Reasons to adopt Open RAN now
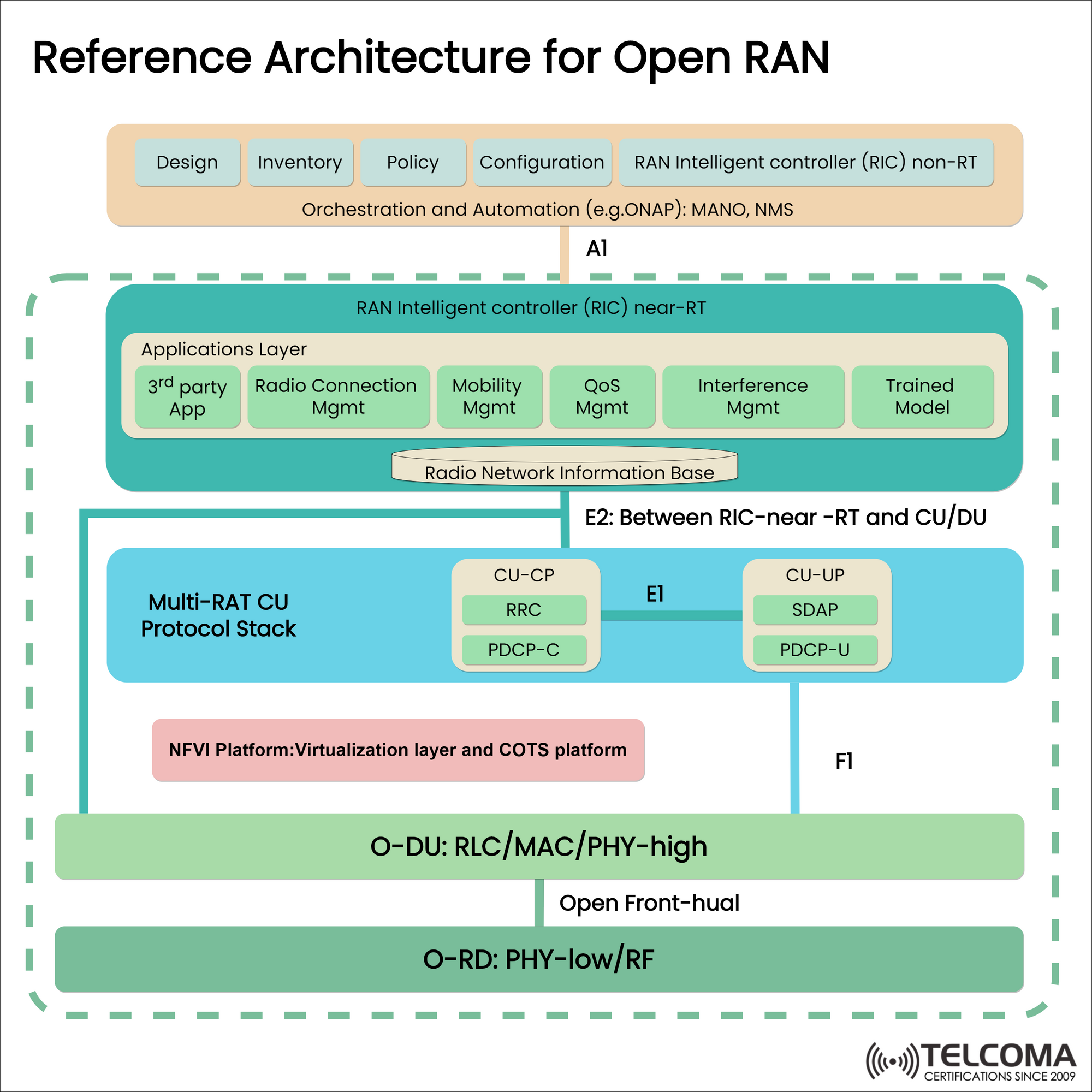
Introduction:
Open RAN (Radio Access Network) is an emerging technology that is rapidly gaining traction in the telecommunications industry. It is a new approach to building and operating cellular networks that replaces traditional proprietary equipment with open and interoperable hardware and software components. In this article, we will discuss the technical reasons for adopting Open RAN now.
What is Open RAN?
Open RAN is a new approach to building and operating cellular networks that replaces traditional proprietary equipment with open and interoperable hardware and software components. Open RAN is based on open standards, interfaces, and APIs, which enable different vendors' components to work together seamlessly. This approach increases competition, reduces costs, and accelerates innovation in the telecommunications industry.
Why Adopt Open RAN Now?
Vendor Lock-In:
One of the primary technical reasons to adopt Open RAN now is to avoid vendor lock-in. Traditional cellular networks are built using proprietary hardware and software components from a limited number of vendors. This approach limits competition and innovation, and makes it difficult and expensive to upgrade or replace equipment. Open RAN enables operators to use components from different vendors, which reduces their dependence on a single vendor and increases competition and innovation.
Interoperability:
Another technical reason to adopt Open RAN now is interoperability. Open RAN components are designed to work together seamlessly, regardless of the vendor or technology used. This approach enables operators to mix and match components from different vendors, which increases flexibility and reduces costs. Open RAN also enables operators to upgrade or replace components without disrupting the entire network.
Cost Reduction:
Open RAN offers several technical benefits that can help reduce costs. Open RAN enables operators to use commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) hardware, which is less expensive than proprietary hardware. Open RAN also reduces the need for specialized skills and training, which can further reduce costs. Finally, Open RAN enables operators to deploy smaller and more flexible networks, which can reduce capital and operational expenses.
Innovation:
Open RAN also enables innovation in the telecommunications industry. Open RAN enables operators to experiment with new technologies and services without being limited by proprietary equipment. Open RAN also enables new vendors to enter the market, which increases competition and innovation.
5G Deployment:
Open RAN is particularly important for the deployment of 5G networks. 5G networks require a significant amount of new equipment, which can be expensive and time-consuming to deploy using traditional methods. Open RAN enables operators to deploy 5G networks more quickly and cost-effectively, which can help accelerate the adoption of 5G.
Challenges of Open RAN:
While Open RAN offers several technical benefits, it also presents some challenges. Open RAN components are still evolving, which can make it difficult to ensure interoperability and compatibility. Open RAN also requires operators to invest in new skills and tools, which can be a significant challenge. Finally, Open RAN requires operators to carefully evaluate the trade-offs between cost, performance, and innovation.
Conclusion:
Open RAN is a new approach to building and operating cellular networks that replaces traditional proprietary equipment with open and interoperable hardware and software components. Open RAN offers several technical benefits, including avoiding vendor lock-in, enabling interoperability, reducing costs, enabling innovation, and accelerating the deployment of 5G networks. However, Open RAN also presents some challenges, including ensuring interoperability and compatibility, investing in new skills and tools, and carefully evaluating the trade-offs between cost, performance, and innovation. To successfully adopt Open RAN, operators must carefully evaluate their needs and goals, and work closely with vendors and industry groups to ensure interoperability and compatibility.
