Samsung 5G Common Core Portfolio Explained: Architecture, Functions & Solutions

Understanding Samsung's 5G Common Core Portfolio
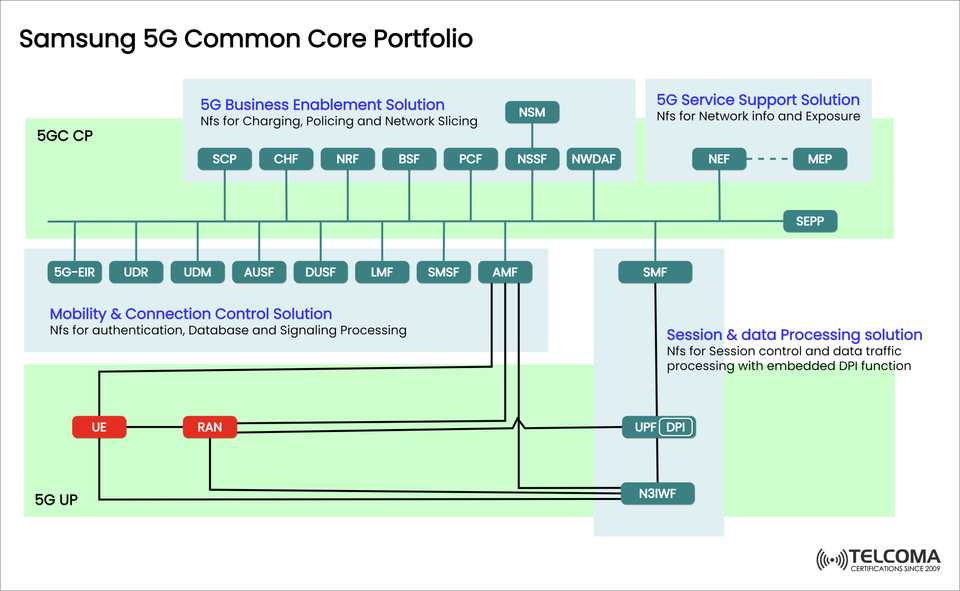
With 5G changing the game in connectivity — offering incredibly low latency, high reliability, and able to support a ton of devices — telecom companies truly need a solid 5G Core (5GC) to make the most of these new capabilities. The Samsung 5G Common Core Portfolio, as shown in the image above, showcases the extensive range of solutions Samsung is bringing to the table for 5G networks.
This portfolio combines control plane (CP) and user plane (UP) functions, providing smooth mobility management, secure authentication, efficient traffic management, and opportunities for service providers to monetize their offerings.
What’s the 5G Core (5GC)?
The 5G Core is the heart of a 5G network, handling everything from connectivity and mobility to session management, authentication, and various services. Unlike the 4G LTE EPC (Evolved Packet Core), here's what sets the 5G Core apart:
It’s cloud-native and service-based, developed with microservices for added flexibility.
It's disaggregated into modular Network Functions (NFs).
It's designed to support network slicing, IoT, and edge computing.
Samsung’s 5G Common Core Portfolio lines up with 3GPP standards while also offering tweaks for better performance and scalability tailored for operators.
Key Solutions in the Samsung 5G Common Core Portfolio
The portfolio breaks down into four main solution groups:
- Mobility & Connection Control Solution
These NFs take care of device authentication, user identity, and signaling control, making sure that users have a smooth experience as they move around the network.
Core NFs in this category include:
UDM (Unified Data Management): A central database for subscribers.
AUSF (Authentication Server Function): Handles authentication using security credentials.
AMF (Access and Mobility Management Function): Manages device registration, connections, and mobility.
SMSF (Short Message Service Function): Enables SMS over NAS.
UDR (Unified Data Repository): Stores structured data about subscriptions and policies.
EIR (Equipment Identity Register): Validates device IMEI for security.
LMF (Location Management Function): Provides accurate user location for services like emergency calls and IoT tracking.
DUSF: Manages signaling processes and database interactions.
Operator Benefit: Reliable mobility management, secure handovers, and seamless subscriber authentication.
- Session & Data Processing Solution
This solution is all about managing sessions, routing traffic, and optimizing data.
Core NFs here are:
SMF (Session Management Function): Manages user sessions, allocates IP addresses, and enforces QoS.
UPF (User Plane Function): Manages user data transfer between RAN and external networks.
DPI (Deep Packet Inspection): Analyzes traffic to optimize it, ensuring quality and security.
N3IWF (Non-3GPP Interworking Function): Connects Wi-Fi or other non-3GPP networks to the 5G core.
Operator Benefit: Improved performance in the data plane and smarter traffic management.
- 5G Business Enablement Solution
This grouping offers monetization and network optimization opportunities through advanced policy and analytics.
Key NFs include:
CHF (Charging Function): Allows for real-time charging and billing.
PCF (Policy Control Function): Implements policies for quality of service, charging, and access control.
BSF (Binding Support Function): Connects session and policy information.
NRF (Network Repository Function): Keeps an NF registry for easier discovery and communication.
NSSF (Network Slice Selection Function): Allocates and manages slices for different services such as IoT, URLLC, and eMBB.
NWDAF (Network Data Analytics Function): Uses AI/ML for data analytics and optimization.
SCP (Service Communication Proxy): Ensures reliable NF communication.
NSM (Network Slice Manager): Manages the lifecycle of network slices.
Operator Benefit: Facilitates network slicing, policy-driven services, and opens up new revenue models for both businesses and consumers.
- 5G Service Support Solution
This group focuses on functions related to exposure and interconnectivity.
Main components include:
NEF (Network Exposure Function): Securely exposes network capabilities to third-party applications (like APIs for IoT developers).
MEP (Management Exposure Point): Works with NEF for broader exposure.
SEPP (Security Edge Protection Proxy): Secures signaling traffic between networks from different operators in roaming situations.
Operator Benefit: Encourages third-party innovation and safe inter-operator roaming.
5GC CP vs 5GC UP
Samsung distinguishes between Control Plane (CP) and User Plane (UP), providing flexibility and scalability.
Component | Control Plane (CP) | User Plane (UP)
Functions | Authentication, policy, mobility, session control | Data forwarding, QoS enforcement, DPI
Key NFs | AMF, SMF, PCF, UDM, AUSF, NRF, NSSF, CHF, NWDAF | UPF, DPI, N3IWF
Focus | Decision-making, signaling, orchestration | High-throughput data transport
How Samsung 5G Core Fuels Next-Gen Networks
The Samsung 5G Core is crafted to:
Support both 5G Standalone (SA) and Non-Standalone (NSA) setups.
Deliver low latency for services like AR/VR, cloud gaming, and self-driving cars.
Provide flexible scaling thanks to its cloud-native microservices.
Ensure strong security through AUSF, SEPP, and NEF.
Enable enterprise services via network slicing and exposure APIs.
Operator Benefits
Agility: The cloud-native approach means quicker service deployment.
Revenue Growth: Opportunities for monetization through charging, slicing, and APIs.
Operational Efficiency: Automation driven by analytics lowers operational costs.
Security & Trust: Strong encryption, secure APIs, and safeguards for inter-operator connections.
Future-Ready: Well-equipped for massive IoT, URLLC, and the upcoming 6G needs.
Challenges in 5G Core Deployment
Even with all its benefits, operators are dealing with:
Complex integration with old networks (like 4G EPC).
High initial costs for deployment.
Skills gap for navigating the cloud-native, microservices-based architecture.
Evolving standards as 5G specs continue to mature.
Conclusion
The Samsung 5G Common Core Portfolio equips telecom companies with a strong, standards-compliant, and cloud-native base for 5G networks. Spanning mobility, session management, business enablement, and service support, it's set to help operators roll out fast, secure, and revenue-generating services.
As 5G adoption speeds up worldwide, this comprehensive suite ensures that operators can efficiently scale, monetize through slicing and APIs, and gear up for future innovations like 6G, AI-driven networks, and extensive IoT ecosystems.
