Technical Characteristics of F5G: Enhanced Broadband, Low Latency, and Full-Fiber Connectivity

Technical Features of F5G: Transforming Fixed Network Performance
The fixed networks have entered their fifth generation, termed F5G (Fifth Generation Fixed Networks). Although mobile 5G gets a lot of the spotlight, F5G is equally essential, providing gigabit broadband, full-fiber connections, and incredibly reliable low-latency experiences.
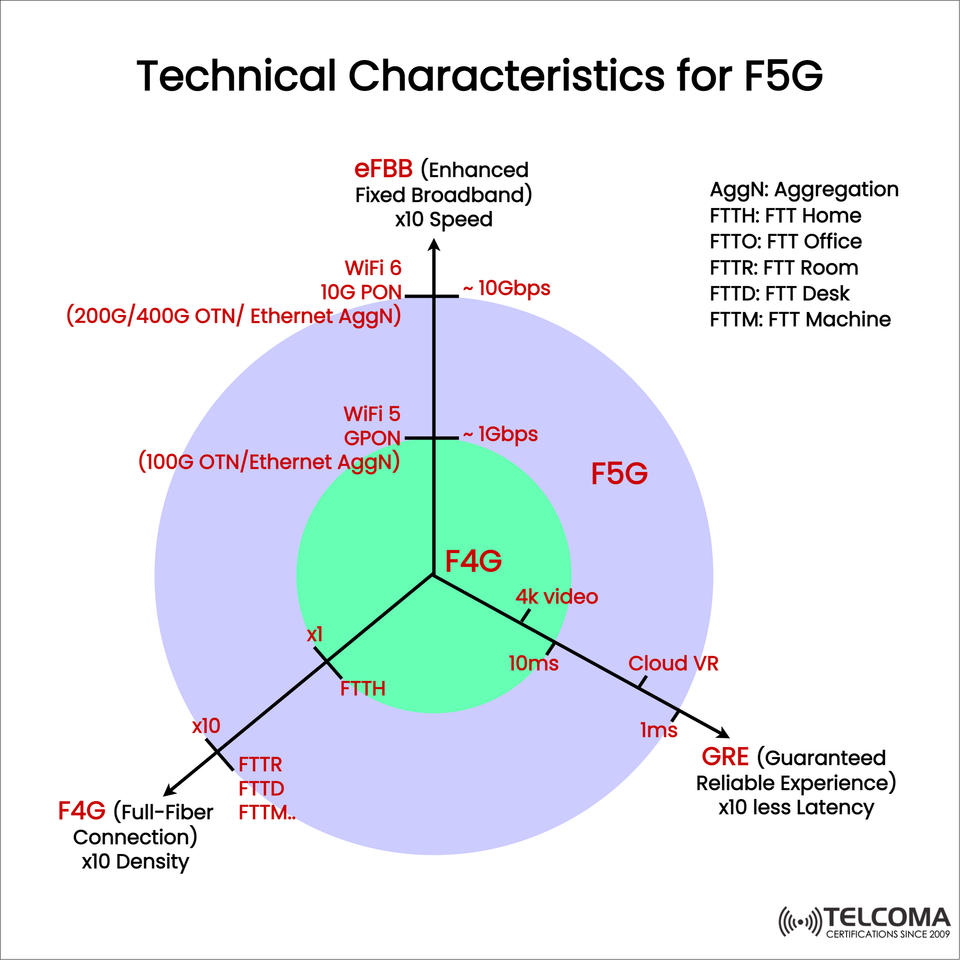
The diagram included showcases F5G’s three main pillars—enhanced broadband (e FBB), full-fiber connection (FFC), and guaranteed reliable experience (GRE)—along with the technical achievements that differentiate it from earlier generations like F4G.
In this blog, we’ll dive into these technical features and discuss how they’re shaping the future of connectivity.
Quick Look at F5G
At its essence, F5G builds upon what F4G offered but brings significant enhancements across three key areas:
e FBB (Enhanced Fixed Broadband): Speeds reaching up to 10 Gbps, thanks to 10G-PON and Wi Fi 6.
FFC (Full-Fiber Connection): Extending fiber beyond just homes to every room, desk, and machine.
GRE (Guaranteed Reliable Experience): Reducing latency by a factor of ten, down to just 1 millisecond.
Combined, these features establish F5G as the fixed equivalent of 5G mobile networks, supporting rich services like Cloud VR, 8K video streaming, and Industry 4.0 applications.
Pillar 1: e FBB (Enhanced Fixed Broadband)
Enhanced Fixed Broadband (e FBB) marks a significant leap in bandwidth capacity with F5G.
Key Features:
Speed Boost: Jumping from around 1 Gb ps in F4G (GPON + Wi Fi 5) to about 10 Gb ps in F5G (10G-PON + Wi Fi 6).
Technologies Involved: * 10G PON (Passive Optical Network) * WiFi 6 (802.11ax) for enhanced speed and efficiency * 200G/400G OTN (Optical Transport Network) / Ethernet Aggregation for scalable backhaul
What This Means:
Supports ultra-high-definition video (4K/8K) with no buffering.
Allows for multiple devices to be used simultaneously at home and in businesses.
Delivers cloud-scale bandwidth, which is crucial for AI, AR/VR, and gaming.
Pillar 2: FFC (Full-Fiber Connection)
While F4G primarily connected fiber to homes (FTTH), F5G takes it further into every environment—offices, rooms, desks, and machines.
Deployment Models:
FTTH: Fiber to the Home
FTTO: Fiber to the Office
FTTR: Fiber to the Room
FTTD: Fiber to the Desk
FTTM: Fiber to the Machine
Benefits of Full-Fiber Density:
Improved density by a factor of 10 over F4G
Reliable end-to-end fiber connectivity
Enhanced network stability and resilience
Supports industrial automation, healthcare systems, and smart city technologies
In short, FFC makes fiber ubiquitous, establishing it as the most dependable medium for future-proof connectivity.
Pillar 3: GRE (Guaranteed Reliable Experience)
The third foundational element of F5G is GRE (Guaranteed Reliable Experience), focusing on latency and reliability.
Technical Advancements:
Latency cut down from 10 ms (F4G) to 1 ms (F5G)
Ultra-low latency accommodates Cloud VR and real-time gaming
Enhances mission-critical services like telehealth, self-driving cars, and industrial IoT
Why GRE Matters:
Traditional fixed networks mainly focused on throughput but often fell short on consistent latency.
GRE guarantees a stable, predictable user experience, which is key for immersive and time-sensitive applications.
F4G vs. F5G Comparison
Feature F4 G F5 G Speed~1 Gbps~10 Gb ps Technology GPON, Wi Fi 510G PON, Wi Fi 6Fiber Reach FTTH FTTH, FTTO, FTTR, FTTD, FTTMLatency~10 ms~1 msApplications4K Video Cloud VR, AR, Smart Cities, Industry 4.0Transport Networks100G OTN200G/400G OTN
Applications Powered by F5G
F5G is not just about faster speeds—it transforms the use cases for fixed networks across various industries:
Consumer Applications
Immersive VR/AR Experiences
Cloud Gaming with virtually no lag
UHD/8K video streaming
Multi-device home networks supported by WiFi 6
Enterprise Applications
Smart Offices utilizing FTTO and FTTR
Smooth video conferencing and collaboration
AI-powered applications needing real-time data
Industry & Smart Cities
FTTM driving Industry 4.0 automation
Healthcare: remote surgery with ultra-low latency
Smart City infrastructure (IoT sensors, traffic management, energy grids)
The Importance of F5G in the Telecom Sector
While mobile 5G gets a lot of buzz, F5G is just as significant:
It provides backbone connectivity for mobile networks.
Ensures consistent quality of service (QoS) for high-bandwidth, low-latency applications.
Promotes fiber adoption at unprecedented density.
Enables digital transformation across various sectors—from entertainment for consumers to essential industries.
Looking Ahead to F6G
Research is already kicking off for the next generation of fixed networks (F6G). Expected advancements include:
Terabit-level fixed broadband
AI-driven network management
Eco-friendly fiber infrastructure
Deep integration with 6G mobile networks
This path highlights the interconnected growth between fixed and mobile ecosystems, ensuring they both advance together to support a digitally connected future.
Understanding Fixed Network Generations: From F1G to F5G and Beyond
The progress of fixed networks is a crucial part of the story in modern telecommunications. Although mobile generations like 2G through 5G often grab the spotlight, fixed networks are the backbone that enable everything from home broadband to 5G backhaul and cloud services.
This guide will walk you through the evolution from F1G to F5G, showing how fixed networks developed over the years. We'll also take a closer look at the key features of F5G, which represents the latest advancement in fiber-based communications.
Quick Overview of Fixed Network Generations
Generation Bandwidth (Down/Up)Services Architecture Key TechnologiesTimelineF1G<2 Mb ps / <2 Mb ps Voice, Dial-up Internet COLEPSTN/ISDN1990F2G2–30 Mb ps / ~512 Kbps HSI, SD Video DSLAMADSL/ADSL2+2000F3G30–100 Mb ps / 15–100 Mb ps HD Video FTTC/FTTBVDSL22007F4G100–1000 Mb ps / 50–500 Mb ps UHD 4K Video FTTH/FTT dp GPON, G.fast2010–2016F5G1–10 Gb ps / 1–10 Gbps VR, Cloud Gaming, Smart Cities FTTH/FTTR10G-PON, Wi Fi 62018–Present
F1G: The Narrowband Era (1988–1993)
Speeds: <2 Mbps down / <2 Mbps up
Services: PSTN/ISDN voice, dial-up Internet
Architecture: COLE
Technologies: RJ11, RJ45, ISDN standards
Timeline: Launched around 1988, with adoption by 1990
This was the voice-first generation. The internet was available, but only at dial-up speeds that struggled to load even basic webpages.
F2G: Early Broadband (1999–2003)
Speeds: 2–30 Mbps down / 512 Kbps up
Services: High-speed Internet (HSI), SD video
Architecture: DSLAM
Technologies: ADSL/ADSL2+, WiFi (802.11b/a)
Timeline: Came out in 1999 and became widely used by 2000
This marked the start of “always-on broadband,” allowing for video streaming, early online gaming, and quicker downloads.
F3G: Fast Broadband Era (2006 Onwards)
Speeds: 30–100 Mbps down / 15–100 Mbps up
Services: HD video, cloud services
Architecture: FTTC/FTTB
Technologies: VDSL2, WiFi (802.11g)
Timeline: Rolled out in 2006
F3G was a transition phase. Fiber reached the main cabinets and buildings while copper handled the last stretch—striking a balance between cost and higher speeds.
F4G: Ultra-Fast Broadband (2010–2016)
Speeds: 100 Mbps–1 Gbps down / 50–500 Mbps up
Services: 4K/UHD video, enterprise cloud use
Architecture: FTTH, FTT dp
Technologies: GPON, G.fast, WiFi (802.11n/ac)
Timeline: GPON deployments (2010–2012), G.fast (2014–2016)
F4G brought fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) into the mainstream. It laid the groundwork for video-heavy services and set up telecoms for the future.
Conclusion
The technical features of F5G—eFBB, FFC, and GRE—distinguish it as a revolutionary phase in fixed networks.
eFBB guarantees 10 Gbps broadband for both homes and businesses.
FFC ensures fiber is accessible everywhere—home, office, room, desk, and machine.
GRE provides a guaranteed reliable experience with latency as low as 1 ms.
For telecom professionals, F5G represents a major opportunity in fiber deployment and service innovation. For tech fans, it’s the unseen force that powers VR, cloud gaming, smart cities, and AI-centric industries.
As F5G spreads globally, it establishes a groundwork for a future where connectivity is limitless, immersive, and highly reliable.
