Test Automation Strategy for 5G Architecture: Enhancing Efficiency and Reliability
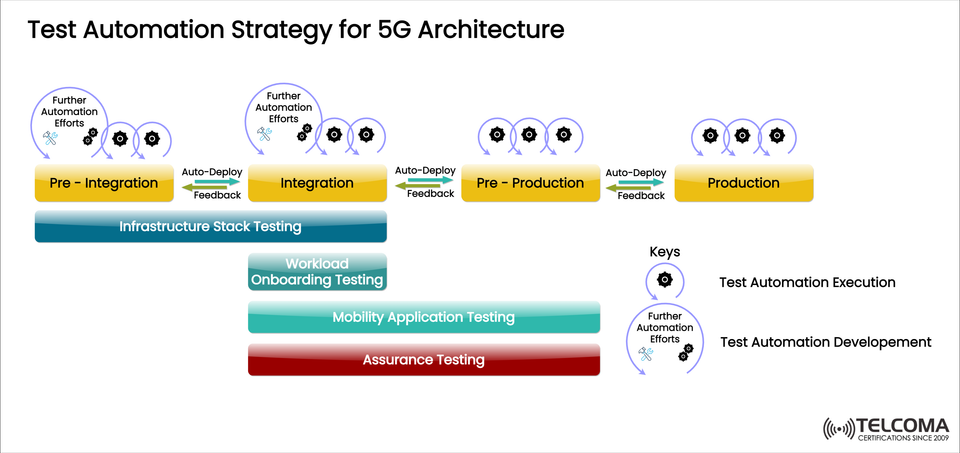

Test Automation Strategy for 5G Architecture
The rollout of 5G networks isn't just about faster internet; it also adds a layer of complexity in how we deploy and validate these systems. That’s where test automation comes into play. It’s a crucial part of the new 5G architecture, helping us ensure that everything runs smoothly, reducing the chances for human error, and speeding up delivery times.
The image provided outlines a comprehensive test automation strategy tailored for 5G systems. It highlights key phases — Pre-Integration, Integration, Pre-Production, and Production — and stresses the importance of continuous feedback and automated deployment methods.
Understanding the Test Automation Lifecycle
The lifecycle of 5G test automation combines both the execution and development processes throughout all deployment phases. Each step in the 5G architecture has its own focus, ensuring that the entire system remains intact and performs optimally.
Key Phases of the 5G Test Automation Strategy
Phase Description Automation Focus Pre-Integration Initial validation of the infrastructure stack and testing frameworks. Automation of setup scripts, basic validation tests. Integration Ensures interoperability between software and hardware components. Automated integration, API, and system-level tests. Pre-Production Staging environment for simulating real-world workloads. Continuous integration (CI), regression, and mobility testing. Production Live deployment validation and assurance testing. Continuous monitoring, anomaly detection, and feedback-driven improvements.
All these phases are linked through auto-deploy and feedback loops, making sure every change is checked before proceeding.
Phase 1: Pre-Integration – Building the Foundation
The Pre-Integration phase is all about validating the infrastructure stack, which is essential for 5G operations. Automation efforts here include:
Infrastructure Stack Testing: Checking the hardware and software setups that form the core of 5G environments.
Environment Setup Automation: Using Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) tools like Terraform or Ansible to automatically create consistent environments.
Static Code Analysis: Tools such as Sonar Qube or Check marx identify potential issues before integration kicks off.
This phase makes sure that the underlying infrastructure is capable of handling complex workloads, setting the stage for the next integration step.
Phase 2: Integration – Bridging Systems and Workloads
During the Integration phase, we verify how different modules—like network functions, applications, and control planes—interact with each other.
Key Automation Strategies in Integration:
Workload Onboarding Testing: Checking how new network functions or apps are added to the 5G platform.
API and Interface Validation: Ensuring that network functions and cloud-native elements communicate properly through automated API tests.
Continuous Integration (CI): Automated pipelines that deploy and test each component update in real-time.
Feedback loops are vital here, enabling the system to quickly spot integration problems and initiate corrective actions through automated redeployment or rollbacks.
Phase 3: Pre-Production – Preparing for Live Operations
The Pre-Production phase mirrors the production environment, allowing for near-real testing conditions ahead of actual deployment.
Automation Focus Areas:
Mobility Application Testing: Automated tests that simulate user mobility across different cells, checking handovers and latency.
Load and Stress Testing: Tools like JMeter or Locust assess how the network performs under heavy user loads.
Regression Testing: Ongoing regression testing ensures that updates don’t disrupt existing features.
By harnessing automation, telecom teams can conduct thorough tests across virtualized and containerized 5G functions, speeding up time-to-market while ensuring reliability.
Phase 4: Production – Continuous Validation and Assurance
In the Production phase, we focus on live monitoring and validation through automated assurance processes.
Assurance Testing Automation:
Real-time Monitoring: AI-driven observability tools detect performance anomalies in real-time.
Self-healing Systems: Automated scripts can restart failing services or shift workloads on their own without human input.
Continuous Feedback Loops: Insights from production feed back into the CI/CD pipeline, enhancing future releases.
Automation here shifts network operations from being reactive to being predictive and adaptive, aligning closely with the self-optimizing goals of 5G architecture.
Core Testing Layers in 5G Test Automation
Infrastructure Stack Testing
This ensures that the foundational layers (compute, storage, and network) are optimized for 5G workloads. This includes checking Kubernetes clusters, virtual machines, and hardware acceleration components.
Workload Onboarding Testing
This validates the smooth deployment and setup of 5G core functions (like AMF, SMF, and UPF). Automated onboarding cuts out manual configuration errors and allows for quicker scalability.
Mobility Application Testing
This focuses on interactions during mobility scenarios, ensuring smooth handovers and low latency. Automation tools simulate thousands of user sessions to ensure accuracy.
Assurance Testing
Combining proactive monitoring, SLA checks, and fault detection, automated assurance makes sure network performance stays consistent and meets service-level agreements.
Key Components of the 5G Test Automation Framework
Component Function Test Automation Development Creating automation scripts, frameworks, and workflows. Test Automation Execution Ongoing execution and validation of test cases across environments. Feedback Mechanisms Automated feedback promotes continuous improvement. Auto-Deployment Pipelines Allow for seamless transitions between stages without manual input.
This cyclical model facilitates continuous delivery (CD) and continuous testing (CT), supporting agile telecom deployment methods.
Benefits of Implementing Test Automation in 5G Networks
Adopting an automation-first approach brings both operational and financial perks:
Accelerated Time-to-Market: Cuts down manual testing cycles and speeds up deployment.
Enhanced Accuracy: Automation reduces human errors in repetitive tests.
Scalability: Facilitates extensive 5G infrastructure testing across various environments.
Cost Efficiency: Optimizes resource use through continuous testing and feedback.
Improved Quality Assurance: Guarantees consistent performance across different network layers.
These benefits make automation a critical part of any successful 5G rollout or upgrade.
Challenges in 5G Test Automation
Despite the advantages, some challenges still exist:
Complex Orchestration: Coordinating various layers of virtual and physical components.
Tool Integration: Aligning different automation and monitoring tools in a single CI/CD framework.
Skill Gap: Engineers need expertise in DevOps, scripting, and telecom protocols.
Dynamic Environments: Quickly changing network setups require flexible automation.
Addressing these challenges calls for careful planning, training for the workforce, and the use of AI-driven test orchestration tools.
Conclusion
The Test Automation Strategy for 5G Architecture lays out a clear path for efficiently and reliably deploying next-gen networks. By automating processes from pre-integration to production, telecom operators can enjoy continuous testing, faster deployments, and solid assurance mechanisms.
This organized approach not only shortens time-to-market but also fits perfectly with the agile and cloud-native vision of 5G. As we look ahead to 6G and beyond, automation will remain key to driving innovation, resilience, and operational excellence.
