Smart BAN Interoperability & Heterogeneity Management Constraints Explained

Body Area Networks, or BANs, are key players in the future of wireless communication. They started out mainly for healthcare purposes, like monitoring patients, but now Smart BANs are branching out into areas such as sports, defense, personal fitness, and smart IoT environments.
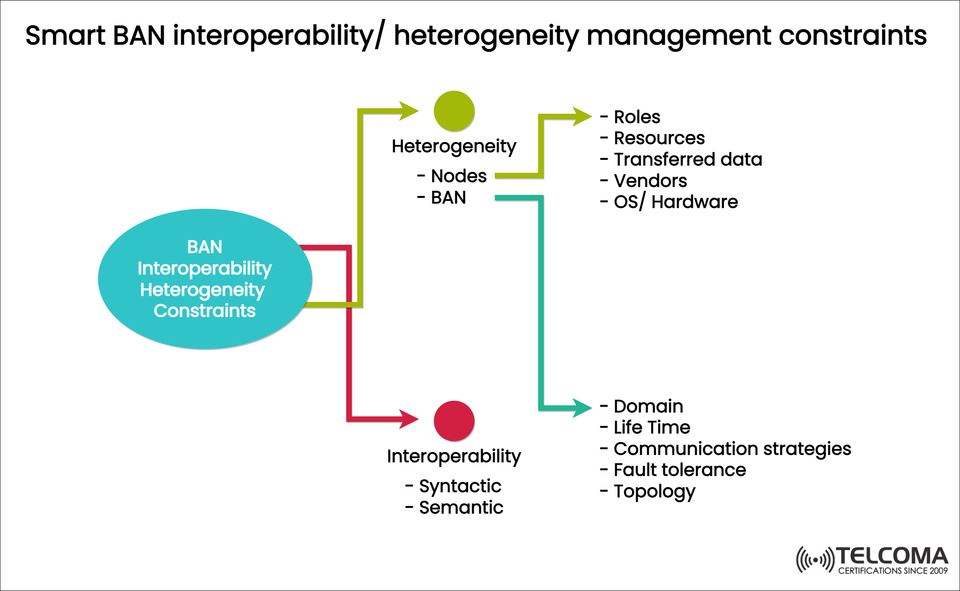
Still, Smart BANs run into two big problems: interoperability and heterogeneity. These issues are crucial because they can either allow different devices to work together smoothly or lead to chaos and inefficiency.
This article dives into the challenges surrounding Smart BAN interoperability and heterogeneity management, using a framework from the accompanying diagram. This should help telecom experts and tech fans grasp the technical hurdles and how to tackle them.
What is Interoperability in Smart BANs?
Interoperability is all about how well systems, devices, or applications can share and understand each other's information. In the context of Smart BANs, it makes sure that various devices—often from different manufacturers—can communicate effectively.
There are two main layers of interoperability:
Syntactic Interoperability
This focuses on how data is structured and formatted.
It ensures that devices can read messages even if they come from different systems.
For example, standards like JSON, XML, and HL7 for healthcare data.
Semantic Interoperability
This makes sure the meaning of the exchanged data stays intact.
It helps avoid misunderstandings between devices.
For instance, a blood glucose reading should be understood the same way across various devices, whether for healthcare or fitness tracking.
Key Constraints Linked to Interoperability:
Domain alignment – devices should be compatible within certain functional areas.
Lifetime management – devices might have different lifespans but should still share data smoothly.
Communication strategies – a unified approach is necessary to prevent miscommunication.
Fault tolerance – interoperability needs to hold up even if one device or node goes down.
Network topology – the arrangement of devices can influence how communication takes place (like star, mesh, or hybrid setups).
Understanding Heterogeneity in Smart BANs
Heterogeneity refers to the mix of devices, software, and resources found in Smart BANs. This diversity is a double-edged sword, offering both advantages and challenges.
The diagram points out sources of heterogeneity such as:
Nodes – things like sensors, actuators, gateways, and wearables.
BANs – different BANs interacting in a shared space.
Expanded Constraints due to Heterogeneity:
Roles – various devices (sensors, hubs, gateways) need to coordinate their specific tasks.
Resources – differences in processing power, memory, and battery life can impact how well everything works.
Transferred data – bandwidth and latency differ based on device types.
Vendors – proprietary designs can create compatibility issues.
OS/Hardware differences – platforms like Android Wear, iOS, or embedded Linux need to find ways to work together.
If we don't manage heterogeneity well, Smart BANs run the risk of becoming fragmented, inefficient, and exposed to security risks.
The Relationship Between Interoperability and Heterogeneity
Interoperability helps devices communicate smoothly, but heterogeneity brings its own challenges. Balancing both can be tricky:
Heterogeneity adds diversity. Different vendors bring in various sensors, operating systems, and architectures.
Interoperability ensures compatibility. Even with differences, devices need to communicate using a shared ‘language.’
In telecom, overlooking either aspect can lead to:
Delays in crucial healthcare monitoring.
Wasted energy in wearable IoT devices.
Security issues if systems with different standards don’t agree on encryption.
Real-World Examples Affected by These Issues
- Healthcare Monitoring Systems
Challenge: There's a mix of wearables (like blood pressure cuffs, ECGs, and glucose monitors) from various manufacturers.
Impact: Interoperability is key so that healthcare providers can read and combine data from all these platforms. Managing heterogeneity ensures devices function reliably throughout their lifespan.
- Smart Sports and Fitness
Challenge: Wearables including smart shoes, wristbands, and sensors come from different ecosystems.
Impact: Syntactic interoperability aligns communication standards (like BLE and ANT+), while managing heterogeneity ensures efficient energy use for ongoing performance tracking.
- Defense Applications
Challenge: Body Area Networks (BANs) used by soldiers must integrate seamlessly with command networks.
Impact: It's crucial to have reliable communication strategies, and managing heterogeneity ensures that gear from various defense contractors can work together seamlessly.
- IoT Smart Environments
Challenge: Multiple BANs operate in smart homes and offices, resulting in cross-domain data flows.
Impact: Effective topology alignment and semantic interoperability are vital to avoid conflicting commands between devices.
Strategies to Tackle BAN Interoperability and Heterogeneity Challenges
- Standardization Initiatives
Protocols like IEEE 802.15.6 offer guidelines specific to BANs.
Implementing HL7 FHIR in healthcare boosts semantic interoperability.
- Middleware Solutions
Serves as a translator among different devices.
For example, IoT middleware platforms help normalize diverse data formats.
- Resource-Aware Communication Protocols
Designed for low-energy devices.
Examples include BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) and ZigBee.
- Fault-Tolerant Architectures
Mesh topologies enhance resilience.
Having redundancy in gateways and relays.
- Collaboration Among Vendors & Open Ecosystems
Fostering multi-vendor interoperability testing.
Supporting open APIs and SDKs.
Key Differences Between Interoperability and Heterogeneity Issues
Aspect Interoperability Heterogeneity Focus Data exchange and interpretation Diversity of devices and resources Core Types Syntactic, Semantic Nodes, BANs Key Challenges Communication, fault tolerance, semantics Vendors, OS/Hardware, roles Impact on BANs Ensures smooth communication Manages device variety Management Strategy Standards, middleware, unified protocols Resource balancing, vendor alignment
Why Telecom Professionals Should Pay Attention
For telecom professionals, Smart BANs are a vital area in the realms of 5G, 6G, and IoT ecosystems. Effectively managing interoperability and heterogeneity can:
Enhance Quality of Service (QoS) for essential applications.
Lower operational costs by reducing incompatibility problems.
Improve security with consistent data exchange standards.
Aid scalability as the number of connected devices keeps rising.
Conclusion
Smart BANs are changing how we connect people, devices, and networks in areas like healthcare, defense, fitness, and IoT ecosystems. Nonetheless, the interoperability and heterogeneity challenges pointed out earlier are significant hurdles to broad adoption.
By grasping these issues—spanning syntactic and semantic data exchange to vendor-driven hardware diversity—telecom experts can implement more efficient, secure, and scalable BAN solutions.
The future of Smart BANs hinges on collaboration, standardization, and smart system design. Only by addressing these challenges can we fully realize the potential of body-centric communication networks in the age of 5G, 6G, and beyond.
