SD-WAN Service Components: Complete Guide to Architecture & Functionality

Introduction
In today’s digital age, businesses need quick, secure, and flexible connectivity across their branches, data centers, and cloud platforms. Traditional WAN solutions often fall short of these needs, mainly because they depend on MPLS circuits and fixed configurations. That’s where Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) comes into play.
SD-WAN uses software-driven intelligence to make the most of traffic routing across various connections like MPLS, broadband, and LTE. It boosts performance, ensures applications are routed properly, and significantly cuts down on operational hassle.
To grasp how SD-WAN functions, it’s important to look at its service components—the core elements that make this modern networking solution efficient, secure, and scalable.
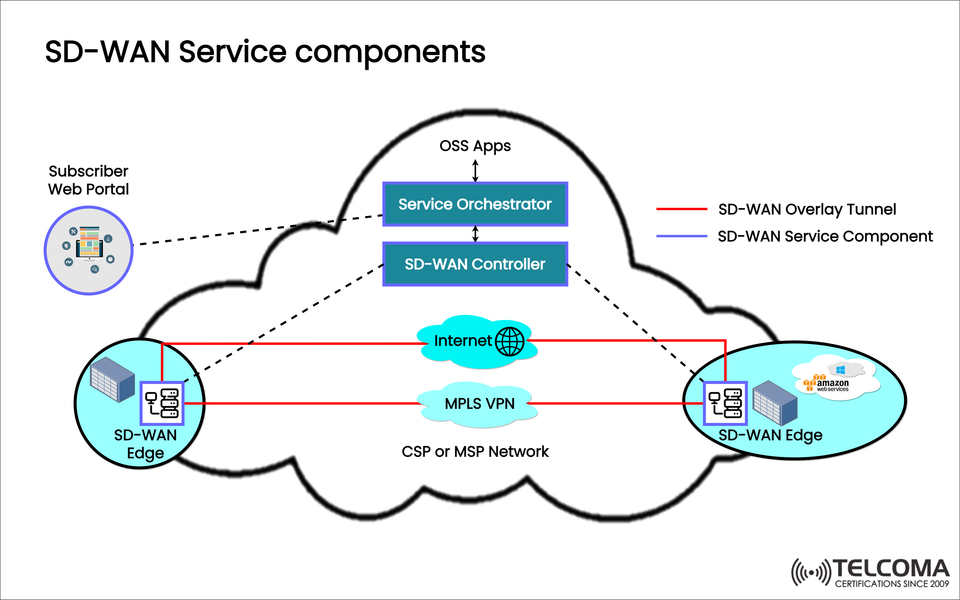
Key SD-WAN Service Components
The diagram provided gives a solid overview of SD-WAN’s crucial elements. Let’s break it down component by component.
- Subscriber Web Portal
The Subscriber Web Portal serves as the main access point for businesses. It offers a self-service interface for tasks like:
Ordering new services
Configuring SD-WAN policies
Monitoring network health and performance
Viewing usage reports and analytics
This portal cuts down on manual intervention and gives businesses more control and visibility over their WAN services.
- Service Orchestrator
The Service Orchestrator is like the brain of the SD-WAN setup. It makes sure automation happens, policies are enforced, and services are provisioned smoothly.
Key functions include:
Automating configurations across SD-WAN edges
Connecting with OSS/BSS applications for managing service lifecycles
Enforcing Quality of Service (QoS) and security policies
Simplifying scaling for multiple-site setups
With the orchestrator, branches can be added easily with zero-touch provisioning, minimizing the need for human effort.
- SD-WAN Controller
The SD-WAN Controller handles the control-plane operations, keeping centralized intelligence for routing decisions.
Core responsibilities encompass:
Managing SD-WAN overlay tunnels
Sharing routing info with SD-WAN edge devices
Implementing application-aware traffic steering policies
Providing secure connectivity through dynamic tunnel establishment
By keeping the control plane separate from the data plane, the controller enhances network agility and reduces complexity.
- SD-WAN Edge
The SD-WAN Edge device is set up at customer locations (like branch offices, data centers, or cloud). It takes care of the actual traffic forwarding while applying policies from the controller and orchestrator.
SD-WAN Edge features include:
Establishing secure overlay tunnels over MPLS or the Internet
Enhancing performance through application-aware routing
Providing integrated security features such as firewalls, encryption, and segmentation
Ensuring seamless connections to cloud providers (like AWS, Azure, Google Cloud)
These edges act as the execution layer within the SD-WAN ecosystem, turning centralized intelligence into local actions.
- CSP/MSP Network (Service Provider Infrastructure)
Typically, SD-WAN services are provided by Communications Service Providers (CSPs) or Managed Service Providers (MSPs). Their infrastructure combines Internet, MPLS VPN, and cloud connectivity to deliver reliable transport options.
This mixed underlay network allows businesses to use the best available path for each application—whether that's MPLS for mission-critical apps or broadband for less critical traffic.
- Overlay Tunnels
The overlay tunnels, highlighted in red in the diagram, are secure logical connections formed between SD-WAN edges. These tunnels run over physical connections (like Internet, MPLS, LTE) and are encrypted to protect data's confidentiality and integrity.
Benefits of overlays include:
Optimizing multiple paths
Ensured end-to-end encryption
Quick failover and redundancy
Easy connectivity between branches
- OSS Applications
OSS (Operations Support Systems) applications work with the orchestrator to manage tasks such as fault management, performance monitoring, and service assurance. They play a vital role in maintaining high availability and consistent SLAs.
How the Components Work Together
These components work in sync to create a seamless and smart SD-WAN network:
Businesses access the Subscriber Web Portal to set up and manage services.
The Service Orchestrator automates service delivery and applies policies.
The SD-WAN Controller carries out control-plane functions, steering routing decisions.
SD-WAN Edge devices create secure overlay tunnels through MPLS or Internet lines.
Data is dynamically optimized and routed based on real-time network conditions.
CSP/MSP infrastructure provides the physical underlay network that supports the overlays.
OSS applications continuously monitor performance and ensure reliability.
Advantages of SD-WAN Architecture
Understanding these components clarifies why businesses are quickly adopting SD-WAN:
Agility & Automation – Zero-touch provisioning speeds up deployment from weeks to just hours.
Cost Efficiency – Using Internet and broadband links cuts reliance on costly MPLS circuits.
Application-Aware Routing – Prioritizes essential applications like VoIP and video chats.
Security – End-to-end encryption and segmentation safeguard against breaches and data leaks.
Cloud Optimization – Direct links to AWS, Azure, and SaaS platforms enhance user experience.
Centralized Management – Simplifies operations and eases IT burden.
SD-WAN Overlay vs Service Components
Aspect Overlay Tunnels (Red)Service Components (Blue)Function Carry user data securely Manage, control, and orchestrate Visibility Encrypted traffic flows Policy, configuration, monitoring Role in SD-WAN Data plane Control & management plane
This clear separation ensures that SD-WAN offers both ease of operation and strong security.
Conclusion
The SD-WAN service components come together to form a flexible and robust networking model that overcomes the drawbacks of traditional WAN. By having separate control, management, and data planes, SD-WAN gives businesses unparalleled agility, scalability, and security.
For telecom professionals, getting a grip on these components is important for designing and deploying next-gen networks. For tech enthusiasts, SD-WAN illustrates how software-defined technologies are transforming networking.
As companies keep leaning towards cloud-first strategies, SD-WAN is set to be the backbone of digital transformation, offering a solution that's ready for the future of hybrid connectivity.
