Standalone Private 5G Networks Isolated from Public Infrastructure
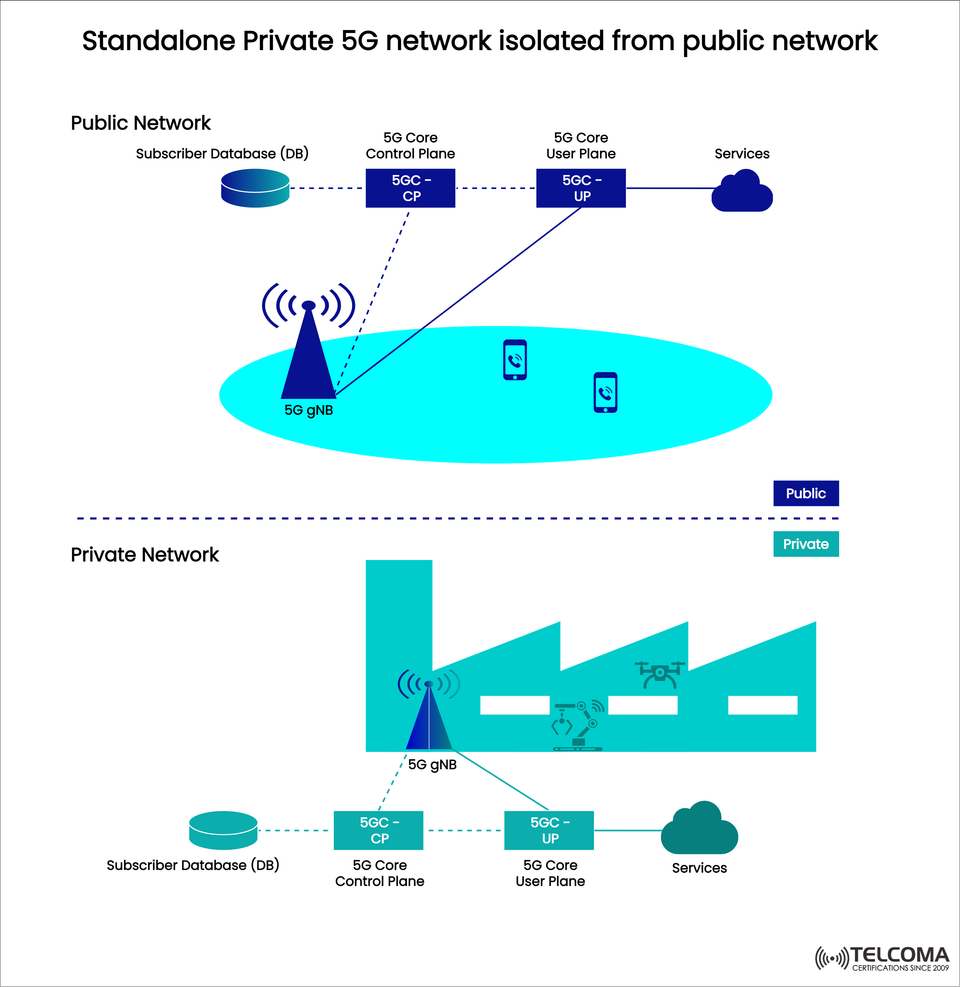

Standalone Private 5G Network: Completely Separate from Public Networks
The rise of 5G technology has created new opportunities for both public mobile networks and private enterprise networks. Public 5G offers broad coverage and mobility, but businesses increasingly need secure, dedicated, and ultra-reliable connections that suit their specific requirements.
This has led to the development of standalone private 5G networks, which function entirely independent of public infrastructure. Unlike hybrid or shared systems, these networks grant companies complete ownership over the radio access, core, spectrum, and services.
The diagram above showcases this setup, clearly distinguishing between the public 5G network and the private enterprise 5G implementation. Let’s dive into how it operates, its benefits, challenges, and practical uses.
Public vs. Standalone Private 5G Networks
Public 5G Network
Managed by telecom providers, public 5G networks cater to both consumers and businesses across vast areas.
Centralized functions for control and user plane.
A managed subscriber database for authentication.
Mobility support across different regions and nations.
Standalone Private 5G Network
Implemented by businesses in a localized area, typically in industrial sites or campuses.
Complete independent 5G core (control and user planes).
An in-house subscriber database for authentication.
Data traffic remains entirely within the organization’s boundaries.
Architecture of an Isolated Standalone Private 5G Network
The diagram outlines two clearly defined domains:
Public Network Components
Subscriber Database (DB): Contains user credentials for mobile operator clients.
5G Core Control Plane (5GC-CP): Manages signaling, authentication, and mobility tasks.
5G Core User Plane (5GC-UP): Oversees data sessions and connects to services provided by operators.
5G gNB: Serves public mobile devices across wide coverage areas.
Private Network Components
Private Subscriber Database (DB): Manages identities of enterprise devices (like robots, IoT sensors, AR devices).
Private 5GC-CP: Takes care of authentication, policy, and signaling specifically for enterprise devices.
Private 5GC-UP: Ensures sensitive enterprise data remains on-site.
Private gNB: Connects enterprise devices to the private 5G network, separate from public systems.
Services: Essential applications such as drones, automation systems, and AI processes.
Key Difference
Unlike shared models, there are no overlaps or shared gNBs between the public and private systems. These networks are fully segregated, ensuring data sovereignty and independence.
Why Choose an Isolated Standalone Private 5G Network?
- Maximum Security
Data never passes through public infrastructure.
Strong isolation prevents the risk of sensitive information leaks.
- Full Control
Enterprises can oversee their own subscriber base, policies, and settings.
No dependence on operator cores for control or signaling.
- Guaranteed Performance
Companies can allocate resources as needed for mission-critical applications.
No competition for spectrum or RAN with public subscribers.
- Regulatory Compliance
Sensitive sectors (like defense, healthcare, energy) can adhere to strict regulations by keeping traffic local.
- Customization
Specialized QoS (Quality of Service) profiles for unique use cases.
Seamless integration with enterprise IT and OT systems.
Challenges of Standalone Private 5G
Even with its perks, standalone private 5G setups encounter some challenges:
High Cost: Requires significant investment in full infrastructure (RAN, core, spectrum, services).
Spectrum Access: Businesses need to obtain dedicated spectrum licenses or use unlicensed bands.
Operational Expertise: Skilled personnel or partnerships are necessary to oversee the 5G core and RAN.
Limited Mobility: Devices face challenges roaming into public networks unless integration models are in place.
Enterprise Use Cases for Standalone Private 5G
Standalone networks shine in areas where security, performance, and independence are crucial.
Smart Manufacturing
Real-time automation and robotics.
Predictive maintenance using AI and IoT sensors.
Instantaneous industrial control systems.
Healthcare
Private hospital 5G networks enabling remote surgeries.
Secure transfer of patient data within hospital premises.
Energy & Utilities
Monitoring the grid with IoT devices.
Secure communication for vital energy infrastructure.
Transportation & Logistics
Smart ports and airports with dedicated connections.
On-site management of autonomous vehicles and drone operations.
Defense and Government
Highly sensitive scenarios where complete isolation from public networks is essential.
Standalone Private 5G vs Hybrid and Shared Models
Feature Standalone Private 5GShared RAN/Hybrid 5GControlFull enterprise control Shared with operator Security Maximum (fully isolated)Medium (shared aspects)Deployment Cost High Moderate Spectrum Requirement Dedicated enterprise spectrum Shared or hybrid spectrum options Mobility Support Limited to enterprise network Seamless roaming via public core Customization Full enterprise customization Limited by operator constraints
Why Enterprises Opt for Isolation
In industries where data integrity, sovereignty, and security are vital, a standalone private 5G network often stands out as the only feasible choice.
Examples:
A pharmaceutical factory that ensures its intellectual property is kept on-site.
A defense contractor safeguarding confidential discussions.
A power grid operator ensuring that critical infrastructure remains strong against cyber threats.
Future Outlook: Standalone Private 5G
As 5G adoption matures, standalone private networks are expected to expand, particularly in:
Sensitive data sectors that can't use public infrastructure.
Areas where governments allocate dedicated enterprise spectrum.
Companies implementing network slicing in 6G, which could push isolation models further.
Future advancements like edge computing, AI-driven orchestration, and automation platforms will simplify management and reduce costs for private 5G systems.
Conclusion
Standalone private 5G networks offer the highest independence and security for businesses. By completely separating from public infrastructure, organizations can achieve:
Full authority over network policies and subscriber management.
Maximum protection for sensitive data.
Custom performance for essential applications.
While the costs and complexities may be higher compared to shared models, the benefits in security, compliance, and reliability make standalone private 5G a critical strategy for industries where failure or compromise isn't an option.
In the evolving telecom landscape, standalone private networks are set to play a significant role in shaping the future of industrial connectivity, critical infrastructure, and digital transformation.
