System Context for Autonomic Networking Operation in 5G Networks
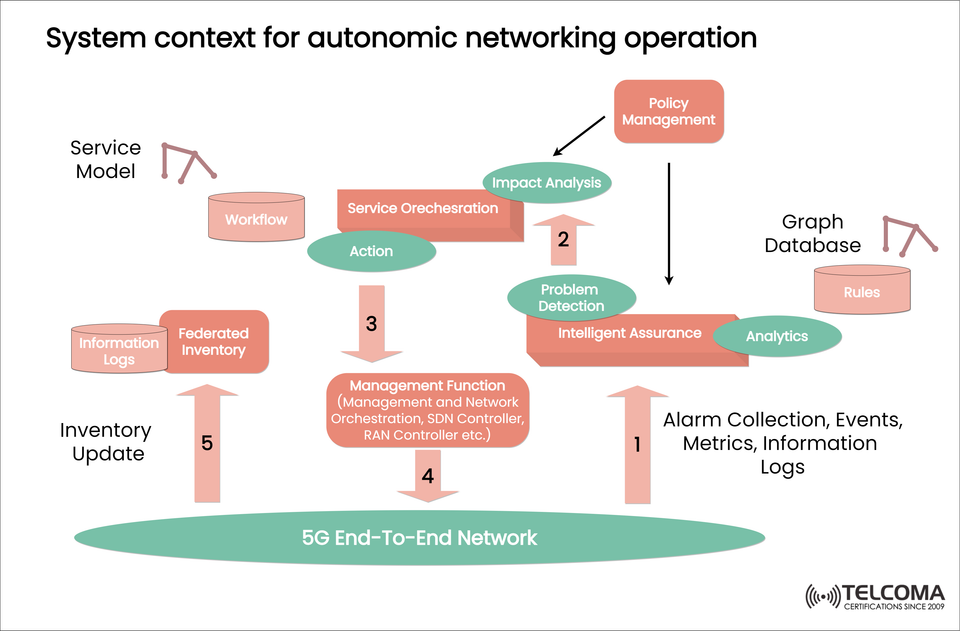

System Context for Autonomic Networking Operation in 5G
Autonomic networking is required to manage the complexity of 5G networks, as it enables the end-to-end network to self-manage, drawing upon intelligent assurance, orchestration, analytics, and automation. The aforementioned image depicts a closed-loop system context for autonomic networking operation; specifically, it can provide an understanding of how all of the components interact to achieve optimal network operation.
🔍 What is Autonomic Networking?
Autonomic networking represents self-managing networks that can, in a largely autonomous fashion, self-monitor, self-analyze, and self-heal because manual or human intervention is minimised. The nature of 5G, with its requirements for reliability, low latency, and dynamic resource allocations, mandates autonomic networking.
🧠 Intelligent Assurance and Problem Detection
Step 1: The process acquires alarms, events, parameters, and information logs from the end-to-end 5G network.
Step 2: The Intelligent Assurance will draw upon the alarms, events, measurements, and information logs, applying analytics and rules from the graph database, and using the results of the problem detection capabilities, to detect anomalies and performance degradation.
What are the key components?
Analytics engine: Real-time and historical data analysis.
The Graph Database and its Rules: The topology of the network, along with logic that can be used for decision making.
Policy Management: Where service providers assign operational thresholds and their operational behaviours.
Impact Analysis and Service Orchestration
When an issue is detected:
- Impact Analysis determines the scope and criticality of the issue.
- Policy Management affects how the network should respond according to rules and SLAs.
- Service Orchestration then automatically implements the corrective steps.
This ensures:
- A quicker response.
- Less manual effort.
- Assurance of service continuity.
Closed-Loop Automation through Management Functions
Step 3: The orchestrated action is passed to the Management Function which encompasses:
- Network Orchestration
- SDN Controller
- RAN Controller
Step 4: These control layers communicate directly with the 5G End-to-End Network and execute the required actions e.g. reconfigure, reroute, scale up/down etc.
Federated Inventory with Feedback Loop
Step 5: After making the changes, the inventory changes are pushed to a Federated Inventory that synchronizes with the Information Logging to ensure the network states are up-to-date.
This feedback loop is essential to ensure:
- Data consistency across the system
- Continuous learning
- Further analytics and orchestration
Key Functions Summary (Tabulated Format)
Function Description
Intelligent Assurance Collecting, gathering metrics, logs, alarms for analysis
Problem Detection Detecting anomalies and faults.
Impact Analysis Assessing impact scope and severity
Policy Management Indicates how to guide decision-making using rules and service models
Service Orchestration Facilitate and execute corrective actions
📡 Advantages of Autonomic Networking in 5G
Autonomic networking architecture in 5G can provide numerous operational and business benefits, including:
🌐 Operational Effectiveness
Automated Fault Recovery: Optimize the handling of complex networks to resolve faults in real time, while minimizing manual troubleshooting.
Real time decisions: Be able to take actions that are driven by analytics in response to the network's real time behaviors.
Resource Optimization: Be able to allocate resources dynamically to align with the service demand and network load.
🔒 Improved Network Reliability and Performance
Proactive Detection of Problems: Detect anomalies earlier so that services don't degrade.
SLA Conformance: Policy based orchestration ensures the service is aligned with the agreed-to service quality.
Consistent Inventory Updates: Ensures that inventory stays updated with network administration effort and configuration drifts are avoided.
🤖 Integration of AI/ML and Intelligent Assurance
AI/ML Algorithms: Enable pattern spotting, efficiency forecasting and root-cause forecasting.
Continuous Learning: Enable a feedback loop that helps the system adapt to changing network behaviors and continues to develop.
📈 Use Case Scenarios for telco Operators
Specific cases of how autonomic networking will help bring benefits to 5G are:
Use Case 1: Dynamic Network Slicing
Situation: QoS and SLA for different applications: IoT, URLLC, eMBB.
Solution: IT Services orchestrate the network in response to the analytics and policies developed over the lifetime of the network.
Use Case 2: Self-Healing Networks
Situation: There is always some downtime from a hardware or software failure.
Solution: Automated recovery actions are triggered as the autonomic network detects a failure and performs a problem detection and impact analysis.
Technologies Supporting Autonomic Networking
For autonomic operations to occur, the following technology stack must be integrated:
Technology Function in Autonomic Networking
AI/ML Prediction, detection, optimization
SDN Centralized control of network behavior
NFV Dynamic instantiation and scaling of network functions
Network Orchestration Automation of service lifecycle management
Graph Databases Real-time topology and dependency mapping
Policy Engines SLA, QoS, and security rule enforcement
Final Thoughts
The system context for operation of autonomic networking is a vision of how modern 5G networks are expected to operate; intelligently, autonomously, and adaptively. The number of connected devices will continue to grow, expectations for ultra-low latency access will be demanded, and service level agreements will become more complicated, while manual network management will become impractical.
Utilizing a closed-loop architecture, driven by data, policies, and automation, will improve network efficiency, while permitting innovation, and the faster deployment of future services such as 6G, AI-native, and more.
The Role of Closed-Loop Automation in Network Autonomy
Closed-loop automation is fundamental to autonomic networking, which follows and adheres to a continuous cycle of:
Observation (a.k.a. alarm collection, events, metrics, logs)
Analysis (intelligent assurance, AI data driven analytics)
Decision Making (impact analysis, policy rules and orchestration logic)
Execution (activities applied by management functions e.g. SDN or RAN
🧩 How Components Work Together - Simplified Flow
Take an illustrated look through each step of the system interactions illustrated in the image:;
Step Component Description
1 Intelligent Assurance Provides real-time information and forwards it to analytics
2 Problem Detection & Impact Analysis Detects faults, predicts impacts, and invokes corrective actions
3 Service Orchestration Calls for pre-defined or AI defined actions
4 Management Function Communicates with the network and makes modifications
5 Federated Inventory Tracks information and contents in the logs to better the accuracy of the components of the system
