The Evolution of Mobile Subscriptions: How 5G Is Set to Dominate by 2027

The Evolution of Mobile Subscriptions: Why 5G Will Be King by 2027
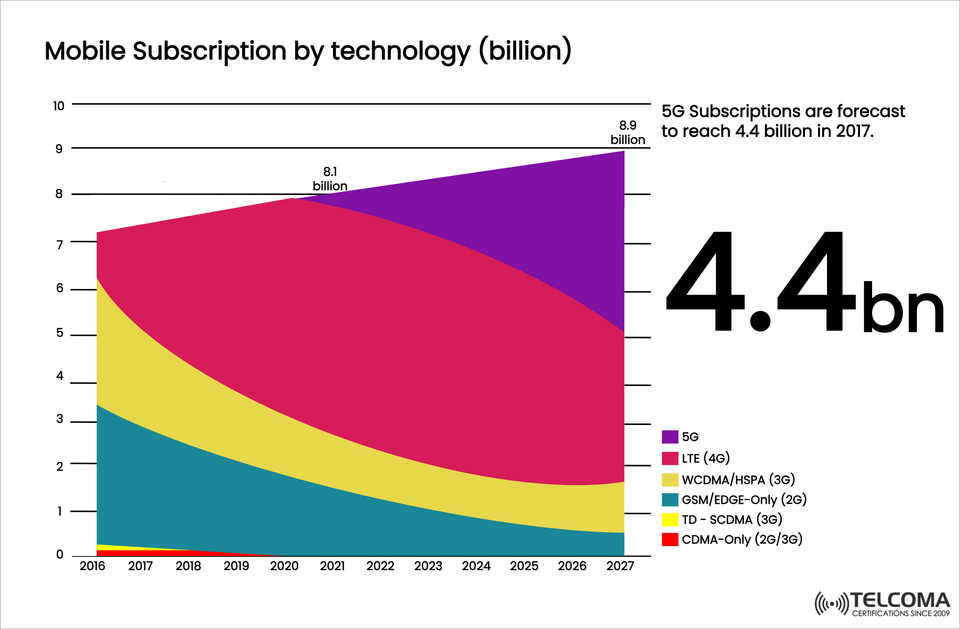
The telecom sector is experiencing a major technological shift. As highlighted in the chart above, mobile subscriptions have evolved across different generations—from 2G and 3G to 4G and now 5G.
By 2027, it’s expected that 5G subscriptions will hit 4.4 billion, making up almost half of all mobile connections worldwide. This rapid growth marks the dawn of a new era characterized by ultra-fast speeds, low latency, and smart connectivity.
In this article, we’ll delve into the trends in mobile subscriptions by technology, looking at the decline of older networks, the stability of LTE, and how 5G is emerging as the backbone of tomorrow’s digital ecosystems.
Global Mobile Subscription Landscape Overview
The graph below shows the growth of mobile subscriptions (in billions) from 2016 to 2027.
2016: About 7 billion subscriptions globally, mainly driven by 2G and 3G.
2021: 4G (LTE) takes the lead as the most popular technology worldwide.
2027 (projected): A total of 8.9 billion mobile subscriptions, with 5G accounting for 4.4 billion.
This increase reflects not just technological advancements but also the growing mobile access in developing regions.
Current Status
Several countries in Europe, North America, and East Asia have already shut down their 3G networks.
2G networks are still in use but mainly for basic M2M/IoT applications, like smart meters and vehicle tracking.
By 2027, 2G and 3G combined are expected to make up less than 10% of total global subscriptions.
LTE (4G): The Transitional Workhorse
The Rise of LTE
4G LTE revolutionized mobile broadband by providing quick internet access, low latency, and reliable coverage. It fueled the growth of mobile video, social media, e-commerce, and mobile banking.
By 2021, LTE accounted for the largest portion of global subscriptions, being the main mobile network technology in most regions.
Ongoing Role of LTE
As 5G expands, LTE will still be crucial because:
Widespread coverage: LTE has established global reach.
Fallback layer: 5G uses LTE for initial connectivity in Non-Standalone (NSA) setups.
Cost-effectiveness: LTE infrastructure continues to support areas lacking 5G.
Forecast
Between 2023 and 2027, LTE subscriptions will slowly decrease as users shift to 5G. Still, it will manage billions of active connections, especially in developing areas.
The 5G Revolution: 4.4 Billion Subscriptions by 2027
The most notable trend from the chart is the remarkable growth of 5G, predicted to reach 4.4 billion users by 2027.
Reasons for the Swift 5G Adoption
Higher Performance: Speeds reaching 10 Gbps, latency under 10 ms, and a high capacity.
Industrial Demand: 5G is essential for Industry 4.0, self-driving cars, smart cities, and IoT systems.
Device Ecosystem: Affordable 5G smartphones and modems are now common.
Government & Operator Investment: Over 250 operators around the globe have rolled out commercial 5G services.
Enterprise Use Cases: 5G supports private networks, AR/VR, edge computing, and critical communications.
Regional Growth Insights
North America and East Asia: 5G uptake will surpass 80%.
Europe: Quick 5G growth facilitated by regulatory support and industry use cases.
Middle East & Africa: Gradual but consistent growth despite infrastructure hurdles.
India: Expected to be a major player in 5G expansion from 2023 onwards.
By 2027, 5G will exceed LTE and become the leading mobile technology, shaping the global digital economy.
Total Mobile Subscriptions: 8.9 Billion by 2027
Although growth in mobile users is slowing in developed markets, IoT and multi-device usage continue to drive overall subscription increases.
Reasons for Growth
IoT and M2M devices (connected cars, sensors, meters).
Multiple SIM ownership in areas like Africa and South Asia.
Rural expansion in developing countries thanks to affordable 4G/5G devices.
Consequently, the total mobile subscriptions are expected to grow from 8.1 billion in 2021 to 8.9 billion by 2027, even as growth in human population levels off.
The Technology Mix by 2027
By 2027, the distribution of mobile subscriptions (approximate projection) will look something like this:
Technology Share of Total Subscriptions Trend 5G ~50% (4.4 billion) Rapid growth 4G (LTE) ~40% Gradual decline 3G (WCDMA, CDMA) <8% Sunset stage 2G (GSM/EDGE) <5% Legacy use only
The overall trend points to a clear shift toward high-capacity, low-latency networks, paving the way for new business models in telecom and beyond.
Implications for Telecom Operators
With the shift in mobile technology, telecom operators are facing both challenges and new opportunities.
Challenges
Network Modernization Costs: Upgrading to 5G requires significant investment.
Spectrum Licensing: Spectrum auctions are competitive and costly.
Device Compatibility: Ensuring easy transition for users.
Opportunities
Private 5G Networks: For businesses in sectors like manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare.
Fixed Wireless Access (FWA): Using 5G to broaden broadband access.
Edge Computing & Cloud Integration: Capitalizing on low-latency services.
Network Slicing: Providing tailored network segments for various applications.
Transitioning from 4G to 5G is more than just a tech upgrade—it’s a fundamental change in business models for the telecom industry.
The Role of Emerging Technologies
The next chapter of telecom innovation hinges on the foundation laid by 5G:
AI and Machine Learning: Enhance network operations and predictive maintenance.
Edge Computing: Facilitates real-time processing near users.
Open RAN (O-RAN): Encourages flexibility and reduces reliance on specific vendors.
Satellite-5G Integration: Extends coverage to underserved and remote areas.
These advancements are set to influence the 6G evolution, where networks will be smart, automated, and everywhere.
Looking Beyond 2027: Getting Ready for the 6G Era
As 5G matures by 2027, the telecom landscape will already be venturing into 6G concepts. 6G aspires to deliver terabit speeds, sub-millisecond latency, and AI-driven self-optimization, integrating terrestrial, aerial, and satellite networks for seamless global coverage.
The groundwork laid by 5G will enable this future—creating a digital environment for a world interconnected through intelligent systems, automation, and immersive experiences.
Conclusion
The Telcoma graph showcases a transformative decade for mobile technology. The global shift from 2G and 3G to 5G is about more than just faster internet; it reflects a structural change towards smarter, more connected societies.
By 2027, with 4.4 billion 5G subscriptions and nearly 9 billion total mobile connections, we’ll be on the verge of a new digital era—driven by innovation, data, and seamless connectivity.
Telecom professionals should start gearing up for this 5G-focused landscape—where everything from industries to economies and daily life will be redefined.
