RAN2 Release 17: Key 5G Protocol Enhancements Explained

As 5G networks continue to grow, there’s a pressing need for advanced protocol enhancements. RAN1 takes care of the physical layer (PHY), while RAN2 handles the Radio Interface Protocol architecture and functionalities above that, including MAC, RLC, PDCP, and RRC.
With the arrival of 3GPP Release 17, RAN2 rolls out a bunch of features aimed at boosting reliability, efficiency, and flexibility for various 5G use cases, like IoT, XR, URLLC, and Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN).
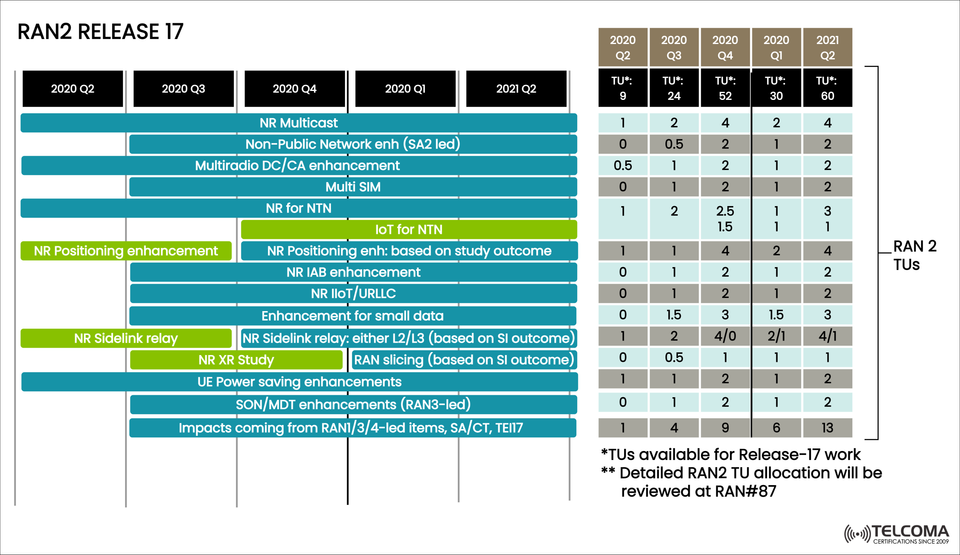
The image above gives a snapshot of the timeline and Technical Unit (TU) distribution for different RAN2 features from Q2 2020 to Q2 2021, highlighting how priorities were set and workloads shared.
Key Highlights of RAN2 Release 17
- NR Multicast
Expands support for multicast transmissions in 5G NR.
This enables smoother content delivery for things like live video streaming, software updates, and IoT signaling.
It helps ease the network load by sending the same data to multiple users at once.
- Non-Public Network Enhancements (SA2-led)
Adapts 5G features for private enterprise networks.
This is huge for industries like manufacturing, logistics, and smart cities, as it allows them to set up secure, dedicated 5G systems.
It also ensures they can connect with public networks for better mobility and coverage.
- Multiradio Dual Connectivity (DC) / Carrier Aggregation (CA) Enhancements
Boosts dual connectivity between LTE and NR, along with NR-DC.
This leads to better throughput, coverage, and spectrum efficiency.
It’s especially important for mid-band and mmWave setups, where we need to minimize coverage gaps.
- Multi-SIM Support
This enhancement improves user experience with multi-SIM devices.
It streamlines connectivity management across personal and work profiles.
It’s key for IoT gateways and devices that require dual-network subscriptions.
- NR for NTN (Non-Terrestrial Networks)
This feature brings 5G to satellite networks, expanding coverage globally.
It’s crucial for remote areas, maritime, aviation, and IoT applications.
Pairing it with “IoT for NTN” supports low-complexity devices in space networks.
- Positioning Enhancements
Builds on findings from Release 16 to offer centimeter-level positioning accuracy.
This is vital for autonomous vehicles, industrial robotics, and emergency services.
It ensures scalability across various use cases.
- NR IAB (Integrated Access and Backhaul) Enhancements
Enhances self-backhauling capabilities of 5G NR.
This enables operators to expand without heavily relying on fiber.
It adds flexibility for both dense urban and rural setups.
- NR IIoT / URLLC Enhancements
Optimizes protocols specifically for Industrial IoT (IIoT) and ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC).
Supports critical applications such as factory automation, remote surgery, and smart grid systems.
- Enhancements for Small Data Transmission
Targets the signaling overhead for IoT devices sending small, infrequent data packets.
It lowers power consumption and boosts efficiency for Reduced Capability (RedCap) devices.
- NR Sidelink Relay
Introduces UE-to-UE relaying to enhance coverage.
Supports L2/L3 relaying based on research outcomes.
It expands connectivity, especially in disaster recovery, vehicular networks, and rural areas.
- RAN Slicing Enhancements
Allows precise resource allocation across logical network slices.
This is useful for enterprise private networks, IoT sectors, and XR applications.
Based on various study results, it meets operators’ slicing needs.
- UE Power Saving Enhancements
Focuses on reducing battery drain in smartphones and IoT devices.
Improves Discontinuous Reception (DRX) cycles for better energy efficiency.
- SON/MDT Enhancements (RAN3-led)
Boosts Self-Organizing Networks (SON) and Minimization of Drive Tests (MDT).
This cuts operational costs by automating optimization and data collection for operators.
- Cross-RAN Impacts (RAN1/3/4, SA, CT, TEI17)
Ensures that features from other working groups align well.
It encompasses impacts on spectrum, architecture, and testing that feed into RAN2 protocols.
Timeline and TU Allocation
The image illustrates how RAN2 distributed Technical Units (TUs) for the features in Release 17:
Quarter | TUs Available | Key Prioritized Features
2020 Q2 | 9 | NR multicast, NR positioning, NR sidelink relay, XR study
2020 Q3 | 24 | Multiradio DC/CA, IAB, NTN, small data, power saving
2020 Q4 | 52 | RAN slicing, URLLC, XR study, NR sidelink relay
2021 Q1 | 30 | IoT for NTN, NR multicast, positioning, RAN slicing
2021 Q2 | 60 | Finalization of NR multicast, sidelink relay, NTN IoT, slicing
This distribution shows a well-balanced approach to meet both immediate operator needs and long-term innovations.
Why RAN2 Release 17 Matters
RAN2's work is crucial because it takes innovations from the physical layer and turns them into usable network features. Here's why it matters for professionals:
Operators → They get more flexibility through network slicing, IAB, and SON automation.
Vendors → They can create new devices with improved multicast, sidelink, and multi-SIM support.
Enterprises → They gain from enhancements in non-public networks and better IIoT support.
IoT Ecosystem → It benefits from small data optimization and power-saving measures for large IoT deployments.
Satellite Players → They can integrate 5G with NTN IoT and positioning features.
🔹 Practical Applications of RAN1 Improvements
NR Sidelink for V2X and Public Safety
Self-driving cars can talk to each other to prevent collisions.
Rescue teams in disaster zones can communicate directly using device-to-device connections, even if the base station is out of service.
NR Positioning
Logistics firms can monitor containers with sub-meter accuracy throughout their supply chains.
Smart city navigation apps can offer precise AR overlays for both pedestrians and vehicles.
IoT over NTN
Isolated oil rigs, ships, and rural farms can stay connected through satellite IoT links.
This guarantees global coverage for NB-IoT and LTE-M, filling in the gaps where terrestrial networks aren’t available.
Low Complexity NR Devices (RedCap)
This allows for affordable wearables like smartwatches and health trackers.
It’s great for sensor-heavy settings (like factories, retail, and agriculture) without breaking the bank on device costs.
Conclusion
RAN2 Release 17 lays the groundwork for protocols that will enable 5G to evolve beyond just smartphones into areas like industrial IoT, XR, NTN, and private networks. With features like NR multicast, sidelink relay, IoT for NTN, RAN slicing, and power saving, it sets the stage for 5G networks to be flexible, efficient, and ready for the future.
Working in tandem with RAN1 (PHY), RAN3 (architecture), and RAN4 (performance), RAN2 makes Release 17 a significant milestone in 5G standardization, paving the way for 5G-Advanced in Release 18.
