SD-WAN Architecture Explained: Key Components, Overlays, and Cloud Connectivity
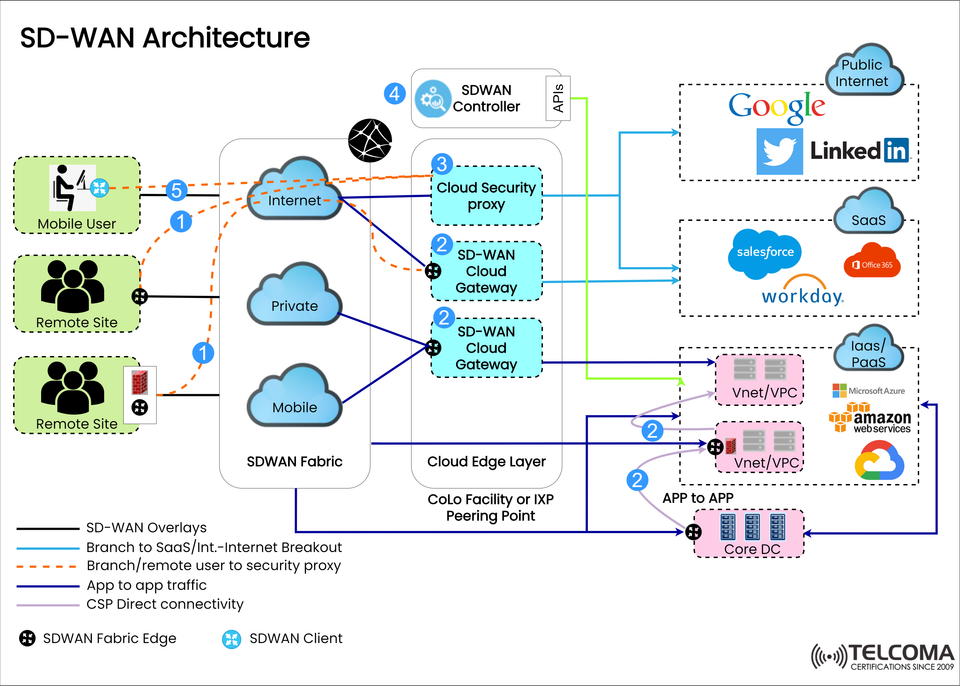

What is SD-WAN Architecture? A Complete Guide for Telecom and IT Professionals
Software Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) is now a go-to connectivity option for businesses of all sizes. It not only optimizes performance of end user applications; but reduces costs and improves agility from the WAN. Instead of being constrained to traditional WAN components, SD-WAN positions multiple networks and deploys routes and controls that are agile, secure, and cloud enabled.
In this blog post, we will break down the SD-WAN architecture depicted in the image above, showing control, data, and security flow between remote sites, cloud services, and enterprise data centers.
SD-WAN Architecture Overview
Accompanied by the SD-WAN architecture diagram, this provides you a layered view of how different network endpoints, applications, and cloud various environments collaboratively operate in an intelligent, secure, software defined overlays.
🧱 Two key components of SD-WAN:
Component Description
SD-WAN Fabric The mesh that connects private, internet, and mobile networks across all remote, and cloud locations.
SD-WAN Fabric Edge The edge device at remote sites, or branches deploying and managing drain traffic.
SD-WAN Client A software agent typically for mobile/remote users.
SD-WAN Cloud Gateway Interconnects remote offices to public and private cloud services delivering SaaS, IaaS, and public internet.
Cloud Security Proxy Provides valuable inspection and security of traffic before reaching Cloud Services.
SD-WAN Controller Central, orchestrating system responsible for deploying policy and managing configuration through API.
Cloud Edge Layer The layer by which traffic has been aggregated at the closest point.
SD-WAN Overlays and Traffic Flows
The architecture identifies five main types of traffic and flows:
1️⃣ SD-WAN Overlays (Black Line)
These create an encrypted tunnel between remote sites, VPC's, core DCs and the cloud.
Allows for application aware routing and optimizes performance.
2️⃣ Branch to SaaS/Public cloud (Blue Arrows)
The ability for direct cloud breakout to a full array of services such as: Google, LinkedIn, Salesforce, Office 365.
Includes SD-WAN Cloud Gateways and a Cloud Edge Layer.
3️⃣ Path through Security Proxy (Orange Dotted Line)
This route use the cloud security proxy for all internet-bound traffic.
This path would be ideal for enforcing a centralized firewall, IDS/IPS and CASB policies.
4️⃣ SD-WAN Controller Integration (Green Line)
The controller connects to all of the different elements of the fabric, and through the various cloud APIs
The controller is ultimately responsible for policy enforcement, telemetry, and zero touch provisioning.
5️⃣ Mobile /Remote Access (Top Left)
There are mobile workers who will access the organization via some form of SD-WAN client.
Access is routed over the cloud securely back through the fabric and proxy to the various cloud/SaaS destinations.
SD-WAN and the Cloud
The architecture supports connectivity to a number of cloud environments without any limitations:
🌐 Supported Cloud Services:
Category Examples
Public Internet Google, Twitter, LinkedIn
SaaS Salesforce, Office 365, Workday
IaaS/PaaS AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud
Enterprise Core Core DCs and on-premise apps
SD-WAN's Cloud Gateway and Cloud Edge Layer enable proximity-based optimized routing, that helps with minimizing latency and packet loss.
Security Within the SD-WAN Architecture
Security exists across multiple levels:
Cloud Security Proxy ; inspect traffic for malware and data loss prevention (DLP)
Encrypted overlays for confidentiality and integrity
Zero Trust enforcement for remote users through SD-WAN clients
API-based controller for automated response and analytics
Benefits of Modern SD-WAN Architecture
✅ Benefits for Enterprises and Telecom Carriers:
Application Performance Improvement : Through Intelligent path selection and QoS
Enhanced Security : Cloud-based proxy and encrypted tunnels
Reduced WAN Cost : Use broadband/4G/5G as a replacement for MPLS
Cloud-native Optimization (Direct breakout) : SaaS and IaaS platforms
Centralized Control : Programmable SD-WAN controllers and APIs
Scalable : Automatically provision potentially thousands of users/sites
Comparison Chart:
SD-WAN vs. Traditional WAN
Feature Traditional WAN SD-WAN
Transport Type MPLS-heavy Hybrid (Internet, LTE, 5G)
Control Plane Static routing Centralized controller
Cloud Access Backhauled Direct breakout
Security Firewall on-prem Cloud security integrated
Cost High Cost optimized
Conclusion: SD-WAN is the Future of Enterprise Connectivity
SD-WAN is no longer a niche networking solution, it is now the infrastructure for secure, intelligent, cloud-ready enterprise networks. The architecture provided above clearly maps business needs to integration of branch offices, mobile users, cloud communications, and our fast-changing connectivity requirements.
Best Practices for Successful Deployment of SD-WAN
Deploying SD-WAN in an enterprise or service provider environment necessitates careful planning and collaboration across multiple domains.
🛠️ Recommended Deployment Process:
Assess Application Requirements
Identify SaaS and IaaS workloads that are mission critical.
Identify and measure current latency, jitter, and packet loss.
Select the Optimal Fabric Design
Assess the business model before selecting hub-and-spoke, full mesh, or hybrid model.
Use CoLo edge facilities or cloud gateways to minimize latency.
Implement Cloud Gateways
Deploy SD-WAN gateways as close to the major cloud platforms (Azure, AWS, GCP) as possible.
Use direct CSP peering to achieve high throughput and security.
Automate Network Security
Route the traffic through the Cloud-Security Proxy for inspection and compliance.
Implement ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access) to support remote/mobile users.
Make it automatic with SD-WAN Controller
Centralize all of your policies for every network through your controller.
Use APIs to enable real-time network provisioning, orchestration, and analytics.
Monitor and Optimize on Continuously
Use telemetry and AI insights to implement dynamic path changes.
Implement QoS policies, business intent, etc., to prioritize actions.
Future of SD-WAN: What's Next?
As cloud and edge computing proliferate, SD-WAN will evolve beyond WAN optimization, and emerge as a foundational and enabling component of Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) and artificial intelligence-based networking.
Cant End: SD-WAN: the New Digital Backbone
In the fast-paced world of digital transformation, incorporated into everything as enterprise demand, agile, secure and cloud-optimized networks, SD-WAN delivers that by abstracting the WAN layer, applying centralized control and interfacing across the entire digital ecosystem including SaaS applications, Public Clouds and even mobile workers.
This SD-WAN architecture lays a foundation for any organization wanting to:
• Quickly accelerate their digital transformation
• Bolt-down application performance
• Protect their network perimeter
• Easily scale business globally
• Operationally scale with ease
Whether you are building a global network for an enterprise or offering managed services as a CSP, SD-WAN gives a programmable, flexible base to build on for next-gen connectivity.
