SDN Architecture for Data Plane Programmability in 5G Networks

Switching to 5G networks really needs a flexible, programmable, and automated setup. The old-school static networking models just can’t keep up with the huge traffic spikes, ultra-low latency, and varying service demands that come with 5G. This is where Software-Defined Networking (SDN) becomes essential.
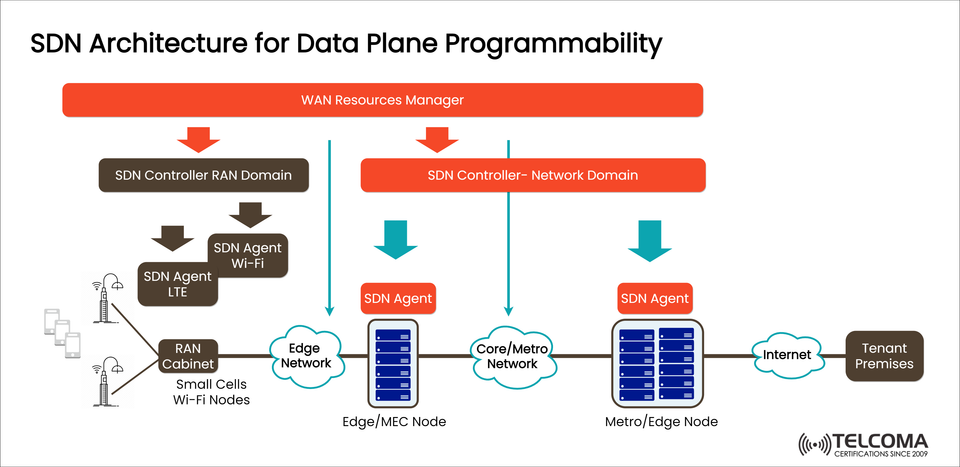
With SDN architecture for data plane programmability, operators can manage and control network resources on the fly across the RAN, edge, and core domains. The diagram we've included shows how SDN controllers, agents, and WAN resource managers work together to create a programmable, service-driven, and scalable network.
In this blog, we’ll dive into:
The basics of SDN in telecom
How SDN architecture supports data plane programmability
The connections between RAN, edge, and core networks
The advantages and applications in 5G networks
What is Data Plane Programmability?
In networking, the data plane is all about forwarding packets between devices, while the control plane makes decisions about how those packets should be handled.
Data plane programmability lets you configure, manage, and optimize packet flows in real time, without being limited by hardware. With SDN, the control plane is separated from the data plane, which allows for centralized control and programmable packet forwarding.
This setup brings a few key benefits:
More flexibility in routing and managing traffic
On-demand bandwidth and resource allocation
Support for network slicing in 5G
Easier automation and orchestration
SDN Architecture for Data Plane Programmability (Explained with Diagram)
The diagram shows a multi-layer SDN architecture that brings together the RAN, edge, metro/core networks, and tenant premises in one programmable framework. Let's break it down:
- WAN Resources Manager
At the top of the architecture is the WAN Resources Manager, which oversees resources across different domains. Its job is to enforce consistent policies, manage traffic, and ensure smooth end-to-end orchestration between the RAN and core/metro domains.
- SDN Controller – RAN Domain
This controller is in charge of the Radio Access Network (RAN). It talks to SDN agents across various RAN technologies like:
LTE (Long-Term Evolution) small cells
Wi-Fi nodes
These agents implement the rules and policies set by the controller, enabling programmability in the RAN data plane.
- SDN Controller – Network Domain
This controller manages the core and metro networks, where big data volumes get processed and routed. It communicates with SDN agents installed in:
Edge/MEC nodes
Core/Metro nodes
The aim here is to facilitate effective traffic control, load balancing, and enforcing QoS across the transport domain.
- SDN Agents
SDN agents serve as the link between controllers and the physical network elements. They carry out commands from the controllers to ensure the network functions as intended.
SDN Agent LTE & Wi-Fi – Add programmability to the RAN.
SDN Agent Edge Node – Optimizes computing and storage resources at the edge/MEC.
SDN Agent Core/Metro Node – Manages backbone transport resources and service delivery.
- Edge/MEC Node
The Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) node brings computing resources closer to users, which helps cut latency and boosts application performance. Here, SDN plays a key role in traffic offloading and content caching.
- Core/Metro Network
The core and metro networks act as the backbone of telecom setups. With SDN controllers, operators can enhance routing capabilities, manage network slicing, and ensure QoS for various services like IoT, AR/VR, and autonomous vehicles.
- Tenant Premises
Ultimately, the architecture connects to tenant premises (like businesses, industries, or cloud services). With programmable networks, operators can offer tailored slices to meet different enterprise needs.
Benefits of SDN-Based Data Plane Programmability
Embracing this architecture brings several perks for telecom operators and enterprises:
- Network Flexibility and Agility
Ability to create and change services dynamically
On-demand network resource provisioning
Orchestration across RAN, edge, and core domains
- Support for 5G Use Cases
Applications needing ultra-low latency (like autonomous vehicles and VR/AR)
Connectivity for a large number of IoT devices
Network slicing tailored for businesses and industries
- Improved Resource Utilization
Smart load balancing across different network layers
Efficient use of spectrum, compute, and storage
Energy-efficient operations
- Centralized Control and Automation
Easier management with centralized SDN controllers
Automated provisioning through APIs
Lower OPEX and quicker rollout for new services
- Enhanced Security and QoS
Fine-tuned policy enforcement across different domains
Comprehensive visibility of traffic flows
Dynamic isolation of potentially harmful traffic
Use Cases of SDN Data Plane Programmability in 5G
Smart Cities * Efficient traffic management with low latency * Better IoT device connectivity
Enterprise Private 5G * Network slicing for dedicated, secure services * Flexible connections for manufacturing facilities
Content Delivery Networks (CDN) * Faster video streaming through edge caching * Optimized content distribution with SDN-based routing
Autonomous Vehicles * Low-latency communication between vehicles * Programmable routing for critical safety applications
Healthcare * Real-time remote surgeries with guaranteed QoS * Safe, isolated network slices for sensitive information
Comparison: Traditional vs SDN-Based Data Plane
Feature Traditional Network SDN-Based Programmable Network Control Plane Distributed, static Centralized, dynamic Data Plane Hardware-bound Programmable, software-driven Flexibility Limited High Automation Manual Automated with APIs Scalability Complex Elastic and scalable5G Support Partial Full support with slicing & MEC
Conclusion
The SDN architecture for data plane programmability is foundational for today’s 5G networks. By decoupling the control and data planes, SDN allows operators to flexibly manage resources across RAN, edge, and core networks, promoting automation and scalability.
Thanks to benefits like network slicing, ultra-low latency, and better resource usage, SDN enables telecom companies and enterprises to respond to the varied demands of future services. From smart cities and autonomous vehicles to private 5G solutions and healthcare, the influence of programmable data planes will transform our connectivity and communication landscape.
As networks continue to develop, SDN-driven programmability will be key to building intelligent, adaptable, and customer-focused networks.
