RedCap in 5G: Bridging the Gap Between LPWA, URLLC, and eMBB for Efficient IoT Connectivity

Getting to Know RedCap: The Future of Scalable 5G IoT Connectivity
As 5G networks grow, it’s clear that we need a variety of devices that can connect. While the focus has been on high-speed broadband (eMBB) and ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC), there’s a whole range of devices out there that don't need super high performance but still require efficient, reliable, and cost-effective connectivity.
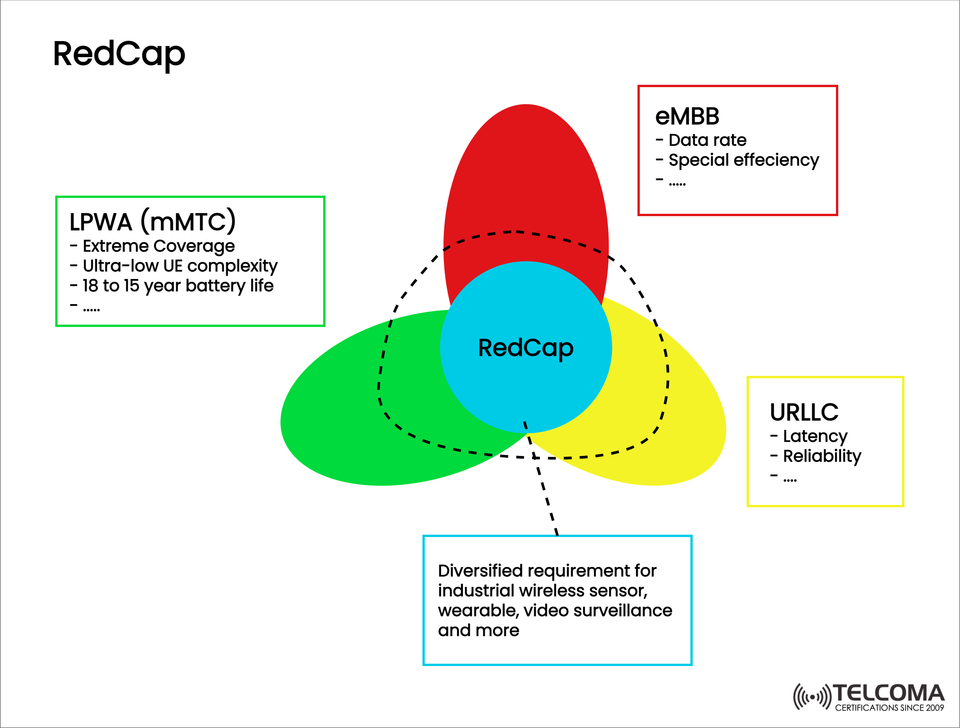
This is where RedCap (Reduced Capability), or NR-Light, steps in. As you can see in the image, RedCap sits at the crossroads of LPWA (Low-Power Wide Area), eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband), and URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication) — combining the strengths of each to enable a new class of 5G devices.
What Exactly is RedCap (Reduced Capability)?
RedCap was rolled out in 3GPP Release 17 as part of the ongoing development of the 5G New Radio (NR) standard. Its aim is to provide 5G connectivity for devices that don’t need the full power of traditional NR but still seek better capabilities than LTE-M or NB-IoT.
In simpler terms, RedCap serves as a middle ground — it delivers moderate throughput, simplifies hardware needs, and boosts power efficiency, making it ideal for IoT, wearables, sensors, and industrial automation.
Where RedCap Fits Among 5G Use Cases
The image shows how RedCap overlaps with three main 5G service types:
LPWA (mMTC) — Massive Machine-Type Communication
eMBB — Enhanced Mobile Broadband
URLLC — Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication
This intersection highlights RedCap’s unique position — blending features from each category to support a variety of applications.
LPWA (mMTC): Low-Power Wide Area Networks
LPWA technologies like NB-IoT and LTE-M are designed for low-bandwidth, power-efficient IoT devices. RedCap takes many of these traits, such as:
Great coverage (even in deep indoor and rural areas)
Ultra-simple device design (easier modem requirements)
Long battery life (some devices can last up to 10–15 years)
Scalability for large IoT setups
However, unlike LPWA, RedCap provides higher data rates and lower latency, making it more fit for demanding IoT scenarios.
eMBB: Enhanced Mobile Broadband
eMBB is all about high-throughput, delivering gigabit speeds for smartphones, tablets, and 5G routers. RedCap borrows from eMBB in these ways:
Higher data rates than older LTE-based IoT technologies
Better spectral efficiency thanks to advanced modulation (up to 64QAM)
Support for decent video and data transmission
In RedCap, these eMBB features are scaled down to keep things efficient — making it a good fit for video surveillance, wearables, and health monitoring devices.
URLLC: Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication
URLLC guarantees low latency and high reliability for crucial applications like robotics, smart grids, and self-driving cars.
RedCap doesn’t quite match URLLC’s full potential but still provides:
Less latency than LPWA technologies
More reliability for industrial sensors and control systems
Precise communication options for timely data
This positions RedCap well for industrial automation, where being responsive and reliable is key, but where URLLC's strict requirements aren’t necessary.
Key Technical Features of RedCap
To grasp RedCap’s role in the 5G landscape, let’s compare its key technical features with those of traditional NR:
Parameter RedCap (NR-Light)Baseline 5G NR Bandwidth Up to 20 MHz (FR1)Up to 100 MHz (FR1)Modulation Up to 64QAMUp to 256QAMMIMO Support1x1 or 2x24x4 or higher Device Complexity Fewer RF chains, simpler baseband Full complexity Latency Moderate (~10 ms)Ultra-low (<1 ms for URLLC)Data Rate50–150 Mbps1–2 Gbps Power Efficiency Tailored for IoT and wearables High-performance mode
These specs show that RedCap delivers a balanced performance — enough to support new use cases while keeping device costs and power consumption low.
Applications and Use Cases of RedCap
The image illustrates RedCap’s role in catering to varied needs for:
Industrial wireless sensors
Wearables and health devices
Video surveillance
Smart city infrastructure
Connected consumer electronics
- Industrial Wireless Sensors
Factories need robust, reliable, and low-latency connectivity for sensors that check temperature, vibrations, and machinery health. RedCap makes this possible by offering:
Lower latency than LPWA
Higher reliability than regular Wi-Fi
Easier integration into private 5G networks
- Wearables and Health Devices
Wearables like smartwatches, fitness trackers, and medical monitors gain from RedCap’s low complexity and energy efficiency. They can stay connected for years without constant battery changes, all while supporting real-time health monitoring.
- Video Surveillance
Unlike NB-IoT, which struggles with video data, RedCap can handle moderate data throughput — making it perfect for low-power cameras used in smart cities and industrial settings.
- Smart Infrastructure
Applications like smart streetlights, traffic management systems, and environmental sensors require long-lasting, low-maintenance connectivity. Devices using RedCap can function for years while maintaining a steady data stream.
- Private 5G Networks
Businesses setting up private 5G networks can effectively use RedCap devices to connect thousands of sensors and IoT endpoints — balancing performance, scalability, and cost.
How RedCap Connects the Dots
RedCap serves as the missing link between low-end LPWA and high-end URLLC/eMBB technologies.
Here’s how it connects those dots:
From LPWA, it takes energy efficiency and wide coverage.
From eMBB, it inherits higher data rates and spectral efficiency.
From URLLC, it gains better reliability and reduced latency.
This makes RedCap the perfect 5G solution for mid-range IoT devices — not too limited, but not over the top either.
Advantages of RedCap Devices
✅ Less Hardware Complexity: Fewer antennas, simpler RF setups, and budget-friendly chipsets.
⚡ Power Efficiency: Designed for devices with multi-year battery life.
🌍 Flexible Deployment: Works smoothly in both public and private 5G networks.
🔒 Enhanced Reliability: Good for semi-critical IoT and industrial systems.
💰 Cost-Effective: Offers a scalable 5G option for the mass market.
Challenges and Industry Adoption
While RedCap has a lot of potential, there are still some hurdles:
Ecosystem readiness: Network support and device chipsets are still developing.
Spectrum efficiency: Need to optimize narrowband use within wide 5G channels.
Standard evolution: Upcoming releases (Rel-18 and Rel-19) are expected to enhance RedCap’s abilities.
Leading chipset manufacturers like Qualcomm, MediaTek, and UNISOC have already announced RedCap-compatible platforms, and telecom operators are starting trials to incorporate these devices into 5G Standalone (SA) networks.
RedCap’s Role in the 5G-to-6G Transition
As networks transition towards 6G, the number of connected devices is set to skyrocket — going from billions today to possibly trillions in the next ten years.
RedCap represents a key evolutionary step for ensuring connectivity for the next wave of IoT advancements:
Smart factories
Wearable healthcare networks
Automated logistics and transport
Sustainable smart cities
By striking a balance between performance, cost, and efficiency, RedCap guarantees that 5G’s reach extends beyond just smartphones to cover the entire connected universe.
Conclusion
5G RedCap is changing the way we perceive IoT connectivity. Placed between LPWA, eMBB, and URLLC, it delivers the right mix of speed, power efficiency, and reliability for next-gen devices.
As the deployments grow and support from chipsets strengthens, RedCap will likely evolve into a key technology in the 5G landscape — enabling industrial sensors, wearables, and video surveillance to function seamlessly across both public and private networks.
In short, RedCap connects the dots between high-end 5G and low-power IoT — paving the way for a smarter, more connected world in the upcoming 5G and 6G landscape.
