The Convergence of 5G, Edge Computing, and AI: Driving Next-Gen Applications
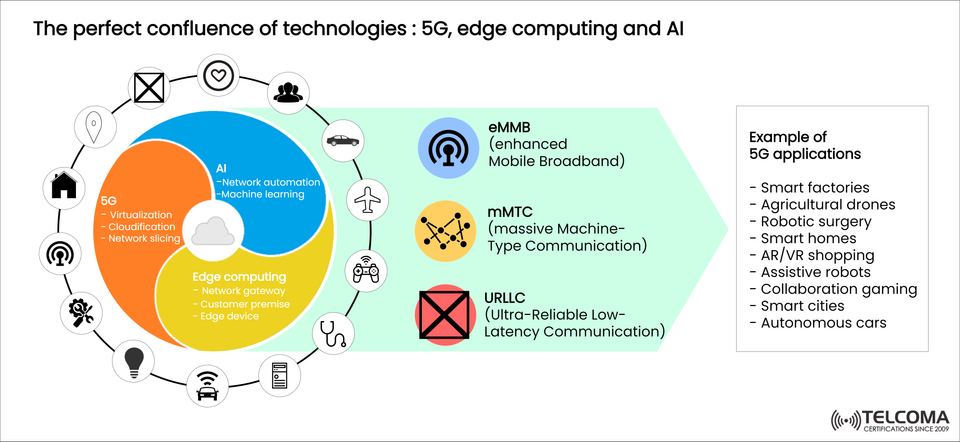

The digital world is changing at lightning speed, fueled by three major technologies—5G, edge computing, and artificial intelligence (AI). Each of these has its own strengths, but when they come together, they’re creating some truly amazing applications across various industries.
These technologies are really transforming fields like healthcare, manufacturing, automotive, agriculture, and smart city initiatives. The infographic illustrates how the intersection of 5G, AI, and edge computing drives innovations such as robotic surgery, smart factories, agricultural drones, and self-driving cars.
- The Role of 5G in the Technology Convergence
5G isn’t just a speed upgrade from 4G; it’s a key player in digital transformation. Its capabilities go beyond just faster connections to support massive IoT deployments, super-low latency, and network slicing.
Core Enablers of 5G:
Virtualization: This allows for flexible, software-based networks.
Cloudification: It moves network functions to the cloud to enhance scalability.
Network Slicing: This creates customized virtual networks for specific needs.
With these features, 5G supports three main service types:
eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband): High-speed internet, AR/VR, and immersive entertainment.
mMTC (Massive Machine-Type Communication): Large-scale IoT solutions for smart cities and agriculture.
URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication): Essential services like robotic surgery and self-driving cars.
- Edge Computing: Bringing Data Processing Closer
Edge computing tackles one of the big challenges in digital transformation—latency. By processing information closer to devices instead of relying solely on centralized cloud servers, edge computing guarantees real-time responsiveness.
Key Components of Edge Computing:
Network Gateway: The initial data aggregation point for quicker transmission.
Customer Premise Equipment (CPE): Edge processing units located at enterprise sites.
Edge Devices: Smart sensors, cameras, and IoT endpoints.
Benefits of Edge Computing:
Cuts down on round-trip delays for critical applications.
Boosts bandwidth efficiency by managing and processing data locally.
Increases data privacy by limiting the sharing of sensitive information with the cloud.
This makes edge computing crucial for applications like autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and AR/VR where every millisecond counts.
- Artificial Intelligence: Driving Automation and Insights
Artificial Intelligence (AI) enhances the capabilities of both 5G and edge computing. By integrating intelligence into networks and devices, AI allows for automation, predictive decision-making, and adaptability.
AI in the 5G Ecosystem:
Network Automation: Streamlining traffic flow, anticipating failures, and creating self-repairing networks.
Machine Learning Models: Facilitating real-time analytics and smart recommendations.
AI-Powered Applications: Enabling advancements in smart healthcare, robotics, and personalized services.
AI not only improves the results of applications, but it also makes the network infrastructure smarter and more efficient, lowering costs and boosting reliability.
- Convergence in Action: Real-World 5G Applications
The real excitement comes from how these three technologies—5G, edge computing, and AI—meld together to create high-value practical applications.
Examples of 5G Applications Enabled by the Convergence:
Smart Factories: AI-enhanced robotics, 5G-connected sensors, and edge analytics streamline production with accuracy and allow for predictive maintenance.
Agricultural Drones: Drones utilizing AI and connected through 5G oversee crops, assess soil conditions, and enhance farming techniques in real-time.
Robotic Surgery: URLLC minimizes latency while AI aids surgeons with accuracy, and edge computing delivers local real-time data analysis.
Smart Homes: AI-driven assistants work with IoT devices over 5G to enable automation, security, and energy savings.
AR/VR Shopping: eMBB powers immersive shopping experiences online, with AI improving personalization and edge computing cutting down on lag.
Assistive Robots: AI-assisted robots provide help to the elderly or those with disabilities, using reliable 5G networks and real-time edge processing.
Collaboration Gaming: Cloud-based multiplayer gaming relies on eMBB for speed, edge computing for quick responses, and AI for adaptive gameplay.
Smart Cities: From managing traffic to ensuring public safety, 5G supports dense IoT networks while AI interprets data and edge computing allows for quick responses.
Autonomous Cars: These vehicles need URLLC for crucial communications, AI for making decisions, and edge computing for instant navigation updates.
- Comparative Table: The Convergence at Work
Technology | Primary Role | Example Applications
5G | Connectivity, speed, scalability, low latency | eMBB, mMTC, URLLC use cases like AR/VR and robotics**
Edge Computing | Localized processing, reduced latency | Autonomous vehicles, smart factories, AR/VR**
AI | Intelligence, automation, predictive analytics | Network automation, healthcare robotics, smart cities
This table outlines how each technology not only plays its part uniquely but also interacts with the others in the ecosystem.
- Why This Confluence Matters
The coming together of 5G, edge computing, and AI isn’t just a technological trend—it’s the cornerstone of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Some key advantages are:
Seamless User Experiences: From engaging gaming to VR-based education.
Operational Efficiency: Industries like manufacturing and agriculture run smoother with predictive analytics.
Life-Saving Applications: Technologies like remote surgeries and self-driving cars decrease risks and can save lives.
Sustainability: Smart cities and precision farming lead to greener, more sustainable growth.
For telecom experts, grasping this convergence is vital to designing networks and services that cater to the needs of current industries.
Challenges in Realizing the Convergence
Even with all its promise, mixing 5G, AI, and edge computing has its set of challenges:
Infrastructure Costs: Building dense 5G networks and edge nodes takes a lot of money.
Interoperability Issues: Making sure that various devices and platforms work well together.
Data Security and Privacy: Handling large amounts of sensitive data at the edge securely.
Regulatory and Spectrum Allocation Barriers: These vary by region and can slow down global adoption.
Tackling these issues is crucial for fully realizing the transformative potential that this technological convergence offers.
Conclusion
The merger of 5G, edge computing, and AI signifies a major change in digital transformation. Each of these technologies stands strong on its own, but together they form an ecosystem that can support the next wave of applications across lots of industries.
From smart factories and self-driving cars to robotic surgeries and engaging AR/VR experiences, this confluence is steering the future of connectivity and intelligence. Although there are hurdles in terms of infrastructure, interoperability, and security, the path ahead is clear—the combination of these technologies is set to shape the next decade of innovation.
For telecom professionals, this means fresh opportunities in designing, deploying, and managing advanced networks. For tech enthusiasts, it’s an exciting glimpse into a hyperconnected, intelligent future.
