Private 5G Network Integrated with Operator Network: Architecture, Benefits, and Use Cases

Integrated Private Network with Operator Networks: A Practical Guide
The trend toward private 5G networks is really picking up across various sectors like smart manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and energy. Some companies go for fully independent private networks, but others are leaning toward a model that merges their private infrastructure with operator networks.
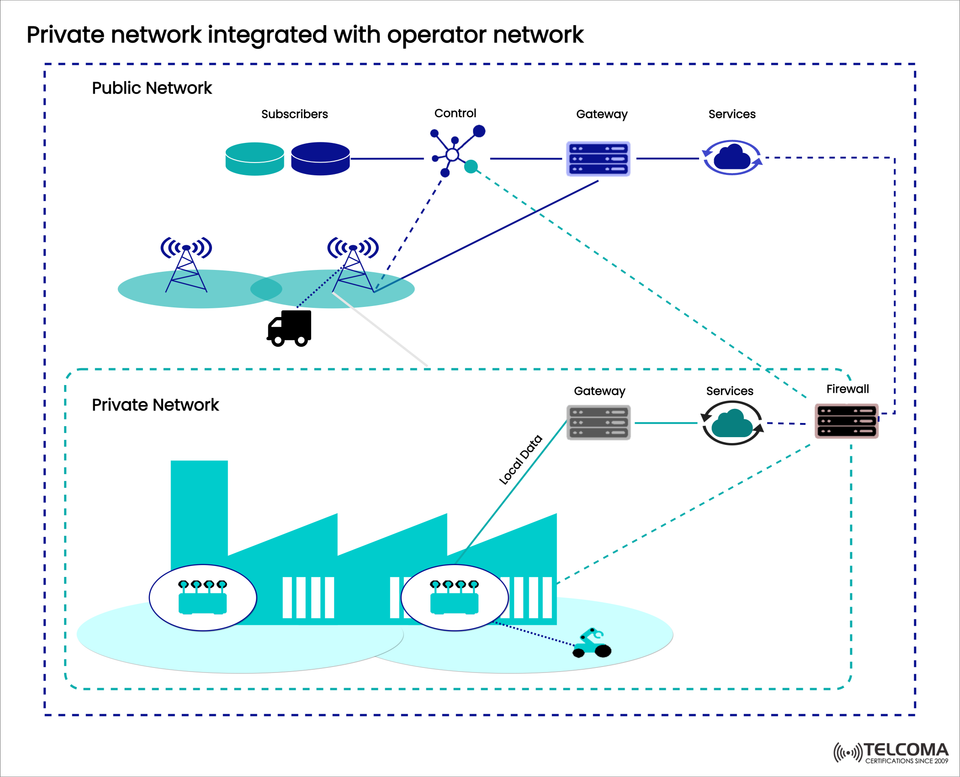
This blend allows businesses to keep their data secure and under control while enjoying the benefits of coverage, scalability, and subscriber management offered by public operator networks. The diagram provided shows this hybrid setup, where private and public networks are linked for better performance.
In this article, we’ll unpack the architecture, key benefits, technical challenges, and enterprise use cases related to integrated private 5G networks.
Understanding the Integrated Private 5G Architecture
The diagram outlines two linked areas:
- Public Network (Managed by Operators)
Subscribers: A central database to handle SIM or device authentication and management.
Control Plane: Manages mobility, session handling, and policy implementation.
Gateway: Connects users to services hosted on the operator network.
Services: Cloud-based apps or internet services from the operator.
- Private Network (Managed by Enterprises)
Subscribers: Devices specific to the enterprise, like robots, sensors, and IoT items.
Local Gateway: Handles local breakout traffic to keep sensitive data within the enterprise.
Services: Internal applications like robotics management, predictive maintenance, and automation systems.
Firewall: Safeguards private workloads while optionally allowing connections to public services.
Integration Layer
The control plane of the public operator works alongside private gateways.
Companies can decide which data routes stay local and which go through the operator’s core.
This split-control model combines the security of private 5G with the scale of operator-managed networks.
Why Integrate Private 5G with Operator Networks?
Businesses are integrating private and public 5G to take advantage of the best of both worlds. Here are the main benefits:
- Better Security with Local Data Control
Sensitive data remains within the enterprise firewall.
Local gateways make sure mission-critical information (like robotics or IoT data) stays on-site.
- Smooth Mobility Across Public and Private Areas
Devices can switch between enterprise locations and the public operator’s network.
This is perfect for industries like logistics, transport, and supply chain, where employees often move between zones.
- Lower Deployment Costs
Businesses don’t have to invest in the entire 5G core stack.
They can rely on operator-provided subscriber management, control plane, and RAN infrastructure.
- Scalability and Flexibility
It's simple to add more subscribers or extend services with the operator’s help.
Companies can use a pay-as-you-grow model rather than making a hefty upfront investment.
- Guaranteed Quality of Service (QoS)
Operators offer end-to-end QoS policies that extend from public RAN to private gateways.
This ensures ultra-low latency for industrial automation and other critical tasks.
Key Use Cases of Integrated Private 5G
This setup shines in situations where data security aligns with mobility needs:
Smart Manufacturing: Robots and IoT devices rely on private 5G for local control while engineers can access operator services.
Logistics & Warehousing: Trucks and forklifts stay connected via the operator’s RAN, while automation in warehouses operates on the private network.
Healthcare: Patient data remains secure within private infrastructure, but public 5G supports telemedicine and roaming across hospital networks.
Smart Cities: Utilities, surveillance systems, and IoT sensors are kept private, while operator-managed connections provide roaming and scalability.
Comparison: Integrated vs. Independent Private 5G
Feature Integrated Private 5GIndependent Private 5GControlShared with operator Full enterprise control Data Security Local breakout + shared Fully isolated Deployment Cost Medium (shared infra)High (dedicated infra)Mobility Seamless roaming Limited to private domain Scalability High (operator-backed)Medium (site-specific)Customization Medium High
Technical Challenges
While the integration sounds appealing, there are also hurdles to consider:
Interoperability: Making sure the operator’s control plane and private gateways work together smoothly.
Policy Alignment: Syncing the enterprise's specific QoS with the service levels set by the operator.
Security Boundaries: Managing firewall settings and preventing data leaks between shared interfaces.
Vendor Lock-In: Relying heavily on one operator may limit flexibility.
Best Practices for Deployment
To get the most out of integrated private 5G, enterprises should:
Establish Clear Data Policies: Decide what data should stay local and what can go through operator networks.
Work Together on SLA Design: Make sure operators commit to guarantees on latency, throughput, and availability.
Plan for Interoperability: Use standardized interfaces (3GPP-compliant) to steer clear of vendor lock-in.
Install Robust Firewalls: Ensure proper boundaries between public and private domains.
Why This is Effective (SEO & Audience Approach)
Keyword Targeting: We cover various terms like "independent private 5G," "integrated private 5G," and "RAN sharing" in each post.
Interlinking: This strengthens our authority and boosts SEO rankings since Google recognizes the series as a cohesive cluster.
Audience Journey:
Beginners can kick things off with the overview.
Engineers and decision-makers can dive into the more detailed posts.
For CTOs, we provide articles focused on comparisons and trends.
Conclusion
Integrating private 5G with operator networks is a smart compromise between fully independent private implementations and entirely public operator-managed solutions.
It offers:
Security through local data control
Scalability and seamless mobility by leveraging operator resources
Cost efficiency compared to isolated private deployments
For businesses looking for a balance among control, cost, and connectivity, this approach is a flexible and scalable option for private 5G adoption.
As industries continue to evolve, integrated private 5G networks are likely to become the cornerstone of digital transformation, enabling firms to confidently embrace Industry 4.0, IoT, and critical connectivity.
