Reduced Capability New Radio (5G NR RedCap): Bridging the Gap Between IoT and 5G

Reduced Capability New Radio (5G NR RedCap): Connecting High-Speed 5G with IoT
As 5G networks grow around the world, they're really changing how industries operate with super-fast speeds, low latency, and massive connectivity. But here's the thing — not every connected device needs that kind of lightning speed or ultra-low latency. A lot of smart IoT devices, wearables, and industrial sensors actually do just fine with moderate data rates, long battery life, and simple device designs — and traditional 5G or LTE categories often miss the mark on those needs.
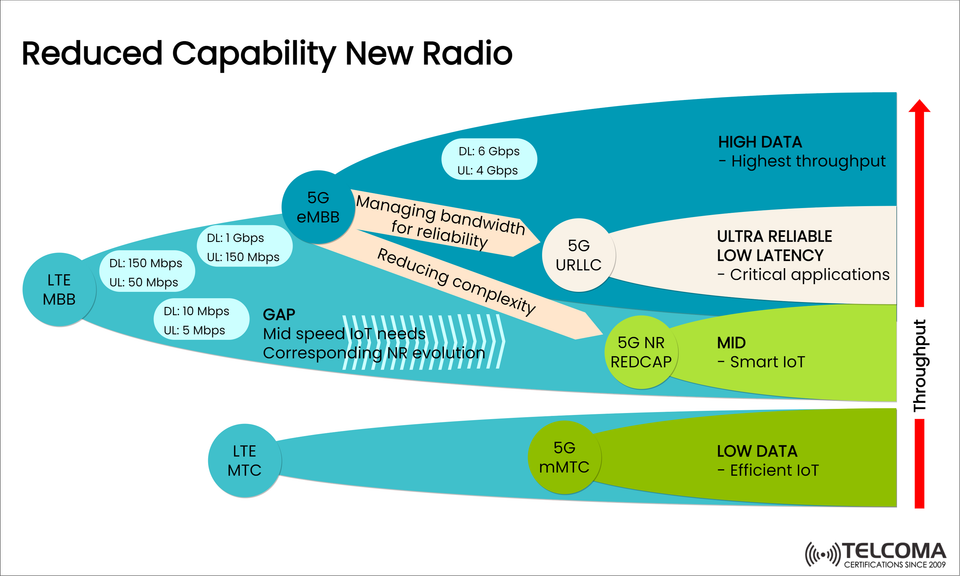
This is where Reduced Capability New Radio (5G NR RedCap) comes in. The diagram titled “Reduced Capability New Radio” shows how RedCap (also known as NR-Light) fills the performance and complexity gap between 5G eMBB (enhanced Mobile Broadband), 5G URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication), and 5G mMTC (massive Machine-Type Communication).
Understanding the 5G Landscape: From LTE to NR
Before we get into RedCap, it helps to have a solid grasp of how 5G developed from LTE and what gaps it aims to close.
LTE Evolution
LTE MBB (Mobile Broadband):
Downlink: up to 150 Mbps
Uplink: up to 50 Mbps
Made for mobile data users and consumer broadband on smartphones.
LTE MTC (Machine-Type Communication):
Tuned for low data rates (up to 10 Mbps DL / 5 Mbps UL)
Ideal for IoT devices, sensors, and industrial telemetry.
With 5G NR, three different use cases came to life:
5G Category | Purpose | Example Use Case
5G eMBB | High throughput | HD video streaming, AR/VR
5G URLLC | Ultra-low latency | Autonomous driving, remote surgery
5G mMTC | Massive IoT | Smart cities, industrial sensors
But there was still a gap — devices that needed mid-tier performance (not as demanding as smartphones, yet more capable than NB-IoT).
That’s precisely where 5G NR RedCap shines.
What is 5G NR RedCap (Reduced Capability New Radio)?
5G NR RedCap, standardized in 3GPP Release 17, is a lighter version of 5G NR. It’s tailored for devices that:
Don’t need the top-tier performance of eMBB/URLLC, and
Require more than what 5G mMTC or LTE-M can offer.
In a nutshell, RedCap strikes a balance between performance and cost, delivering mid-range throughput with reduced complexity and lower power consumption.
Key Features of 5G NR RedCap
Parameter | 5G eMBB | 5G NR RedCap | 5G mMTC
Downlink Speed | Up to 6 Gbps | Up to 150 Mbps | < 10 Mbps
Uplink Speed | Up to 4 Gbps | Up to 50 Mbps | < 5 Mbps
Bandwidth | Up to 100 MHz | ≤ 20 MHz | ≤ 5 MHz
Antenna Configuration | 4x4 MIMO | 1x1 or 2x2 MIMO | Single antenna
Latency | < 1 ms | < 10 ms | > 50 ms
Power Consumption | High | Moderate | Very Low
Use Case | Smartphones, AR/VR | Wearables, Cameras, Industrial IoT | Smart meters, sensors
From the image, it's clear that RedCap occupies a space between the high-performance eMBB/URLLC and the low-power mMTC domains — just right for smart IoT and industrial applications.
How RedCap Simplifies 5G Device Design
The “Reduced Capability” idea isn’t just about performance; it's also about simplifying hardware and software requirements.
Simplifications Introduced:
Narrower Bandwidth:
Cut down from 100 MHz to 20 MHz in sub-6 GHz bands.
Lowers power use and hardware complexity.
Fewer Antennas:
Supports up to 2x2 MIMO instead of 4x4, which brings down RF front-end costs.
Simplified Modulation:
Utilizes lower-order modulations (like 64-QAM instead of 256-QAM).
Reduced Processing Requirements:
Smaller buffer sizes and less complicated baseband processing.
Optimized Power Management:
Features like enhanced Discontinuous Reception (eDRX) and Power Saving Mode (PSM) help extend battery life.
Bridging the Gap: The Role of RedCap in 5G Architecture
The diagram illustrates how 5G RedCap fills a “GAP” between low data IoT and high-performance 5G:
5G eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband): Delivers ultra-high throughput (up to 6 Gbps DL, 4 Gbps UL). Perfect for applications that need a lot of data, like VR and 4K streaming.
5G URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication): Focuses on low latency and reliability for essential tasks such as industrial automation.
5G mMTC (Massive Machine-Type Communication): Targets large-scale IoT with minimal data needs and efficient power use.
5G NR RedCap: Sits snugly in the middle — offering moderate throughput (up to 150 Mbps), lower latency, and optimized power usage for smart IoT and wearable tech.
In short:
RedCap effectively manages bandwidth for reliability while cutting down on system complexity — setting the stage for the next wave of mid-tier 5G devices.
Use Cases of 5G NR RedCap
- Industrial IoT (IIoT)
Monitoring and controlling machines
Robotics and automation
Predictive maintenance with sensors
- Wearables and Health Devices
Smartwatches and fitness trackers
Medical devices requiring low latency but long battery life
- Surveillance and Smart Cameras
Medium-bandwidth streaming
Remote monitoring of industrial sites
- Smart Grids and Utilities
Reliable data transmission from distributed sensors and control units
- Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) Lite
Affordable broadband for homes and small businesses without the high costs of full eMBB hardware
Benefits of 5G NR RedCap
Lower Cost and Complexity
Simplified RF design and smaller modems mean RedCap devices are cheaper to produce.
Better Battery Life
Power-efficient operations help extend battery life for IoT devices and wearables.
Wider Coverage
Works well in mid-band and low-band spectrum, giving better reach.
Future-Proof Design
Built on 5G NR architecture, making sure it’s compatible with 5G networks and future upgrades.
Flexible Deployment
Can work alongside eMBB and URLLC traffic in the same 5G setup.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Although 5G NR RedCap offers a lot, a few challenges still exist:
Network Deployment: Operators will need to upgrade network slices and cores for RedCap devices to work efficiently.
Ecosystem Maturity: Modem vendors and chipset makers are still making affordable RedCap solutions.
Spectrum Allocation: Balancing RedCap within shared mid-band frequencies will need careful management.
Looking ahead, 3GPP Release 18 (5G Advanced) is expected to improve RedCap even more by adding energy efficiency enhancements, better coverage, and support for multicast and positioning services.
Conclusion
The Reduced Capability New Radio (5G NR RedCap) represents a significant milestone in the 5G journey — bridging the divide between super-fast 5G and low-power IoT.
By providing mid-level throughput, easier implementation, and energy efficiency, RedCap opens up new possibilities for devices — from industrial sensors and wearables to smart cameras and connected health gadgets.
As the diagram shows, RedCap’s unique position between 5G eMBB, URLLC, and mMTC highlights how it delivers balanced performance, reliability, and efficiency — making it the perfect fit for Smart IoT ecosystems and the future of connected devices in 5G.
