Pseudo Random Time Hopping System Explained: Secure Wireless Communication

Pseudo Random Time Hopping System: Boosting Wireless Security
As wireless communication systems develop, data security and managing interference have become really important. Today’s networks need to support billions of devices while making sure they’re well-protected against eavesdropping and jamming. One of the best ways to tackle this issue is by using pseudo random time hopping systems.
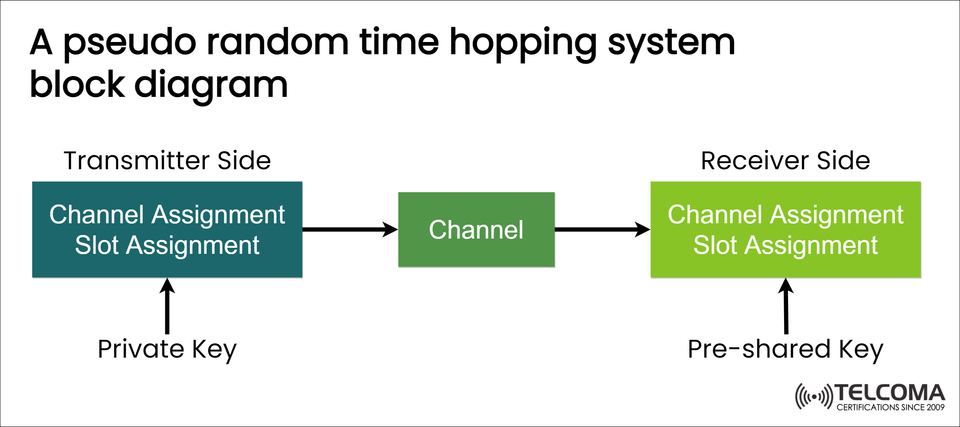
The image shows a block diagram of a pseudo random time hopping system, which illustrates how secure communication is created between a transmitter and a receiver through channel assignment, slot assignment, and cryptographic keys.
In this blog, we’ll break down how the system works, step by step, and dive into its technical foundation and why it matters to tech enthusiasts and telecom professionals alike.
What is Pseudo Random Time Hopping?
Time hopping is a spread spectrum technique that sends data over different time slots in a pseudo-random fashion. Unlike fixed time-slot communication, which can be predictable, hopping spreads the signal across various slots, making it tougher for intruders to intercept or jam the signal.
When you combine time hopping with pseudo random sequences, only those authorized and who share a cryptographic key can make sense of the communication. This adds a strong layer of security to wireless communications.
Key Characteristics:
Anti-jamming: Random slot selection stops targeted interference.
Security: Only users with the right key can sync up the hopping patterns.
Efficiency: It boosts spectral efficiency by reducing collisions.
System Architecture: A Block Diagram Overview
The provided image gives a simple block diagram of a pseudo random time hopping system, showcasing both transmitter and receiver operations.
The main components include:
Transmitter Side
Communication Channel
Receiver Side
Let’s take a closer look at each part.
- Transmitter Side
On the transmitter end, two key processes take place: channel assignment and slot assignment, both controlled by a private key that ensures randomness and security.
Channel Assignment: Chooses which frequency channel to use.
Slot Assignment: Decides the time slot for transmission.
Private Key: A unique cryptographic key that generates pseudo random sequences for hopping.
The transmitter relies on this private key to determine when and at what frequency to send data packets.
Channel
The channel is essentially the medium through which the data travels. It can be:
Wireless Spectrum: For example, radio frequencies like those used in 4G/5G, Wi-Fi, or Bluetooth.
Optical Spectrum: This includes infrared or laser communication.
Because the signal hops across different slots randomly, the channel becomes resistant to interference and eavesdropping. Even if a bad actor tries to capture the data, they can’t predict the hopping sequence without the private key.
- Receiver Side
The receiver's structure is pretty much a mirror of the transmitter’s, handling channel assignment and slot assignment with a pre-shared key.
Pre-shared Key: This key is securely shared between the transmitter and receiver before they start communicating.
Synchronization: The receiver uses this key to align with the transmitter’s hopping pattern.
Decoding: Data packets can only be pulled in successfully if the hopping sequence matches.
This setup makes sure that only the authorized receivers can decipher the transmitted messages.
How Pseudo Random Time Hopping Works
Here’s a simplified rundown of the operations:
Key Initialization: The transmitter and receiver agree on a pre-shared key.
Pseudo Random Generation: The transmitter uses its private key to create random slot assignments.
Transmission: Data is sent through the randomly assigned slots and channels.
Reception: The receiver, with the pre-shared key, anticipates the hopping sequence and retrieves the correct packets.
Advantages of Pseudo Random Time Hopping Systems
- Security
Stops eavesdropping because unauthorized parties can’t guess the hopping patterns.
Strong cryptographic integration guarantees confidentiality.
- Anti-Jamming
If a jammer disrupts one slot, data can keep flowing through another slot.
Increases resilience against denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
- Spectrum Efficiency
Reduces collisions in crowded frequency areas.
Dynamically optimizes channel usage.
- Reliability
Guarantees reliable communication even in noisy environments.
Ideal for mission-critical systems like defense, healthcare, and IoT.
Applications of Pseudo Random Time Hopping
This technique is used widely in secure and high-reliability communication systems:
Military Communication: Provides secure and jam-resistant communication in the battlefield.
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN): Allows for energy-efficient and interference-resistant data transfer.
Bluetooth Technology: Uses frequency and time hopping for secure short-range communication.
5G and Beyond: Helps make networks more resilient against cyber threats.
Medical Devices: Ensures secure transmission of patient data in wireless body area networks (WBANs).
Comparison: Traditional vs. Pseudo Random Time Hopping
Feature Traditional Fixed Slot Pseudo Random Time Hopping Security Low – predictable High – unpredictable Resistance to Jamming Weak Strong Spectral Efficiency Limited Improved Implementation Complexity Simple Moderate Use Cases Legacy telecom, IoT Military, 5G, Secure IoT
Challenges in Implementation
While pseudo random time hopping is powerful, it does come with some challenges:
Synchronization Overhead: The transmitter and receiver need to stay perfectly in sync.
Complex Key Management: Distributing pre-shared keys securely can be tricky in larger networks.
Computational Load: Generating random sequences takes processing power, which might strain low-energy IoT devices.
Latency: Hopping can introduce small delays in time-sensitive applications.
Future of Time Hopping Systems
The future of secure wireless communication lies in blending pseudo random time hopping with new technologies:
5G & 6G Networks: Enhancing ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC).
Quantum Cryptography: Pairing with quantum key distribution for unbreakable security.
Artificial Intelligence: Using AI for real-time optimization of hopping.
Massive IoT: Ensuring secure communication for billions of connected devices.
Conclusion
The pseudo random time hopping system provides a secure and robust method for wireless communication. By combining channel and slot assignment with cryptographic keys, it shields against eavesdropping, jamming, and data interception.
For telecom professionals and tech enthusiasts, this model is key to understanding the modern secure communication frameworks used in Bluetooth, 5G, IoT, and defense systems.
As networks keep expanding in scale and complexity, pseudo random time hopping will stay a fundamental part of secure, interference-free communication.
