Roadmap of RIC-Enabled Use Cases: Automating 5G RAN Optimization

RIC-Enabled Use Cases Roadmap: Automating 5G RAN Optimization
The Radio Intelligent Controller (RIC) stands out as a groundbreaking advancement in the Open RAN (O-RAN) framework. Think of it as the “brain” behind the RAN, enabling real-time and near-real-time network tweaks through AI-based analytics and policy control.
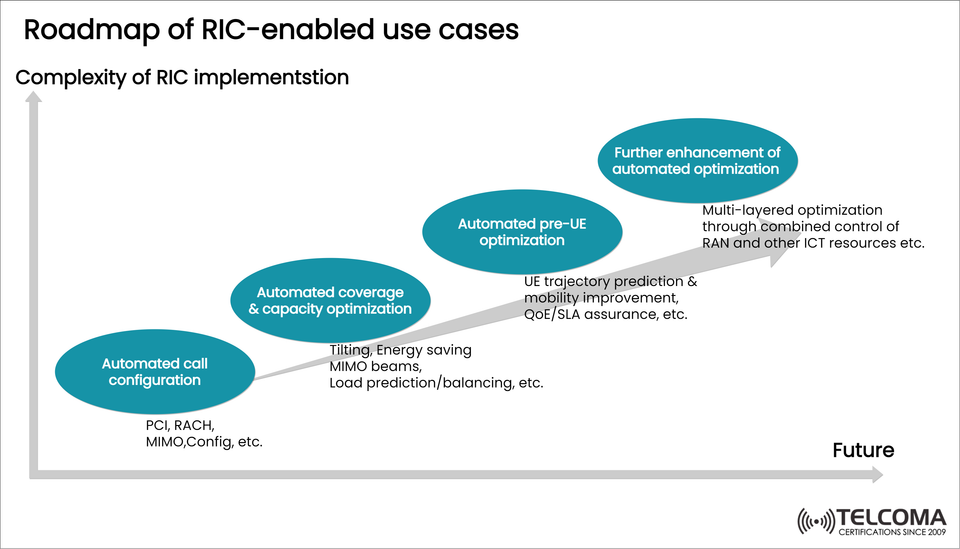
The roadmap diagram included highlights the evolution of RIC-enabled use cases—starting from basic automation and moving toward sophisticated multi-layered optimization. This progression isn’t just about slight improvements in efficiency but shows a major shift toward self-optimizing, adaptable 5G networks.
In this blog, we’ll dig into the roadmap, breaking down each phase of RIC implementation and its significance for the telecom sector.
What’s the Radio Intelligent Controller (RIC)?
The RIC is a software-defined part of the O-RAN architecture, aimed at boosting the performance of the Radio Access Network (RAN).
It brings in programmability, AI/ML intelligence, and open interfaces, letting operators optimize network performance in real-time.
RIC comes in two versions: * Near-Real-Time RIC (near-RT RIC): Works within a 10ms to 1s time frame for dynamic radio resource management. * Non-Real-Time RIC (non-RT RIC): Operates on a timescale greater than 1s, focusing on policy management, training ML models, and long-term optimizations.
Together, these controllers lay the groundwork for RIC-enabled use cases, as shown in the roadmap.
Roadmap Overview
The roadmap depicted in the image outlines four key stages of RIC-enabled automation:
Automated Call Configuration
Automated Coverage & Capacity Optimization
Automated Pre-UE Optimization
Further Enhancement of Automated Optimization
Each stage marks a step toward increased complexity, intelligence, and integration of RIC into 5G networks.
Stage 1: Automated Call Configuration
This is the initial step of RIC-enabled automation, where basic configuration tasks get automated.
Examples: * PCI (Physical Cell Identity) assignment * RACH (Random Access Channel) configuration * MIMO configuration
Impact: * Cuts down on manual work in cell planning. * Reduces configuration mistakes. * Speeds up network rollout and reconfigurations.
By automating tedious and error-prone tasks, operators can redirect their efforts to more valuable activities while maintaining basic network efficiency.
Stage 2: Automated Coverage & Capacity Optimization
Next up, RIC assists in dynamic optimization of coverage and capacity.
Examples: * Antenna tilting for better coverage. * Energy-saving via dynamic beamforming (MIMO beams). * Load prediction and balancing among cells.
Impact: * Lowers energy use. * Balances traffic loads in real-time. * Boosts overall Quality of Service (QoS).
This stage marks the start of intelligent, self-healing networks, where the system adapts on its own to shifting conditions.
Stage 3: Automated Pre-UE Optimization
At this stage, RIC shifts its focus from cell-level to user equipment (UE)-centric optimization.
Examples: * Predicting user movements (mobility prediction). * Improving handovers to minimize call drops. * Ensuring QoE (Quality of Experience) and SLA (Service Level Agreement) compliance.
Impact: * Smooth mobility across cells and networks. * Better user experience, particularly in high-mobility situations (think vehicles and trains). * Enhanced network efficiency through predictive analytics.
Here, RIC utilizes machine learning models to forecast network demand, aligning with the goal of proactive network optimization.
Stage 4: Further Enhancement of Automated Optimization
The last stage on the roadmap envisions multi-layered optimization, where RIC connects RAN with other ICT (Information and Communication Technology) resources.
Examples: * End-to-end orchestration across RAN, transport, and core networks. * Coordinated optimization across compute, storage, and edge resources. * AI-driven closed-loop automation across layers.
Impact: * True network intelligence, adapting comprehensively instead of in silos. * Support for advanced functions like network slicing, ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC), and massive IoT. * Sets the stage for 6G and beyond, where networks operate as fully autonomous systems.
This stage embodies the future vision of RIC-enabled networks: self-optimizing, context-aware, and AI-driven ecosystems.
Comparison of RIC-Enabled Roadmap Stages
Stage Focus Area Key FunctionsBenefits1. Automated Call Configuration Basic configuration PCI, RACH, MIMO settings Faster rollout, fewer errors2. Automated Coverage & Capacity Optimization Radio optimization Antenna tilting, load balancing, energy saving Improved coverage, efficiency3. Automated Pre-UE Optimization User-centric Mobility prediction, SLA assurance Better mobility, QoE4. Further Enhancement of Automated Optimization Multi-layer orchestration Cross-domain control, AI-driven closed loops Fully autonomous, intelligent networks
Why RIC is a Game-Changer for 5G
The growth of RIC-enabled use cases tackles several major challenges in deploying 5G:
Managing Complexity: 5G brings significant complexity with massive MIMO, network slicing, and densification. RIC simplifies operations.
Cost Efficiency: Automation cuts down OPEX by reducing manual tasks.
Energy Savings: Dynamic optimization decreases energy usage, supporting environmentally-friendly networking.
User Experience: Predictive optimizations guarantee seamless connectivity, even in crowded or dynamic environments.
Future-Readiness: RIC paves the way for integrating AI-driven intelligence across 5G and future 6G networks.
Future Outlook
As 5G networks advance toward 6G, RIC’s role will only grow:
Integration with edge computing for ultra-low latency services.
AI-native networks, where every function from core to edge is optimized in real-time.
Cross-domain orchestration, enabling synergy between telecom and cloud-native infrastructures.
The roadmap emphasizes that the RIC journey is progressive, and its ultimate promise lies in multi-layered, AI-driven network intelligence.
Conclusion
The Roadmap of RIC-enabled use cases illustrates how telecom networks will progress from basic automation to advanced, AI-driven orchestration.
Stage 1 kicks off with automated call configuration, making deployments easier.
Stage 2 moves to coverage and capacity optimization, enhancing efficiency.
Stage 3 brings in user-centric predictive optimization, boosting mobility and QoE.
Stage 4 wraps up with multi-layered optimization, inching us closer to fully autonomous, intelligent networks.
For telecom professionals, the takeaway is clear: embracing RIC isn’t just about operational efficiency—it’s about future-proofing networks for what’s on the horizon.
The future of wireless is automated, intelligent, and adaptive—and RIC is leading the charge.
