The Core Design Principles of 6G: Building Efficient, Secure, and Sustainable Wireless Networks

6G Design Principles: Creating Efficient, Secure, and Sustainable Wireless Solutions
The transition from 5G to 6G isn’t just about faster speeds or better connectivity; it’s about crafting a sustainable, smart, and secure communication framework that meets the demands of our increasingly digital and interconnected world.
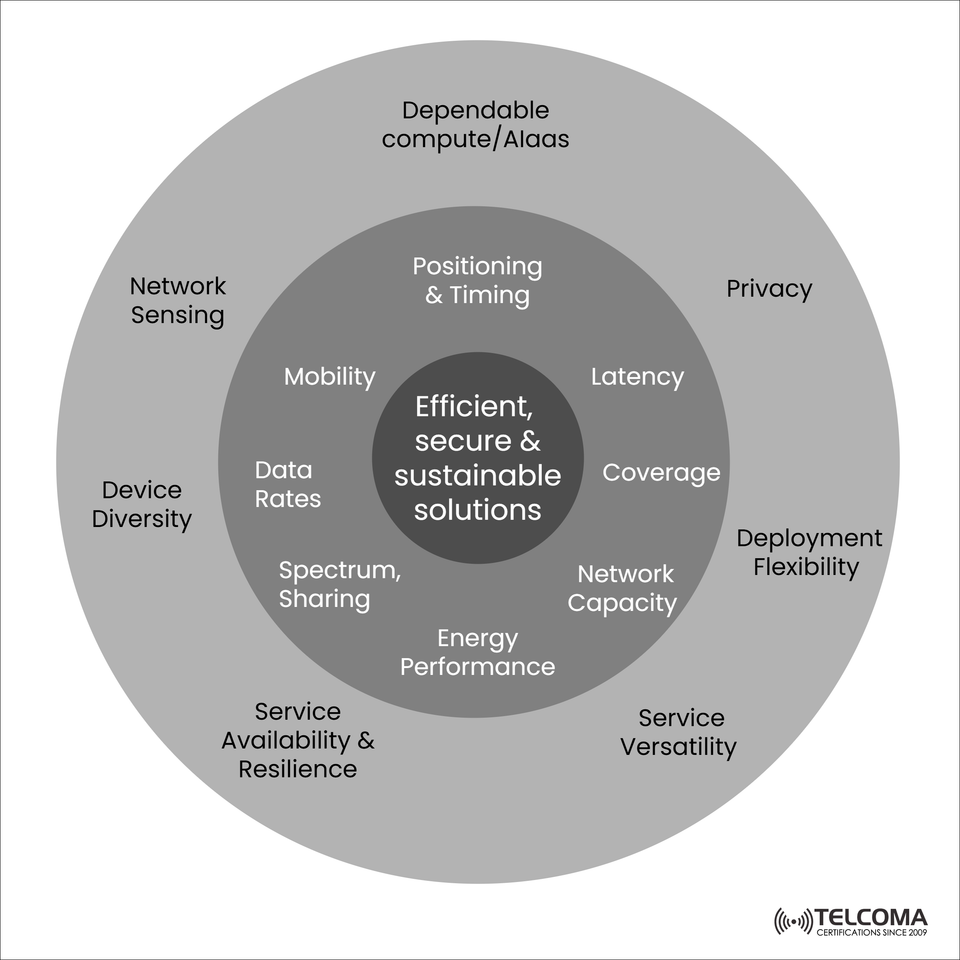
The diagram included captures the key objectives of 6G architecture, with “Efficient, Secure & Sustainable Solutions” right at the center. Surrounding this main concept are vital performance indicators like latency, coverage, mobility, data rates, and energy efficiency, bolstered by broader enablers such as AI, network sensing, privacy, and flexible deployment.
This layered design approach highlights how 6G aspires for comprehensive optimization—striking a balance between speed, security, resilience, and environmental consciousness.
The Core Vision: Efficient, Secure, and Sustainable 6G Solutions
At the core of the 6G design ideology is the combination of efficiency, security, and sustainability. These three core concepts will shape the way future wireless networks are created, rolled out, and maintained.
Efficiency
6G networks are set to provide unmatched spectral and energy efficiency, allowing for massive device connectivity and data transfer without draining too much power.
AI-fueled resource allocation will constantly tweak network performance.
Edge computing will cut down on data transport needs.
Energy-conscious protocols will boost battery life for IoT and mobile gadgets.
Security
In 6G, security goes beyond just encryption. It brings in quantum-safe algorithms, trust management systems, and AI-driven threat detection to safeguard both our physical and digital infrastructures.
Some key features include:
End-to-end encryption paired with post-quantum cryptography.
Zero-trust frameworks for continuous verification.
AI-driven real-time anomaly detection.
Sustainability
The sustainability aim of 6G aligns with global green tech goals, focusing on reducing carbon footprints by implementing:
Energy-efficient hardware and software.
Dynamic spectrum sharing to optimize resource use.
Circular economy models that prioritize recyclable network components.
When you put these three pillars together, 6G becomes not just faster, but also smarter, greener, and safer.
Key Technical Enablers in the 6G Design Framework
The accompanying image outlines several core technical elements supporting the central goal. Each element enhances network performance and service continuity.
Mobility
6G will facilitate smooth mobility across land, air, and satellite, ensuring uninterrupted connections even at high speeds (think hyperloop or low-orbit flights).
AI-enabled handover prediction.
Edge-assisted mobility management.
Supporting ultra-dense mixed environments.
Latency
Aiming for sub-millisecond latency, 6G is set to be crucial for the tactile internet, remote surgeries, and self-driving vehicles.
Real-time processing at the edge.
Network slicing tailored for low-latency tasks.
Predictive analytics to avoid transmission lags.
Coverage
Going beyond just cities, 6G aspires for global coverage, incorporating non-terrestrial networks (NTN) like satellites and high-altitude platforms, ensuring reliable connections for remote locations, disaster areas, and maritime industries.
Network Capacity
6G networks are engineered for massive capacity growth through new spectrum bands—particularly sub-THz frequencies.
Ultra-massive MIMO.
Dynamic bandwidth aggregation.
Smart spectrum allocation.
Energy Performance
Here, sustainability and performance come together. 6G networks will employ AI-focused energy optimization to lower power consumption across RAN, core, and devices. Techniques like sleep modes for base stations and energy harvesting systems will support eco-friendly operations.
Enabling Spectrum and Data Innovations
Spectrum and Sharing
The effective use of the radio spectrum is crucial for 6G. The system will integrate cognitive spectrum management, allowing AI to assess and reallocate frequencies in real-time.
Dynamic sharing between terrestrial and satellite links.
Spectrum reusability for low-power IoT.
Transparent governance for collaboration among multiple operators.
Data Rates
With anticipated peak speeds of up to 1 Tbps, 6G will transform data consumption experiences. This will be realized through:
THz spectrum utilization.
Massive multi-band aggregation.
Advanced waveform design to enhance spectral efficiency.
Positioning and Timing: Precision Beyond Communication
In 6G, positioning and timing will become essential features of the network rather than just add-ons. These capabilities will allow:
Centimeter-level accuracy for industrial robotics and logistics.
Synchronized systems for drone coordination and vehicle safety.
Integrated localization and communication (ILAC) for mission-critical tasks.
This integration enables networks to sense, locate, and connect simultaneously, a significant advancement from the communication-only model of 5G.
Expanding the Outer Layer: Resilience, Diversity, and Privacy
The outer ring of the image showcases system attributes vital for 6G’s real-world adaptability.
Service Availability & Resilience
6G networks will feature self-healing abilities, ensuring continuous service even during hardware breakdowns or cyberattacks.
AI-based fault detection and recovery.
Multi-layer redundancy plus distributed cloud storage.
Proactive reconfiguration for emergencies or overloads.
Device Diversity
From tiny devices to self-driving cars, 6G will support universal device interoperability.
Standardized communication protocols across IoT, wearables, and industrial gear.
Adaptive connectivity that balances low-power needs with high-bandwidth demands.
Network Sensing
A standout innovation in 6G—networks will be able to sense their surroundings. By utilizing radio waves as sensors, they’ll detect motion, surfaces, and even environmental factors. This will enhance smart infrastructures, traffic control, and immersive digital experiences.
Dependable Compute / AI-as-a-Service (AIaaS)
AI will be a core layer of service. 6G networks will offer AI-as-a-Service, allowing operators, industries, and users to deploy AI models directly over the network.
Edge-based inference for time-sensitive AI tasks.
Shared cloud resources for scalable computing.
Autonomous optimization of data flows and QoS.
Privacy
6G networks will incorporate privacy-protecting measures at both hardware and software levels. Techniques like federated learning and homomorphic encryption will enable AI training without sacrificing personal data privacy, ensuring adherence to future global data protection regulations.
Deployment Flexibility
The focus will be on modular, software-defined deployments, allowing networks to scale as needed.
Cloud-native network functions (CNFs).
Open RAN architecture to encourage vendor diversity.
Rapid deployment through edge virtualization.
Service Versatility
6G will serve as a service enabler for various sectors—healthcare, manufacturing, education, and entertainment—offering customized connectivity through network slicing. Each slice can be fine-tuned for its own latency, bandwidth, and reliability needs, leading to context-aware, on-demand communication.
Balancing Performance and Sustainability
The design of 6G is centered around finding harmony between technological progress and environmental stewardship. As performance metrics like data rates and capacity continue to advance, they are counterbalanced by:
Energy-efficient chips and antennas.
Carbon-aware orchestration systems.
Lifecycle management aimed at reducing e-waste via modular upgrades.
This reflects the industry’s commitment to net-zero communication systems.
Conclusion: The Future of 6G is Intelligent and Responsible
The 6G design framework stands for a new approach in network engineering—one that prioritizes performance, security, and sustainability equally.
As illustrated in the image, 6G aims not just to improve traditional metrics like data rates, latency, and mobility—it’s also set to introduce new levels of intelligence, ranging from AI-driven automation to environmental sensing and sustainable infrastructure.
