RAN1 Release 17 Explained: 5G Enhancements, Timeline, and Key Features

The growth of 5G New Radio (NR) is largely dependent on the ongoing efforts of 3GPP RAN1 — the group that deals with the physical layer specifications, radio features, and waveform improvements. With Release 17, RAN1 has rolled out some important updates that push 5G capabilities beyond just smartphones. This opens the door for new applications like satellite IoT (NTN), XR services, low-complexity devices, and advanced industrial IoT.
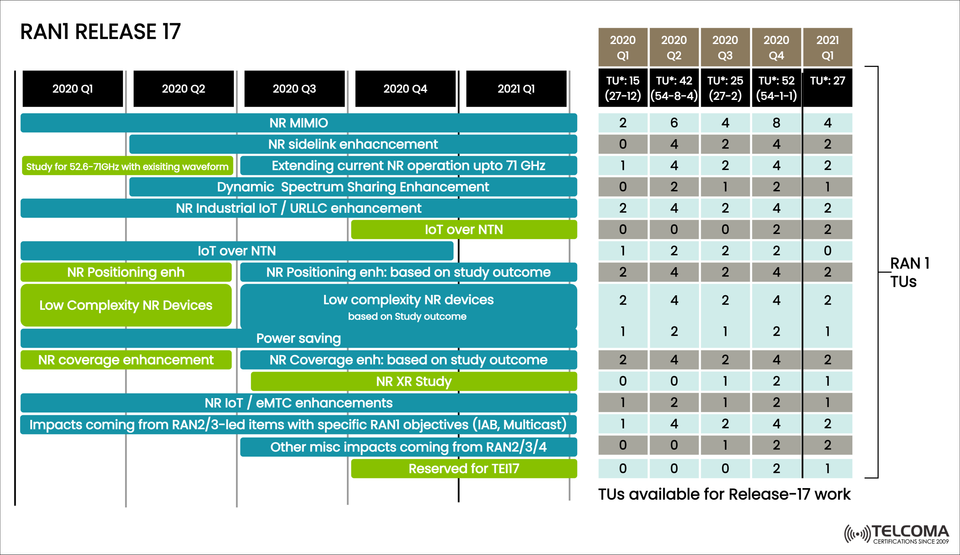
The image we've uploaded shows a timeline of RAN1 activities in Release 17 (2020–2021), highlighting key improvements, studies, and technical unit (TU) allocations. Let’s dive into these milestones and what they mean for the telecom landscape.
Key Enhancements in RAN1 Release 17
RAN1's activities in Release 17 focus on boosting coverage, capacity, efficiency, and use cases. Here’s a rundown of the major updates and why they matter:
- Massive MIMO Enhancements (NR MIMO)
Better beamforming and spatial multiplexing.
Improved performance in dense urban areas and high-frequency ranges.
Increases capacity and spectrum efficiency.
- Sidelink Enhancements
Enhances device-to-device (D2D) communication.
Important for vehicle-to-everything (V2X) and public safety applications.
Supports advanced cooperative driving and autonomous tech.
- Spectrum Expansion up to 71 GHz
Allows NR operation to go beyond 52.6 GHz, up to 71 GHz.
Opens new spectrum for ultra-high data rate services.
Facilitates future applications like immersive XR and industrial automation.
- Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) Enhancements
Aids coexistence between 4G LTE and 5G NR.
Eases the transition for operators launching 5G on existing LTE spectrum.
- Industrial IoT and URLLC Improvements
Boosts reliability and reduces latency for mission-critical scenarios.
Assists automation in industries like manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare.
- IoT over Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN)
Supports satellite-based 5G IoT connectivity.
Extends coverage to remote, maritime, and rural locations.
Vital for disaster recovery and global IoT solutions.
- NR Positioning Enhancements
Improves accuracy to sub-meter levels.
Great for indoor navigation, asset tracking, and AR/VR applications.
Based on study results, this paves the way for next-gen location-based services.
- Low Complexity NR Devices (RedCap)
Simplifies design and cuts costs for 5G devices.
Focuses on wearables, industrial sensors, and smart utility meters.
Supports longer battery life and reduced device costs.
- Power Saving Enhancements
Energy-efficient designs for IoT and battery-operated devices.
Key for sustainability and long-term IoT applications.
- Coverage Enhancements
Enhances 5G coverage in challenging environments (like indoors and rural areas).
Ensures more reliable connectivity for users.
- Extended Reality (XR) Study
Looks into the needs for AR/VR/MR services.
Aims to optimize latency, jitter, and throughput for immersive experiences.
- IoT / eMTC Enhancements
Expands 5G’s connection with legacy IoT technologies (like LTE-M and NB-IoT).
Ensures industries invested in LTE IoT can keep moving forward.
Timeline of RAN1 Release 17
The chart outlines how activities were distributed throughout 2020 and early 2021.
Q1 2020: * Focus on NR MIMO, IoT over NTN, and positioning studies. * Preliminary work on RedCap devices and coverage improvements.
Q2 2020: * Spectrum expansion studies and sidelink enhancements pick up pace. * Work on DSS and URLLC enhancements kicks off. * TU allocation rises significantly to manage the workload.
Q3 2020: * Good progress on low complexity devices, positioning, and coverage. * The XR study gets underway. * Various impacts from RAN2/3/4 considered.
Q4 2020: * High TU allocation dedicated to finalizing sidelink, NTN, and coverage studies. * Reserved slots for TEI17 items.
Q1 2021: * Refinements based on study outcomes (positioning, low complexity devices). * Consolidation of power saving and IoT/eMTC enhancements. * Activities lead into Stage 3 work.
Impact of RAN1 Release 17
The updates in Release 17 RAN1 are set to transform the telecom industry in various ways:
For Operators: * Easier 5G coverage expansion, particularly in rural and indoor settings. * New possibilities in satellite IoT integration.
For Vendors: * Opening markets for RedCap devices and XR-compatible infrastructure. * Enhanced spectrum efficiency through DSS and MIMO improvements.
For Enterprises: * More reliable and cost-effective industrial IoT adoption. * Improved precision and reliability in location-based services.
For Consumers: * More affordable 5G wearables and IoT devices. * Better-performing XR and AR/VR services.
Understanding How RAN1 Fits into the Overall Release 17 Landscape
RAN1 is all about the physical layer (PHY) innovations, but it’s not alone. Other groups like RAN2, RAN3, and RAN4 play crucial roles in shaping the standardization effort, focusing on higher-layer protocols, architecture, and performance. To really get a grasp of Release 17, it’s important to see how these teams work together.
🔹 RAN1: Focus on the Physical Layer
This group handles aspects like radio waveforms, channel coding, modulation, and MIMO.
Their job is to make sure there’s physical connectivity, effective use of spectrum, and advanced radio techniques are in place.
Key points in Release 17 include MIMO, NTN IoT, positioning, RedCap, and XR studies.
🔹 RAN2: Focus on Radio Protocols
RAN2 defines the protocols that sit above the physical layer, including RLC, MAC, PDCP, and RRC.
They take care of scheduling, handovers, security, and making dual connectivity work smoothly.
For Release 17, some highlights are improvements in PDCP duplication, enhancements for URLLC, and better multi-RAT coordination.
🔹 RAN3: Focus on Architecture
This group specifies the interfaces that connect base stations to core networks.
They manage things like X2/Xn handovers, integrating gNB and eNB, and the dual connectivity architecture.
Key points for Release 17 include support for integrated access/backhaul (IAB), integrating non-terrestrial networks (NTN), and enhancements in OAM.
🔹 RAN4: Focus on Performance and RF Requirements
RAN4 sets the standards for RF parameters, conformance, and performance testing.
They ensure that both devices and base stations comply with spectrum regulations.
Highlights for Release 17 include expanded frequency bands, improvements in coverage performance, and better coexistence.
Conclusion
RAN1 Release 17 marks a significant milestone in the progression of 5G, bringing new dimensions in coverage, affordability, and innovation. With developments in IoT over NTN, RedCap devices, and advanced positioning and XR studies, the RAN1 team has set a solid foundation for the next wave of 5G adoption.
The clear timeline and TU allocations for Release 17 ensured that essential physical layer enhancements were primed for market readiness, paving the way for 5G-Advanced (Release 18).
For those in the telecom field, grasping the details of RAN1 Release 17 is vital, as it reflects the core radio innovations fueling the next decade of 5G expansion.
