Services Offered by AMF in 5G Core: Communication, Event Exposure & Location

Overview of AMF in 5G Core
In the architecture of the 5G Core (5GC), the Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF) is essential. It serves as a control-plane component, managing the signaling between User Equipment (UE) and the core network. The AMF oversees tasks related to access, mobility, and connections, ensuring that users have a seamless experience while it collaborates with other Network Functions (NFs) like the SMF (Session Management Function), PCF (Policy Control Function), and UDM (Unified Data Management).
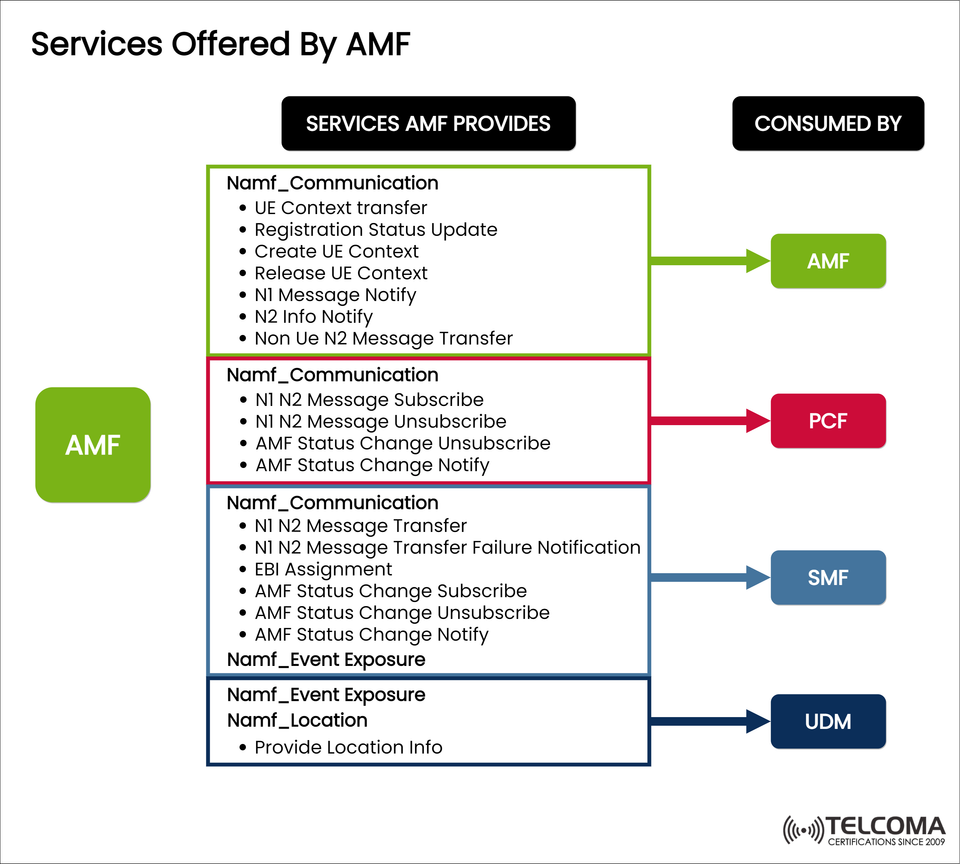
The services provided by the AMF are outlined via service-based interfaces (SBI) and are utilized by other NFs depending on their specific roles in session management, mobility handling, or policy oversight. As laid out in the image above, AMF services fall into three main categories: communication, event exposure, and location services.
Categories of AMF Services
AMF delivers a wide range of services, primarily categorized into three groups:
Namf
_Communication – Focused on signaling and managing context.
Namf
_Event Exposure – Monitoring network events.
Namf
_Location – Handling location-related data.
Each of these service categories is utilized by specific NFs based on their unique functional requirements.
AMF Communication Services (Namf
_Communication)
The communication services are fundamental to the AMF's operations. They handle UE context, signaling messages, and notifications exchanged between the AMF and other network functions.
- Services Used by AMF Itself
AMF can leverage its own services for inter-AMF signaling and managing context:
UE Context Transfer – Moves UE context between AMFs during load balancing or mobility.
Registration Status Update – Provides the latest updates on UE registration status.
Create UE Context – Sets up a new UE context.
Release UE Context – Deletes UE context when it’s no longer needed.
N1 Message Notify – Alerts about N1 signaling messages (NAS).
N2 Info Notify – Sends N2 signaling updates relevant to the RAN.
Non-UE N2 Message Transfer – Manages non-UE-specific signaling messages.
- Services Used by PCF
The Policy Control Function (PCF) taps into AMF services to implement policy decisions and steer network behavior:
N1 N2 Message Subscribe – Lets PCF subscribe to certain N1/N2 messages.
N1 N2 Message Unsubscribe – A way for PCF to unsubscribe.
AMF Status Change Unsubscribe – Stops tracking changes in AMF status.
AMF Status Change Notify – Notifies PCF of changes in AMF status.
These services help PCF monitor signaling and make policy-guided choices based on AMF updates.
- Services Used by SMF
The Session Management Function (SMF) relies heavily on AMF communication for managing session-related signaling:
N1 N2 Message Transfer – Facilitates both NAS and RAN signaling messages.
N1 N2 Message Transfer Failure Notification – Reports any failure in message delivery.
EBI Assignment – Assigns EPS Bearer IDs for interworking situations.
AMF Status Change Subscribe – SMF subscribes to updates regarding AMF status.
AMF Status Change Unsubscribe – Stops receiving those updates.
AMF Status Change Notify – Informs SMF about AMF’s operational state changes.
SMF utilizes these services to ensure effective session setup, adjustments, and tear-down.
AMF Event Exposure Services (Namf
_Event Exposure)
Event exposure services allow for the monitoring and reporting of significant network events. They enable other NFs to subscribe to conditions and receive alerts when specified criteria are met:
Consumed by SMF – SMF subscribes to events like changes in mobility states, UE reachability, or registration updates to enhance session management.
Consumed by UDM – UDM could use event exposure for aligning subscriber data management with UE activities.
Event exposure boosts visibility throughout the network, aiding automation and orchestration.
AMF Location Services (Namf
_Location)
Location services are another vital function offered by AMF. They provide location information about the UE to other NFs, ensuring accuracy in services reliant on user positioning:
Provide Location Info – This service is mainly utilized by UDM and other functions needing subscriber location data, like emergency services or location-specific applications.
Accurate location data enhances user experience and helps meet regulatory standards.
Summary Table of AMF Services
Service CategoryKey FunctionsConsumed By
Namf
_Communication | UE Context Transfer, Registration Update, Message Notify, Status Change | AMF, PCF, SMF
Namf
_Event Exposure | Event Subscription and Notification | SMF, UDM
Namf\n_Location | Provide Location Info | UDM
Importance of AMF Services in 5G
The services provided by AMF are crucial for:
Mobility Management – Enabling smooth UE transitions across networks.
Session Continuity – Supporting seamless handovers and maintaining active sessions.
Policy Control – Assisting PCF in enforcing QoS and charging regulations.
Service Orchestration – Helping SMF and UDM optimize resources and sustain session quality.
Regulatory Compliance – Facilitating lawful interception and emergency services via location and event exposure functions.
Conclusion
The AMF stands as the central hub for signaling and mobility management in the 5G Core. By offering communication, event exposure, and location services, it allows for smooth interactions among NFs such as SMF, PCF, UDM, and other AMFs. These services guarantee that users enjoy uninterrupted mobility, reliable connectivity, and effective policy enforcement.
For professionals in telecommunications and network architecture, grasping the services provided by AMF is key to designing robust, future-ready 5G networks. These networks must cater to a variety of use cases, ranging from enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) to critical communications and IoT.
