences for gaming, online learning, and corporate training.
Video calls and virtual meetings: Smooth, high-def, and lag-free conferencing for global teamwork.
Fixed Wireless Access (FWA): Reliable wireless alternatives to fiber broadband, especially in areas that lack service.
UHD Video Streaming: Smooth delivery of 4K/8K content.
Video Monitoring: Instant surveillance in smart cities and businesses.
Mobile Cloud Computing: Accessing cloud-based applications and computing power while on the move.
Key takeaway: eMBB enhances human-to-human communication and boosts human-to-machine interactions with unmatched speed and quality.
Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC) Use Cases
mMTC tackles the challenge of efficiently and securely connecting billions of IoT devices. Its impact is felt across various industries and communities.
Wearables: Health trackers and other devices giving real-time health info.
Networking between devices: Tying together personal gadgets and IoT systems.
Healthcare monitoring: Keeping tabs on patients remotely to cut down on hospital visits.
Smart Homes and Smart Cities: IoT-powered solutions for energy savings, safety, and comfort.
Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I): Smart traffic signals and features for road safety.
Industrial Automation: Factories that use connected sensors and robotics for smarter production processes.
Key takeaway: mMTC drives the IoT boom by allowing scalable, dependable, and secure connections among humans, machines, and devices.
Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (URLLC) Use Cases
URLLC is the most crucial and mission-focused element of 5G, providing ultra-low latency (down to 1 ms) and high reliability. This is where interaction between humans and machines, as well as machine-to-machine communication, can truly shine.
Public Safety: Emergency systems, real-time monitoring, and crisis management.
Remote Surgery: Surgeons handling robotic tools from thousands of miles away with no noticeable delay.
Vehicle-to-Pedestrian (V2P): Keeping pedestrians safe with connected cars and smart crosswalks.
Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V): Preventing collisions and enabling cooperative driving.
Industrial Automation: Factories managing critical tasks where downtime isn't an option.
Key takeaway: URLLC supports life-saving, mission-critical applications where reliability and speed are absolutely essential.
Distribution of 5G Use Cases: Humans and Machines
The diagram included shows how 5G use cases are spread out among human-to-human, human-to-machine, and machine-to-machine communications.
Communication Type Example Use Cases5G Service Category Human-to-Human Video calls, AR/VR, social networking eMBB Human-to-Machine Healthcare monitoring, smart homes, wearable smMTC, URLLC Machine-to-Machine Industrial automation, V2V, V2I communication mMTC, URLLC
This layered perspective shows that 5G isn't a one-size-fits-all solution but a platform capable of meeting a wide array of needs.
Strategic Implications for Telecom Operators
For those in telecom, grasping the distribution of 5G use cases is vital. Operators should:
Invest in Network Slicing: Tailor networks for eMBB, mMTC, and URLLC needs.
Boost Security: Protect sensitive applications like healthcare and V2X communications.
Support Edge Computing: Set up infrastructure closer to users for ultra-low latency.
Collaborate Across Industries: Team up with healthcare, manufacturing, and automotive sectors to tap into 5G’s full potential.
Categories of 5G Services
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB):
Virtual and augmented reality experiences
Ultra-high-definition video streaming
Fixed wireless internet access
Video calls and remote teamwork
Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC):
Internet of Things (IoT) wearables
Smart homes and cities
Vehicle-to-infrastructure communication
Automation in industrial settings
Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (URLLC):
Remote surgical procedures
Vehicle-to-vehicle safety systems
Emergency services applications
Real-time factory management
Conclusion
The potential distribution of 5G use cases across humans and machines really highlights the transformative power of this technology. Whether it's facilitating engaging human-to-human connections or driving self-sufficient machine-to-machine communications, 5G is paving the way for innovation in every field.
As telecom leaders, developers, and businesses harness eMBB, mMTC, and URLLC, they’re building the groundwork for a hyper-connected world where humans and machines work together seamlessly.
In short, 5G is more than just faster internet—it’s about reshaping connectivity for the future of society, industry, and daily life.
