The 6G Timeline: From Research to Commercial Launch (2022–2031)
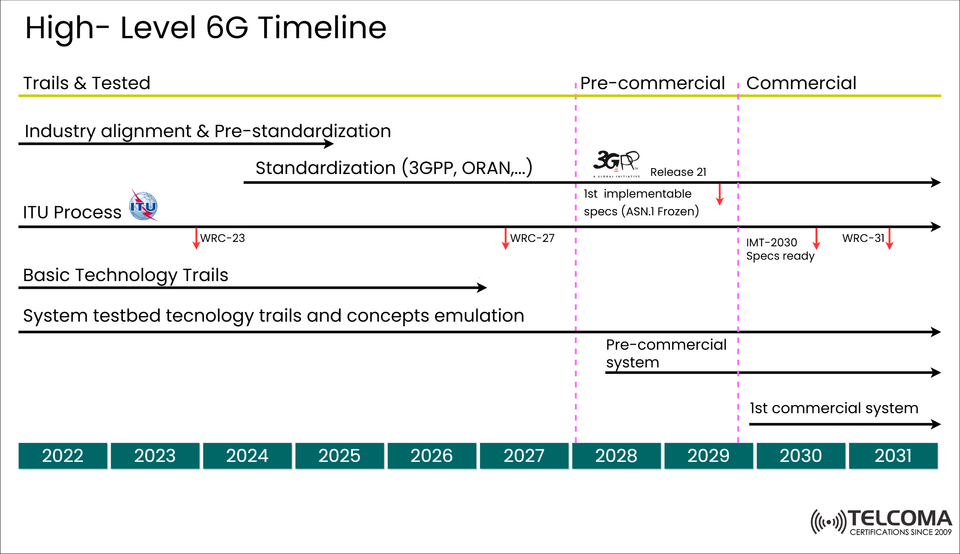

The High-Level Timeline for 6G: From Idea to Implementation
The journey towards 6G technology is in full swing, and the next ten years are shaping up to be filled with research breakthroughs, international teamwork, and strategic standard-setting. The accompanying image, titled “High-Level 6G Timeline,” offers a visual overview of how the telecom sector, with leadership from organizations like 3GPP, ITU, and ORAN Alliance, is navigating the road from initial studies to widespread deployment.
Covering the years 2022 to 2031, this timeline illustrates the systematic development of 6G, featuring stages like pre-standardization, technology trials, standard releases, and commercial system launches.
The Early Stage (2022–2024): Industry Alignment and Pre-Standardization
The groundwork for 6G development kicked off soon after 5G became stable worldwide. Between 2022 and 2024, key players from the industry, research groups, and standard-setting organizations began to converge on 6G concepts and requirements.
Key Focus Areas:
Defining 6G use cases: Ranging from holographic communications to AI-driven networks.
Collaborative research: Initiatives like Hexa-X (Europe), Beyond 5G (Japan), and Next G Alliance (North America).
Spectrum exploration: Looking into sub-THz and visible light bands for ultra-high capacity.
Sustainability objectives: Embedding energy-efficient design principles from the get-go.
This phase stresses global cooperation, as building early agreement is crucial for ensuring that everything works well together when formal standards begin to take shape.
ITU Process and Early Framework (2023–2027)
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has a key role in shaping the technical and regulatory groundwork for 6G.
The ITU’s Role:
The ITU sets the IMT (International Mobile Telecommunications) framework, which governs each mobile communication generation.
For 6G, this will be known as IMT-2030.
In this timeline, WRC-23 (World Radiocommunication Conference 2023) marks an early milestone. In this period, global regulators will discuss spectrum policies, identify potential frequency bands, and lay out initial goals for 6G capabilities.
The ITU process will continue through WRC-27, refining performance criteria, evaluation standards, and technical specs for IMT-2030.
Expected Outcomes by 2027:
Consensus on 6G candidate spectrum bands (100 GHz–1 THz range).
Initial IMT-2030 performance framework established.
Cross-industry agreement on target KPIs (data rates, latency, reliability, energy efficiency).
Laying this foundation allows technical entities like 3GPP and ORAN to start the standardization process.
Standardization Phase (2025–2029): The 3GPP and ORAN Efforts
As pre-standardization studies gain maturity, formal standardization kicks off, mainly driven by 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) and ORAN Alliance.
3GPP Release 21: Setting the 6G Standard
According to the timeline, 3GPP Release 21 will mark the first official milestone for 6G standardization. Expected around 2028–2029, this release aims to deliver:
Initial implementable specifications (ASN.1 frozen) for 6G radio access (6G-NR).
Enhanced core network architecture for AI-driven automation and sensing.
Open RAN interfaces that allow for flexibility and vendor-neutral deployment.
During this timeframe, global collaboration will ensure that every element of the 6G system — from the physical layer to the cloud-native core — is interoperable, secure, and scalable.
Technology Trials and Testbeds (2024–2028): Bridging Ideas and Reality
Alongside the work of the ITU and 3GPP, technology trials and testbeds play an essential role in testing 6G concepts.
The timeline indicates two levels of experimentation:
Basic Technology Trials (2024–2028)
Concentrating on validating enabling technologies like terahertz communications, AI-native network management, and combined communication and sensing.
Early prototype testing will be led by university and vendor collaborations.
System Testbed and Concept Emulation (2025–2029)
Transitioning from component trials to end-to-end network testing.
Includes real-world emulation of 6G environments, like smart factories and autonomous mobility networks.
Assessing latency, spectral efficiency, and energy performance under realistic conditions.
These trials are crucial for fine-tuning specifications before commercial rollout, ensuring reliability, scalability, and sustainability.
The Pre-Commercial Era (2028–2029)
The pre-commercial phase signifies the shift from research to real-world application.
By 2028, several pre-commercial systems are expected to be up and running, built on insights from earlier testbeds.
Telecom companies like Nokia, Ericsson, Huawei, and Samsung are set to showcase full-stack 6G prototypes.
Governments and telecom regulators will run pilot deployments to evaluate performance in urban and rural settings.
Goals of Pre-Commercial Systems:
Validate 3GPP Release 21 in real-life scenarios.
Ensure backward compatibility with 5G Advanced networks.
Test for compliance with IMT-2030 standards.
Start initial device interoperability testing with chipset manufacturers.
By late 2029, the IMT-2030 specifications will be finalized by the ITU, concluding the standardization phase and setting the stage for commercial launch.
Commercialization and Global Launch (2030–2031)
The image points out 2030–2031 as the window for commercial rollout of 6G networks.
Once the IMT-2030 specs are finalized and the WRC-31 wraps up on spectrum bands, operators will commence nationwide rollouts of 6G infrastructure.
Anticipated Features of Initial Commercial Systems (2030+):
Peak speeds of up to 1 Tbps with ultra-low latency (<0.1 ms).
AI-native architecture for automated resource management.
Integrated sensing and communication for real-time awareness.
Global coverage through a mix of terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks (NTNs).
End-to-end energy efficiency aimed at hitting net-zero carbon targets.
Early adopters are expected to include smart cities, autonomous industries, immersive entertainment platforms, and AI-driven healthcare systems.
The IMT-2030 Framework: The Official 6G Standard
By 2030, the ITU’s IMT-2030 standard is set to establish the performance benchmarks for 6G, similar to how IMT-2020 set them for 5G.
Core IMT-2030 Objectives:
Category Target Capability
Peak Data Rate ≥ 1 Tbps
Latency < 0.1 milliseconds
Energy Efficiency 10× better than 5G
Mobility Up to 1,000 km/h
Reliability 99.999999% (8 nines)
Connection Density 10 million devices/km²
Spectrum Efficiency 2–3× improvement
Positioning Accuracy Centimeter-level
These objectives will serve as the global performance yardstick for 6G networks.
Strategic Impact on the Telecom Ecosystem
The 6G timeline illustrates not just technological milestones, but also reshapes business models, innovation pathways, and regulatory frameworks.
Key Impacts:
Operators will embrace new monetization models based on AI-as-a-Service (AIaaS) and network slicing.
Vendors will push for sustainable hardware innovations using advanced materials and chips.
Governments will invest in spectrum readiness and policy frameworks to ensure secure 6G deployment.
Enterprises will employ 6G for automation, extended reality, and global IoT ecosystems.
Conclusion: The Path Forward for 6G
The 6G timeline (2022–2031) outlines a clear, methodical journey from research to reality. Unlike what we’ve seen with past generations, 6G development is all about emphasizing collaboration, sustainability, and intelligence from the start.
By the time we reach 2031, the world is set to enter a new era of hyper-connected intelligence, where communication networks don’t just send data but also sense, learn, and optimize in real-time.
As 5G keeps evolving, grasping this timeline will help industry professionals, policymakers, and innovators stay ahead and be ready to shape the 6G-driven digital future.
