RIC in Open RAN: Enabling Intelligence and Automation for Vertical Industries
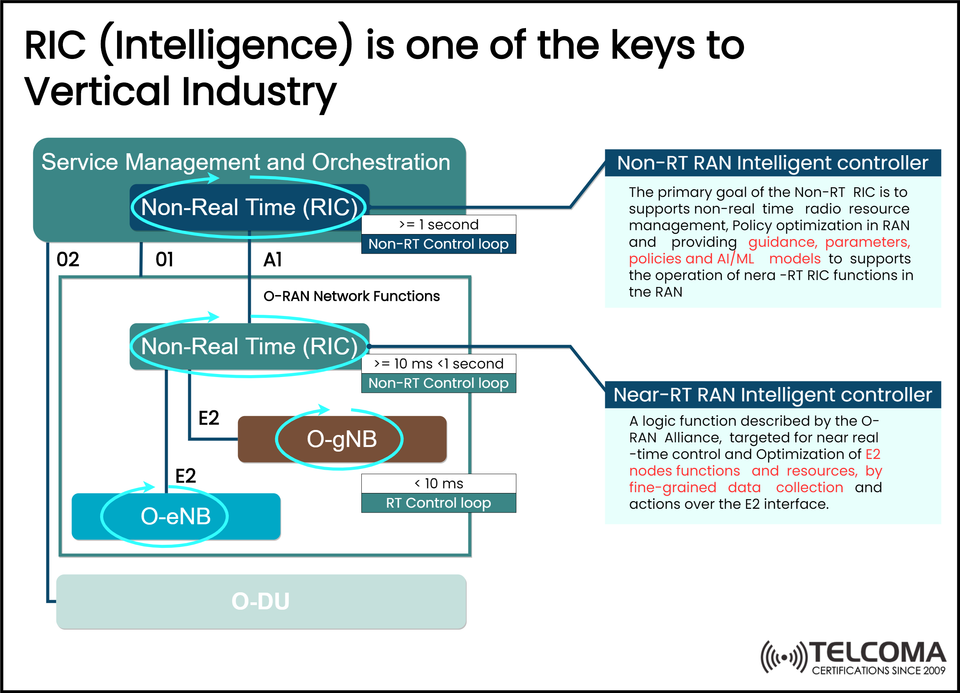

RIC (RAN Intelligent Controller): Powering AI-Driven Intelligence in Open RAN
As we build modern 5G networks, intelligence, automation, and flexibility are key—especially as we support specific industry verticals such as manufacturing, healthcare, and transportation. This is where the RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) comes in. The RIC is a key building block of the O-RAN architecture and infuses AI/ML into their radio networks.
To help clarify the roles of Near-Real-Time (Near-RT) and Non-Real-Time (Non-RT) RICs, we have separated out their descriptions and will demonstrate how they fit together, timing loops, and hooks to both the O-DU, O-gNB, and O-eNB, from the previous visual reference.
🧠 What is RIC in O-RAN?
The RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) is a virtualized software platform that enables programmable control, automation, and optimization of RAN functions with AI/ML models, policies, and data analysis available to make decisions.
There are two types of RIC:
Type Overview Timing
Non-RT RIC Performs tasks that are not time-critical, such as: training AI/ML models, policy enforcement, and general analytics. ≥ 1 second
Near-RT RIC Purpose is to perform time-critical tasks. This includes radio resource management (RRM) and optimizing user experience (QoS) by making use of fine-grained data. ≥ 10 ms and < 1 sec.
Besides the RIC architecture components we just mentioned, it is useful to touch upon the various control loops in the RIC architecture in this context.
Non-Real-Time RIC (Non-RT RIC)
The Non-RT RIC resides in the Service Management and Orchestration (SMO) layer and is responsible for:
Train and improve AI/ML models
Defining policies, guidance, and parameters
Providing insights to the Near-RT RIC through the A1 interface
Operating on a non-real-time control loop (minimum 1 second).
High-level Tasks
Policies management
Analysis and forecasting over the long-term
Optimizing radio resources over time
Cross-layer orchestration with SMO
Near Real-Time RIC (Near-RT RIC)
The Near-RT RIC resides closest to the RAN (i.e. O-gNB, O-eNB). It is responsible for:
Optimizing RAN functions in such a way that it minimizes the effect of latency as much as possible (e.g. E2 node feedback to inform the Near-RT RIC decision can occur in 10 ms to 1s).
Communicating with the E2 nodes (gNB/eNB) of the RAN via the E2 interface in order to control RAN functions.
Core Tasks
Fine-grained data collection and analysis
Real-Time Traffic Steering
Enforcement of QoS/QoE targets
Load balancing/ beam optimization
Interfaces in the RIC Architecture Framework
Interface Function
A1 Management connection between Non-RT RIC and Near-RT RIC to send guidance, AI/ML models, and policy and define parameter for application space
E2 Real-time control with E2 nodes (gNB/eNB) with Near-RT RIC (for RAN optimization)
O1 and O2 Used by the SMO to manage lifecycle and performance of O-RAN functions
💡 RIC Opportunities for Vertical Industries
RIC enables specialized network behavior for use cases, such as:
Smart Manufacturing Real-time fault prediction, analyzing machine telemetry
Healthcare Low-latency slices for guaranteed low-latency devices
Transport & Logistics Dynamic traffic prioritization between autonomous vehicles
Energy Secured and resilient allocation of radio resources for smart grid.
Potential RIC benefits in vertical use cases include:
✅ AI/ML-enabled RRM
✅ Support of multiple vendors through open interfaces
✅ Dynamic and intent-based policy commitment
✅ Application-aware resource slicing
✅ Integration with edge compute
🚀 Future Vision: Evolution of Intelligent RAN
The future evolution of RIC will only lead to further realization of an Intelligent RAN.
Future Feature Expected Outcome
Real-time AI loop Closed-loop automation < 10ms
Federated learning models AI training without data sharing
Cross-domain orchestration Core and transport domain integrations
Intent-based networking Translating policies to autonomous RAN behavior
📍 RIC Deployment Models and Integration Layers
RIC functional components may be deployed flexibly with regard to latency and network design and if there are any other service constraints.
Model Deployment
🔹 RIC Deployment Centralized RIC
The Non-RT RIC will be hosted in a centralized cloud or datacentre with the SMO.
This suits Non-RT RIC if there is a requirement for running policy engines with a cloud-based analytic platform or for ML model training.
Centralizing all functions would help reduce any hardware footprint on the edge.
🔹 RIC Deployment Distributed Near-RT RIC
The Near-RT RIC will almost always be distributed to be closer to the edge, or possibly co-located with CU/DU RAN elements.
This allows for a low latency option to event handling (cell congestion, handovers etc.) and there is greater likelihood of offering service continuity in the case that the central links are degraded.
🤖 AI/ML within RIC: Intelligence that Learns and Adapts
RIC Design Goals: Intelligent Autonomous RAN Behaviour Utilizing AI/ML Models.
AI/ML Workflows supported in the RIC
Step Function
Data Collection (E2) Real-time RAN Metrics from gNB/eNB
Model Training (Non-RT RIC) Offline ML training with historical and live data
Model Inference (Near-RT RIC) Real-time decisions based on trained model
Feedback Loop AI support for iterative learning and policies
By developing these capabilities, operators can transition themselves from rule based automation to predictive and adaptive decision-making.
🧠 Summary: Why RIC is the Catalyst for 5G Intelligence
Feature Benefit
Open APIs (A1, E2) Vendor interoperability
AI/ML Intelligence Predictive and adaptive automation
Real-Time Optimization Enhanced user experience, efficiency
Policy Enforcement Governance and network alignment
Edge-Aware Control Localized decisions for latency-sensitive apps.
✅ Conclusion:
The RIC is the Brain of Open RAN
The RIC is not merely a component of an Open RAN architecture—the RAN Intelligent Controller is the brain of the Open RAN architecture. The RIC provides real-time, and no-time, control loops, AI/ML based optimization capabilities, and open interoperability which advances mobile networks.
In conclusion, the RIC is a critical component in and making 5G networks smarter, leaner, and more responsive to changes in application requests and demands across vertical industries.
